Clin Orthop Surg.
2009 Sep;1(3):161-164. 10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.161.
Stress Fracture of the Proximal Fibula in Military Recruits
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. itchu@hanmail.net
- KMID: 999395
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.161
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
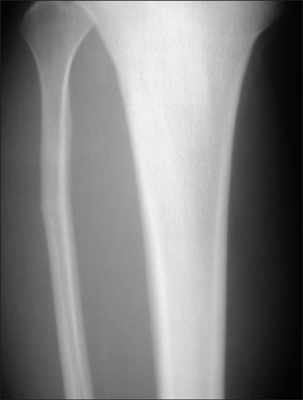
We wanted to report on stress fracture of the proximal fibula and to suggest the pathomechanism of this fracture. METHODS: Between April 2004 through April 2005, the military recruits who complained of leg pain during the 6 weeks basic training in the Republic of Korea Marine Corps education and training group were evaluated according to their clinical manifestations and plain radiographs. RESULTS: Twelve recruits of 635 recruits who complained leg pain were diagnosed as having fibular stress fracture. Eleven cases (10 recruits) appeared at the junction of the proximal and middle 1/3 of the fibula and 2 cases (2 recruits) were in the middle 1/3 of the fibula, as assessed radiologically. Tenderness was the most reliable clinical manifestation. All the fractures occurred after repetitive walking or jumping in a squatting position. Conservative treatments that included bed rest, immobilization and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs administration according to the symptom severity were satisfactory. CONCLUSIONS: Proximal fibular stress fracture is not rare in military recruits. The shearing force on the proximal fibula and the repetitive stress by walking or jumping in a squatting position contribute to the stress fracture of the proximal fibula.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mattila VM, Niva M, Kiuru M, Pihlajamaki H. Risk factors for bone stress injuries: a follow-up study of 102,515 person-years. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007. 39(7):1061–1066.2. Anderson MW, Greenspan A. Stress fractures. Radiology. 1996. 199(1):1–12.
Article3. Daffner RH, Pavlov H. Stress fractures: current concepts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992. 159(2):245–252.
Article4. Burr DB, Milgrom C, Boyd RD, Higgins WL, Robin G, Radin EL. Experimental stress fractures of the tibia: biological and mechanical aetiology in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72(3):370–375.
Article5. Peiro V, Herrador MA, Leyes M, Guillen P. Bilateral stress fracture of the proximal fibula in a young soccer player on bone scanning. Clin Nucl Med. 2003. 28(1):49–51.
Article6. Lehman TP, Belanger MJ, Pascale MS. Bilateral proximal third fibular stress fractures in an adolescent female track athlete. Orthopedics. 2002. 25(3):329–332.
Article7. Lacroix H, Keeman JN. An unusual stress fracture of the fibula in a long-distance runner. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1992. 111(5):289–290.
Article8. Losito JM, Laird RC, Alexis MR, Mora J. Tibial and proximal fibular stress fracture in a rower. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003. 93(4):340–343.
Article9. Symeonides PP. High stress fractures of the fibula. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980. 62(2):192–193.
Article10. Breithaupt . Zur pathologie des menschlichen fubes. Med Zeitg. 1855. 24:169–177.11. Ha KI, Hahn SH, Chung MY, Yang BK, Yi SR. A clinical study of stress fractures in sports activities. Orthopedics. 1991. 14(10):1089–1095.
Article12. Matheson GO, Clement DB, McKenzie DC, Taunton JE, Lloyd-Smith DR, MacIntyre JG. Stress fractures in athletes: a study of 320 cases. Am J Sports Med. 1987. 15(1):46–58.13. Pavlov H, Torg JS, Hersh A, Freiberger RH. The roentgen examination of runner's injuries. Radiographics. 1981. 1(1):17–34.
Article14. Burr DB, Milgrom C. Musculoskeletal fatigue and stress fractures. 2001. Boca Raton: CRC Press;1–36.15. Lappe JM, Stegman MR, Recker RR. The impact of lifestyle factors on stress fractures in female Army recruits. Osteoporos Int. 2001. 12(1):35–42.
Article16. Luchini MA, Sarokhan AJ, Micheli LJ. Acute displaced femoral-shaft fractures in long-distance runners: two case reports. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983. 65(5):689–691.
Article17. Castillo M, Tehranzadeh J, Morillo G. Atypical healed stress fracture of the fibula masquerading as chronic osteomyelitis: a case report of magnetic resonance distinction. Am J Sports Med. 1988. 16(2):185–188.
Article18. Protzman RR, Griffis CG. Stress fractures in men and women undergoing military training. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59(6):825.
Article19. Belkin SC. Stress fractures in athletes. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980. 11(4):735–741.
Article20. McBryde AM Jr. Stress fractures in runners. Clin Sports Med. 1985. 4(4):737–752.
Article21. Blair WF, Hanley SR. Stress fracture of the proximal fibula. Am J Sports Med. 1980. 8(3):212–213.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stress Fractures of the Leg and Shin Splint in the Recruits
- Femoral Stress Fractures in Civilians who are not military recruits and athlethes :Two cases report
- Fatigue Fractures of Tibial and Fibular Shaft in Soldiers
- Stress Fractures in Pubic Bone: Report of 3 Cases
- Proximal Tibia Stress Fracture Caused by Primary Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis with Varus Deformity