J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2016 Oct;51(5):437-442. 10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.5.437.
Proximal Tibia Stress Fracture Caused by Primary Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis with Varus Deformity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. drjmlee@naver.com
- KMID: 2355510
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.5.437
Abstract
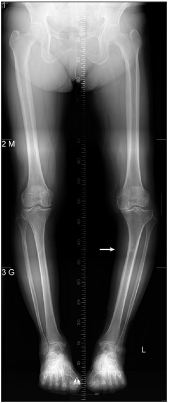
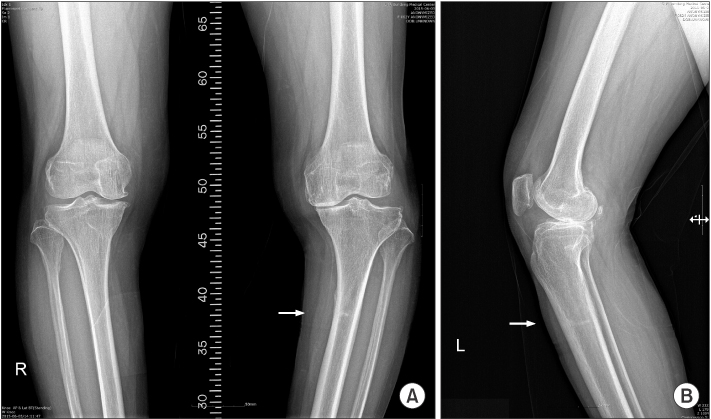
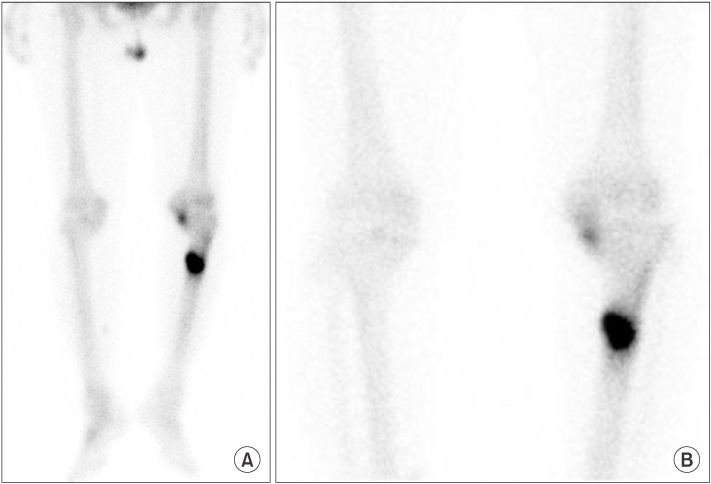
- Stress fractures of the tibia are relatively common in military and young people. However, stress fracture of the proximal tibia is rare in elderly patients, but has been reported in association with osteoporosis, Paget disease, rheumatoid arthritis, pyrophosphate arthropathy, and knee deformities. We experienced a 65-year-old patient who did not have a chronic disease, with a stress fracture with primary degenerative knee osteoarthritis with varus deformity, which occurred at the proximal tibia, and we report on this unusual case with a literature review.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Devas M. Stress fractures. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;1975.2. Resnick D, Guerra J Jr. Stress fractures associated with adjacent osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1981; 8:161–164.Grundy M. Fractures of the femur in paget's disease of bone. Their etiology and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970. 52:252–263.4. Young A, Kinsella P, Boland P. Stress fractures of the lower limb in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981; 63:239–243.
Article5. Ross DJ, Dieppe PA, Watt I, Newman JH. Tibial stress fracture in pyrophosphate arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983; 65:474–477.
Article6. Reynolds MT. Stress fractures of the tibia in the elderly associated with knee deformity. Proc R Soc Med. 1972; 65:377–380.7. Kelly JM. Stress fractures in the tibia associated with knee deformities. J Ir Med Assoc. 1974; 67:97–99.8. Sourlas I, Papachristou G, Pilichou A, Giannoudis PV, Efstathopoulos N, Nikolaou VS. Proximal tibial stress fractures associated with primary degenerative knee osteoarthritis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009; 38:120–124.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Bone Mineral Density of the Proximal Tibia, Lumbar Spine and Proximal Femur and Its Correlation with the Alignment of the Lower Extremity in Knee Osteoarthritic Patients
- The Clinical Results After Open Wedge Osteotomy of Proximal Tibia in Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis
- Preoperative Varus-Valgus Stress Angle Difference Is Valuable for Predicting the Extent of Medial Release in Varus Deformity during Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Valgus Deformity after Non-displaced Fracutre of the Proximal Tibia in Children
- A Clinical Study on Fracture of Femoral Neck in Children