Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2024 Nov;28(4):527-534. 10.14701/ahbps.24-033.
Robotic management of huge hepatic angiomyolipoma: A case report and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA
- 2Department of Pathology, Virginia Commonwealth University Health System, Richmond, VA, USA
- 3Department of Transplant Surgery, Virginia Commonwealth University Health System, Richmond, VA, USA
- KMID: 2561587
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.24-033
Abstract
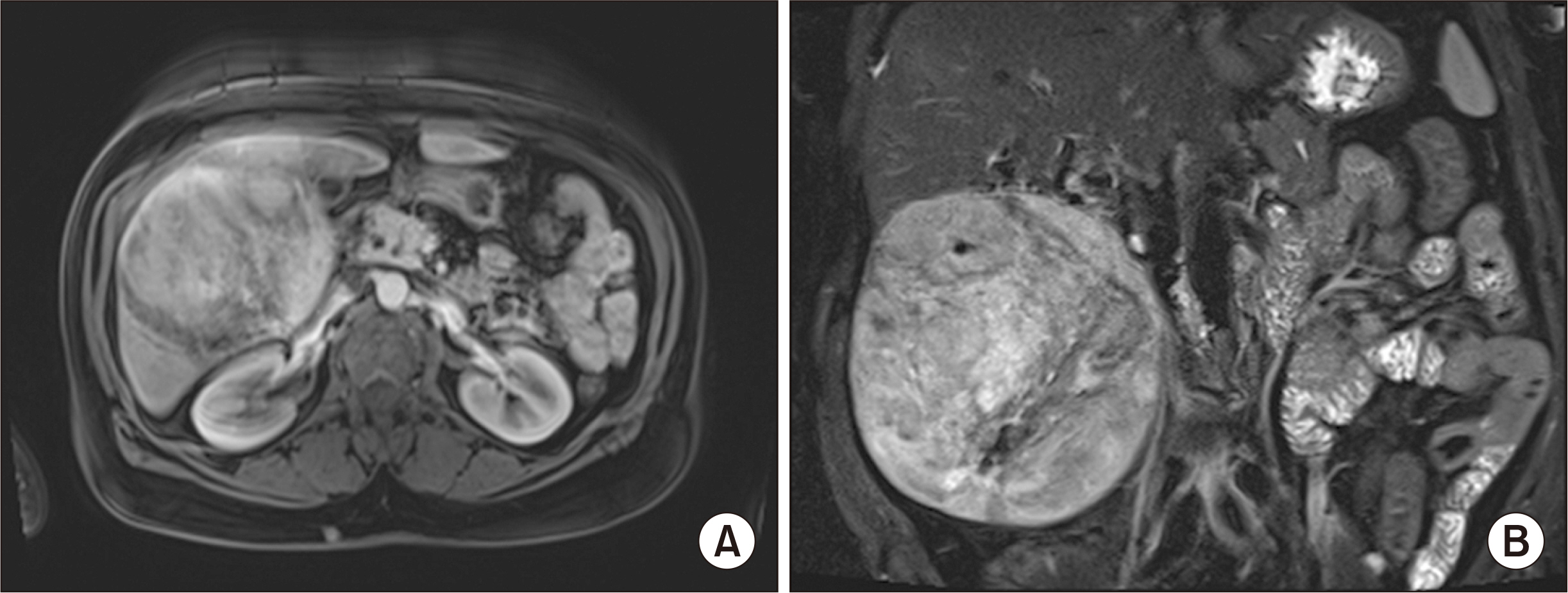
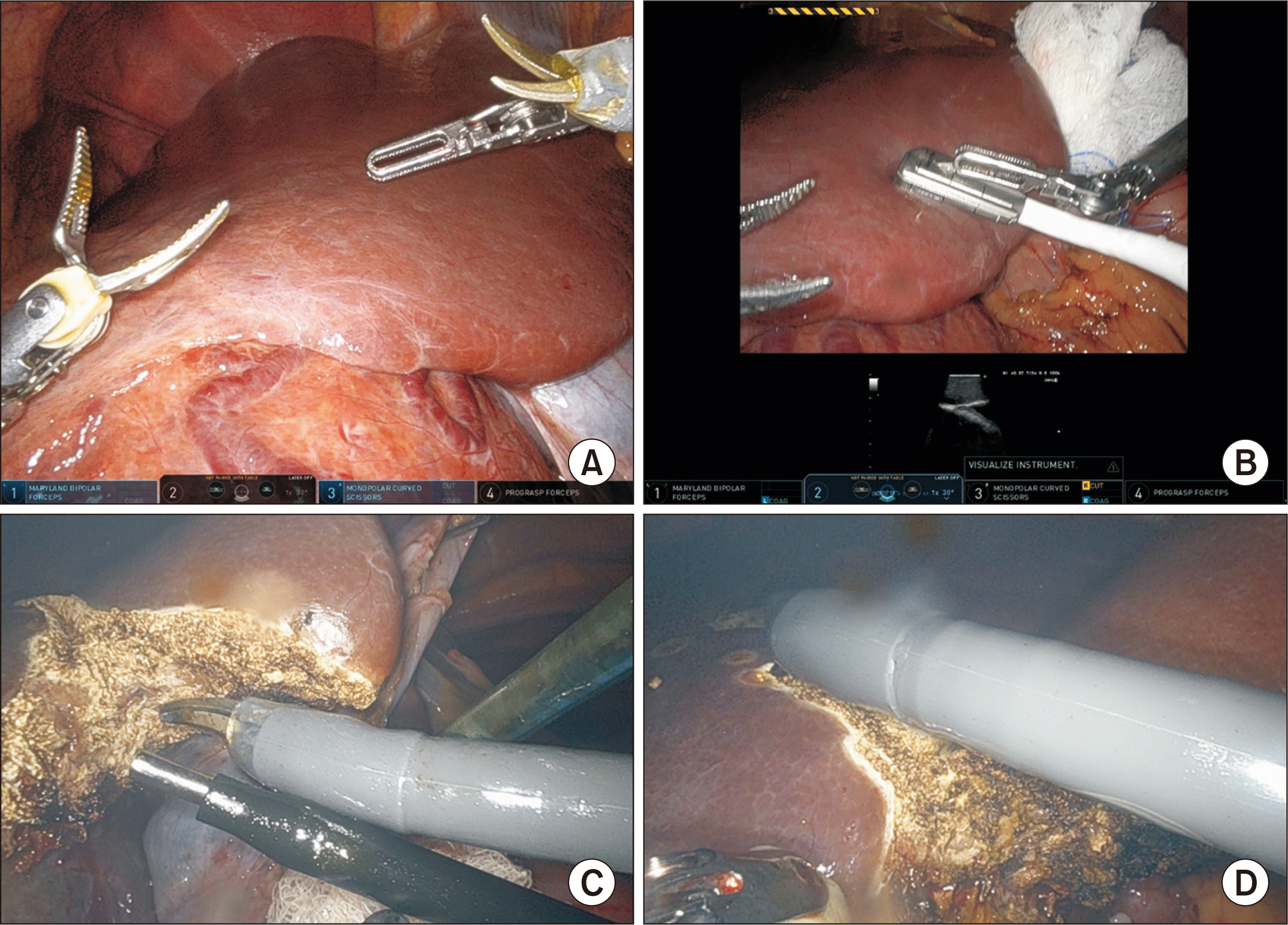
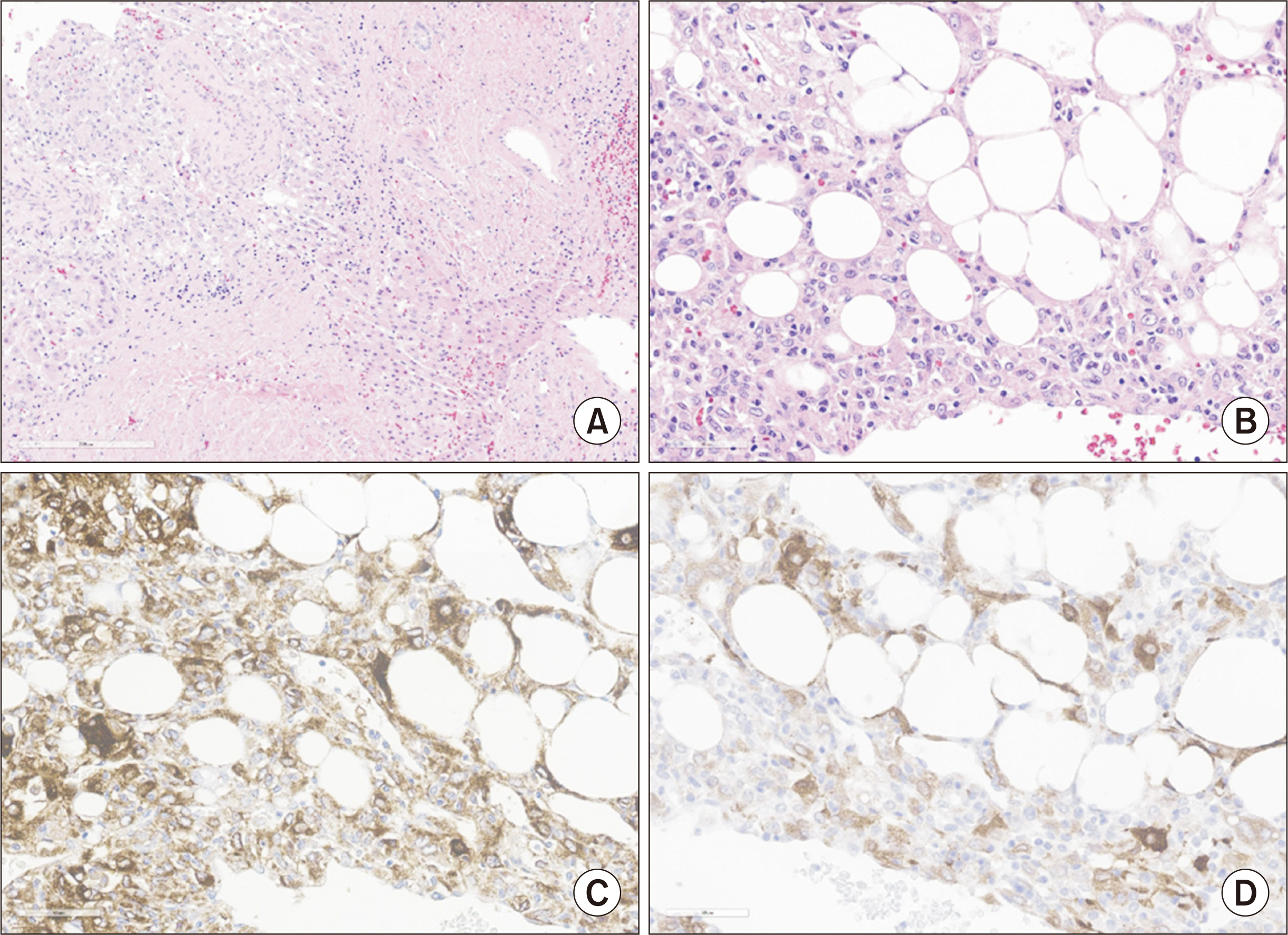
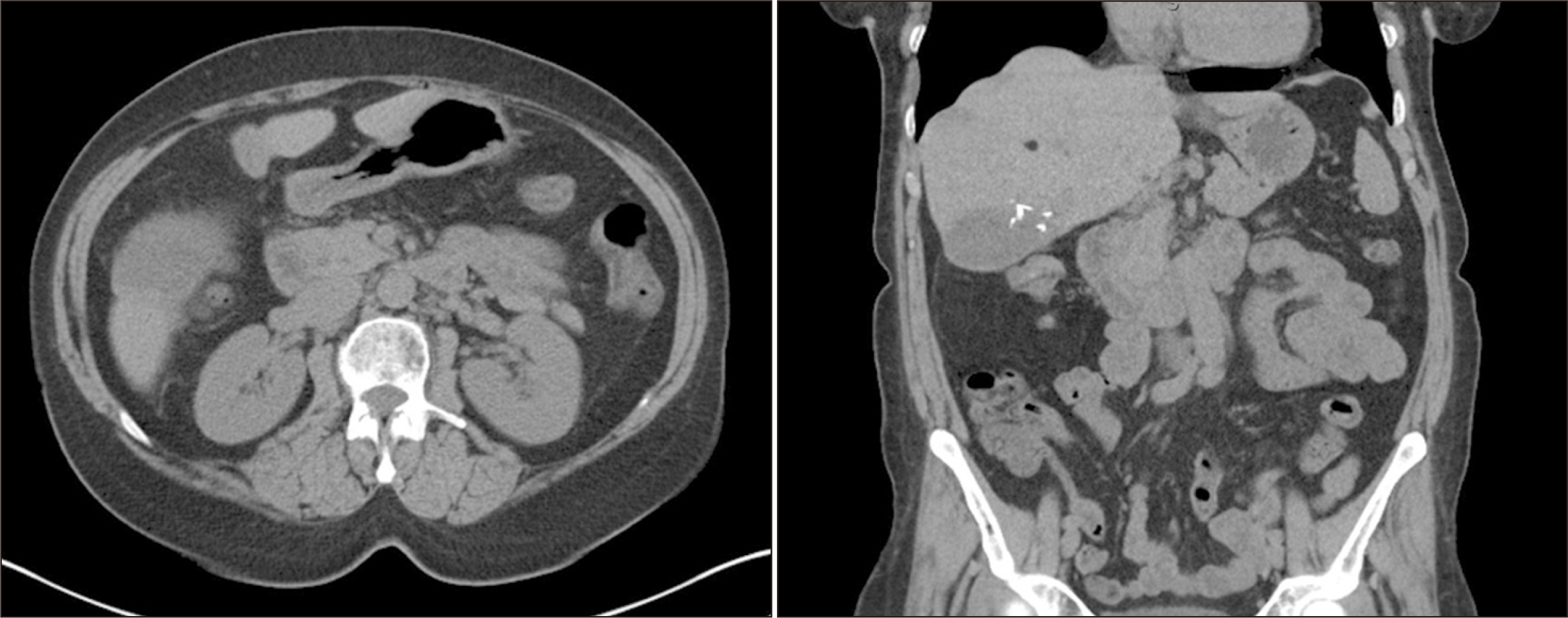
- Hepatic angiomyolipoma (HAML) is a rare, benign mesenchymal liver tumor encountered in Asia, primarily in females, and can be found within the right hepatic lobe, but also in other areas of the liver. Immunohistochemically, HAMLs are characteristically positive for human melanoma black-45 antigen (HMB-45) and can histochemically vary in the composition of angiomatous, lipomatous, and myomatous tissue, together with the presence of epithelioid cells. In this case report, we discuss a previously healthy patient presenting with bloating and previously documented concern of liver lesions, found to have HAML confirmed by surgical pathology. Surgery was decided, as HAMLs greater than 10 cm are at risk of rupture. This is one of the first documented cases of HAML resected through robot-assisted bisegmentectomy and cholecystectomy, and therefore, intraoperative images have been included to assist in the planning of future robotic cases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bashir O, Molinari A, Knipe H. 2012. Hepatic angiomyolipoma [Internet]. Radiopaedia;Available from: https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-17271. cited 2023 Oct 12. DOI: 10.53347/rID-17271.2. Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Garmpi A, Nonni A, Sakellariou S, Margonis GA, et al. 2017; Angiomyolipoma of the liver: a rare benign tumor treated with a laparoscopic approach for the first time. In Vivo. 31:1169–1173. DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11185.3. Günster SA, Kim M, Lock JF, Krajinovic K. 2020; Hepatic angiomyolipoma: a case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 77:345–348. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.11.045. PMID: 33212308. PMCID: PMC7683232.4. Klompenhouwer AJ, Dwarkasing RS, Doukas M, Pellegrino S, Vilgrain V, Paradis V, et al. 2020; Hepatic angiomyolipoma: an international multicenter analysis on diagnosis, management and outcome. HPB (Oxford). 22:622–629. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.09.004. PMID: 31619346.5. Petrolla AA, Xin W. 2008; Hepatic angiomyolipoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 132:1679–1682. DOI: 10.5858/2008-132-1679-HA. PMID: 18834230.6. Kamimura K, Nomoto M, Aoyagi Y. 2012; Hepatic angiomyolipoma: diagnostic findings and management. Int J Hepatol. 2012:410781. DOI: 10.1155/2012/410781. PMID: 23320180. PMCID: PMC3540709.7. Butte JM, Do RK, Shia J, Gönen M, D'Angelica MI, Getrajdman GI, et al. 2011; Liver angiomyolipomas: a clinical, radiologic, and pathologic analysis of 22 patients from a single center. Surgery. 150:557–567. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.03.006. PMID: 21621235.8. Ortiz S, Tortosa F. 2016; Epithelioid angiomyolipoma of the liver: clinicopathological correlation in a series of 4 cases. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 108:27–30. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2015.3947/2015. PMID: 26765232.9. Ding GH, Liu Y, Wu MC, Yang GS, Yang JM, Cong WM. 2011; Diagnosis and treatment of hepatic angiomyolipoma. J Surg Oncol. 103:807–812. DOI: 10.1002/jso.21814. PMID: 21283992.10. Zhu J, Wang G, Sun G, Xie B, Xiao W, Li Y. 2022; Primary hepatic epithelioid angiomyolipoma: a small case series. ANZ J Surg. 92:1803–1808. DOI: 10.1111/ans.17777. PMID: 35578781.11. Theodosopoulos T, Dellaportas D, Tsangkas A, Tsangkas N, Psychogiou V, Yiallourou A, et al. 2013; Clinicopathological features and management of hepatic vascular tumors. A 20-year experience in a Greek University Hospital. J BUON. 18:1026–1031. DOI: 10.1155/2013/763702. PMID: 23738184. PMCID: PMC3659466.12. Yang X, Lei C, Qiu Y, Shen S, Lu C, Yan L, et al. 2018; Selecting a suitable surgical treatment for hepatic angiomyolipoma: a retrospective analysis of 92 cases. ANZ J Surg. 88:E664–E669. DOI: 10.1111/ans.14323.13. Shimizu A, Ito M, Lefor AK. 2022; Laparoscopic and robot-assisted hepatic surgery: an historical review. J Clin Med. 11:3254. DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123254. PMID: 35743324. PMCID: PMC9225080.14. Chong CCN, Lok HT, Fung AKY, Fong AKW, Cheung YS, Wong J, et al. 2020; Robotic versus laparoscopic hepatectomy: application of the difficulty scoring system. Surg Endosc. 34:2000–2006. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-019-06976-8. PMID: 31312961.15. Tsilimigras DI, Moris D, Vagios S, Merath K, Pawlik TM. 2018; Safety and oncologic outcomes of robotic liver resections: a systematic review. J Surg Oncol. 117:1517–1530. DOI: 10.1002/jso.25018. PMID: 29473968.16. Cheung TT, Liu R, Cipriani F, Wang X, Efanov M, Fuks D, et al. International robotic and laparoscopic liver resection study group investigators. 2023; Robotic versus laparoscopic liver resection for huge (≥10 cm) liver tumors: an international multicenter propensity-score matched cohort study of 799 cases. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 12:205–215. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-22-283. PMID: 37124684. PMCID: PMC10129897.17. Dalager T, Jensen PT, Eriksen JR, Jakobsen HL, Mogensen O, Søgaard K. 2020; Surgeons' posture and muscle strain during laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Br J Surg. 107:756–766. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.11394. PMID: 31922258.18. Navarro JG, Rho SY, Choi GH. 2020; Robotic liver resection. Ann Robot Innov Surg. 1:15–32. DOI: 10.37007/aris.2020.1.1.15.19. D'Hondt M, Devooght A, Willems E, Wicherts D, De Meyere C, Parmentier I, et al. 2023; Transition from laparoscopic to robotic liver surgery: clinical outcomes, learning curve effect, and cost-effectiveness. J Robot Surg. 17:79–88. DOI: 10.1007/s11701-022-01405-w.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of the Kidney with Distant Metastasis
- Huge Hepatic Angiomyolipoma Mimicking Low Grade Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Case of Hepatic Angiomyolipoma Showing Different Uptake on F-18 FDG and C-11 Acetate PET
- Renal Angiomyolipoma: Report of 6 cases and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Hepatic Angiomyolipoma Diagnosed by Fine -needle Aspiration Biopsy