Child Kidney Dis.
2024 Oct;28(3):116-123. 10.3339/ckd.24.012.
Assessing the prognostic impact of KDIGO criteria on acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants: a critical insight
- Affiliations
-
- 1Programa de Pós Graduação em Ciências da Saúde, Universidade de Caxias do Sul, Caxias do Sul, Brazil
- 2Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, Hospital Geral de Caxias do Sul, Caxias do Sul, Brazil
- KMID: 2560481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.24.012
Abstract
- Purpose
To evaluate the incidence and identify risk factors for acute kidney injury (AKI) within the first 15 days of life in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants in a neonatal intensive care unit. Additionally, this study will examine whether AKI correlates with increased mortality rate in this population.
Methods
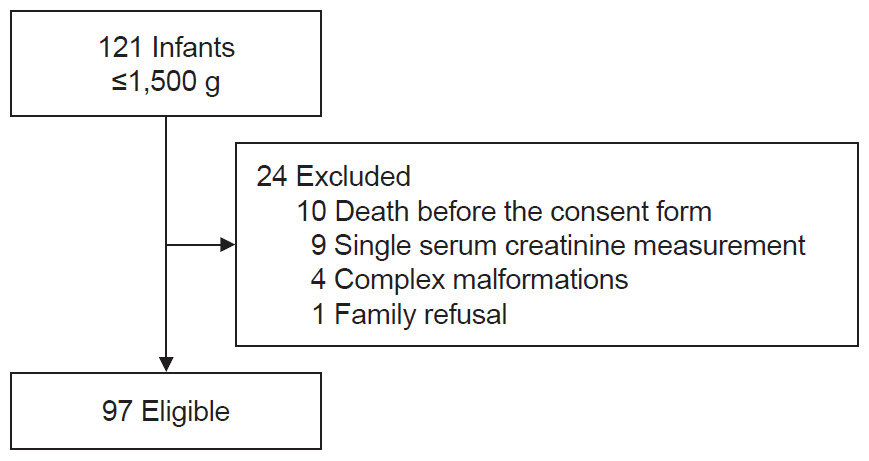
A prospective analysis was conducted on VLBW infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit from March 2017 to July 2021, diagnosing AKI based on the neonatal modified Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes criteria. Neonates who died before obtaining consent, had complex malformation, or only one serum creatinine measurement were excluded.
Results
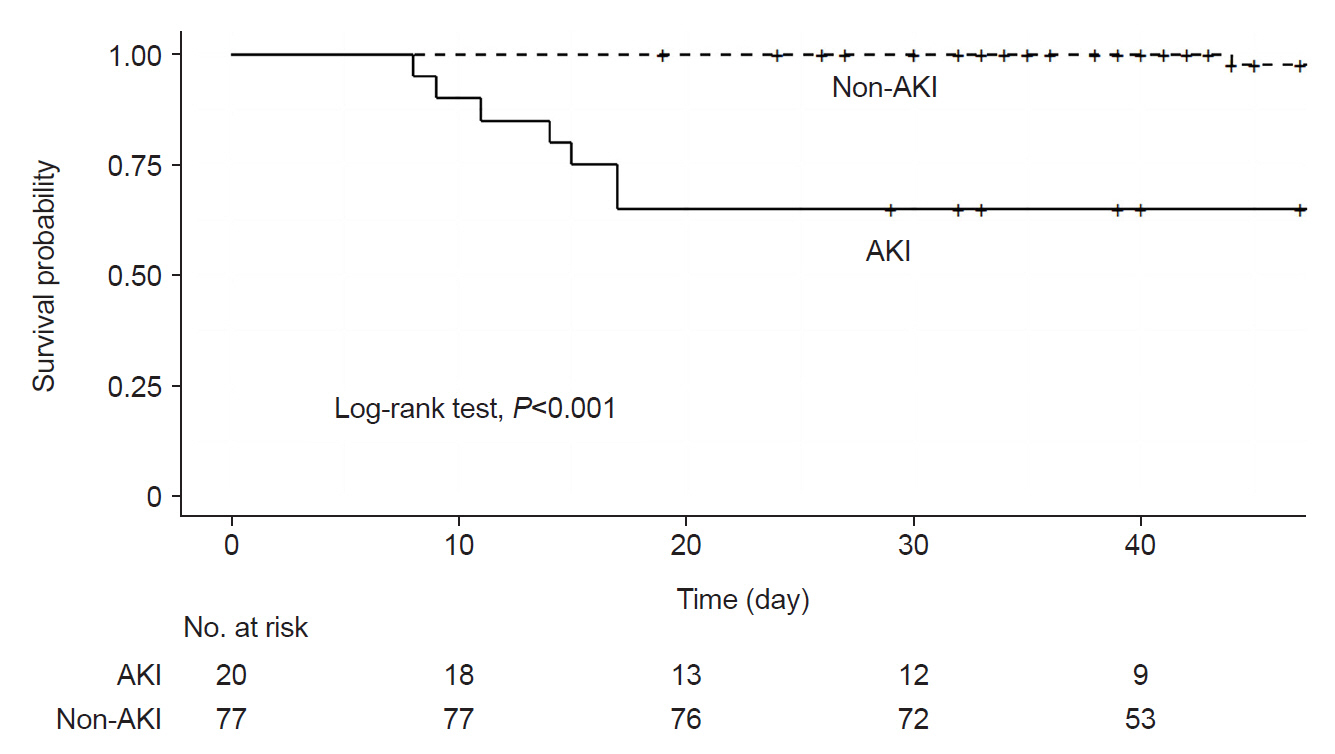
Out of 121 admitted VLBW infants, 97 were analyzed, with 20 (20.6%; 95% confidence interval, 12.6–28.7) diagnosed with AKI. Among these, 50% had creatinine abnormalities, 30% had urinary output changes, and 20% had both. Severe AKI (stage 2 or 3) was observed in 30% of cases, none required dialysis. AKI was associated with higher SNAPPE-II (Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology with Perinatal Extension-II) scores, more frequent severe intraventricular hemorrhage, and an increased mortality rate (35%). Multivariate analysis identified AKI as an independent risk factor for mortality, with a 9.72-fold increased risk (95% confidence interval, 2.53–37.4; P<0.01), and a shorter time to death.
Conclusions
Our findings underscore a significant incidence of AKI among VLBW infants, along with its strong association with increased mortality. These results highlight the critical need for thorough assessment of both serum creatinine and urinary output when diagnosing AKI in this vulnerable population.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants: challenges, risk factors, and outcomes
Jeong Yeon Kim
Child Kidney Dis. 2025;29(1):1-3. doi: 10.3339/ckd.25.006.
Reference
-
References
1. Mercier K, McRitchie S, Pathmasiri W, Novokhatny A, Koralkar R, Askenazi D, et al. Preterm neonatal urinary renal developmental and acute kidney injury metabolomic profiling: an exploratory study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017; 32:151–61.
Article2. Jetton JG, Boohaker LJ, Sethi SK, Wazir S, Rohatgi S, Soranno DE, et al. Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): a multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2017; 1:184–94.
Article3. Askenazi DJ, Heagerty PJ, Schmicker RH, Griffin R, Brophy P, Juul SE, et al. Prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in extremely low gestational age neonates (ELGAN). Pediatr Nephrol. 2020; 35:1737–48.
Article4. Jetton JG, Guillet R, Askenazi DJ, Dill L, Jacobs J, Kent AL, et al. Assessment of worldwide acute kidney injury epidemiology in neonates: design of a retrospective cohort study. Front Pediatr. 2016; 4:68.
Article5. Section 2: AKI definition. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2012; 2:19–36.6. Zappitelli M, Noone D. The long and the short of it: the impact of acute kidney injury in critically ill children. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2020; 96:533–6.7. Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, et al. Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics. 2015; 136:e463–73.
Article8. Sutherland SM, Alobaidi R, Gorga SM, Iyengar A, Morgan C, Heydari E, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in children: a report from the 26th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) consensus conference. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024; 39:919–28.
Article9. Mammen C, Al Abbas A, Skippen P, Nadel H, Levine D, Collet JP, et al. Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 59:523–30.
Article10. Goldstein SL, Akcan-Arikan A, Alobaidi R, Askenazi DJ, Bagshaw SM, Barhight M, et al. Consensus-based recommendations on priority activities to address acute kidney injury in children: a modified Delphi consensus statement. JAMA Netw Open. 2022; 5:e2229442.11. Zappitelli M, Ambalavanan N, Askenazi DJ, Moxey-Mims MM, Kimmel PL, Star RA, et al. Developing a neonatal acute kidney injury research definition: a report from the NIDDK neonatal AKI workshop. Pediatr Res. 2017; 82:569–73.
Article12. Richardson DK, Corcoran JD, Escobar GJ, Lee SK. SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J Pediatr. 2001; 138:92–100.
Article13. Muktan D, Singh RR, Bhatta NK, Shah D. Neonatal mortality risk assessment using SNAPPE-II score in a neonatal intensive care unit. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19:279.14. Burgmaier K, Zeiher M, Weber A, Cosgun ZC, Aydin A, Kuehne B, et al. Low incidence of acute kidney injury in VLBW infants with restrictive use of mechanical ventilation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024; 39:1279–88.
Article15. Daga A, Dapaah-Siakwan F, Rajbhandari S, Arevalo C, Salvador A. Diagnosis and risk factors of acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017; 58:258–63.
Article16. Srinivasan N, Schwartz A, John E, Price R, Amin S. Acute kidney injury impairs postnatal renal adaptation and increases morbidity and mortality in very low-birth-weight infants. Am J Perinatol. 2018; 35:39–47.17. Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL; AWARE Investigators. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:11–20.
Article18. Harer MW, Askenazi DJ, Boohaker LJ, Carmody JB, Griffin RL, Guillet R, et al. Association between early caffeine citrate administration and risk of acute kidney injury in preterm neonates: results from the AWAKEN Study. JAMA Pediatr. 2018; 172:e180322.19. Haynes N, Bell J, Griffin R, Askenazi DJ, Jetton J, Kent AL, et al. Receipt of high-frequency ventilation is associated with acute kidney injury in very preterm neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024; 39:579–87.
Article20. Turker G, Ozsoy G, Gunlemez A, Gokalp AS, Arisoy AE, Bircan Z. Acute renal failure SNAPPE and mortality. Pediatr Int. 2011; 53:483–8.
Article21. Askenazi D, Patil NR, Ambalavanan N, Balena-Borneman J, Lozano DJ, Ramani M, et al. Acute kidney injury is associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia/mortality in premature infants. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015; 30:1511–8.
Article22. Wu Y, Wang H, Pei J, Jiang X, Tang J. Acute kidney injury in premature and low birth weight neonates: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37:275–87.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants: challenges, risk factors, and outcomes
- Successful Peritoneal Dialysis in an Extremely Preterm Infant
- Acute kidney injury in hospitalized adults with chronic kidney disease: comparing cROCK, KDIGO, and combined criteria
- Sequential Cases of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome in Very Low Birth Weight Infants
- Clinical Study of Prematurity and Low Birth Weight Infants