Anat Cell Biol.
2024 Sep;57(3):419-430. 10.5115/acb.23.284.
Exploring the therapeutic potential: Apelin-13’s neuroprotective effects foster sustained functional motor recovery in a rat model of Huntington’s disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biology and Anatomical Sciences, School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 2Hearing Disorders Research Center, Loghman Hakim Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 3Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Research Institute for Non-Communicable Diseases, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran
- 4Laser Application in Medical Sciences Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 5Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, AJA University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 6Proteomics Research Center, Faculty of Paramedical Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 7Rayan Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Ravan Sazeh Company, Tehran, Iran
- KMID: 2559761
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.23.284
Abstract
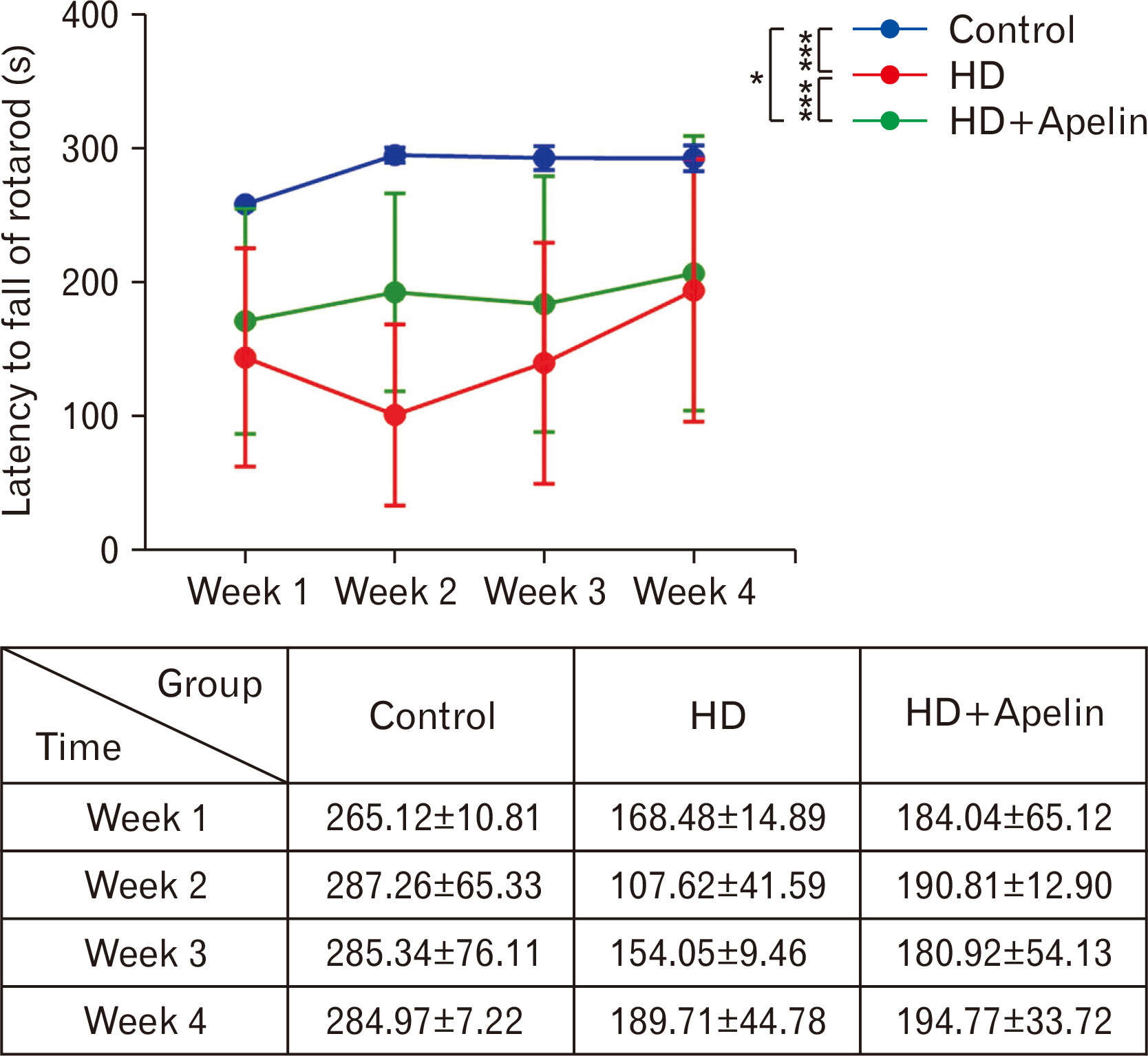
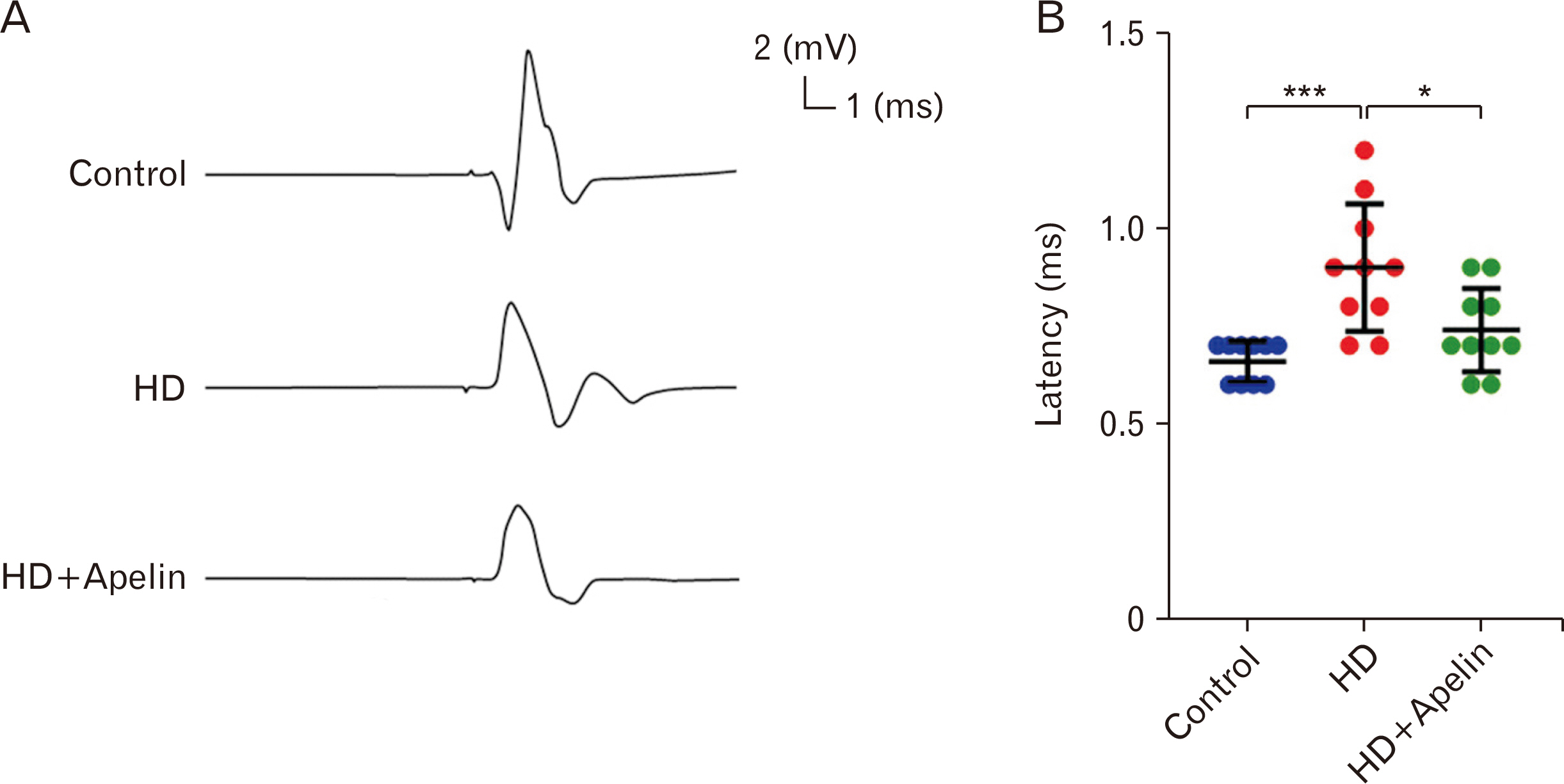
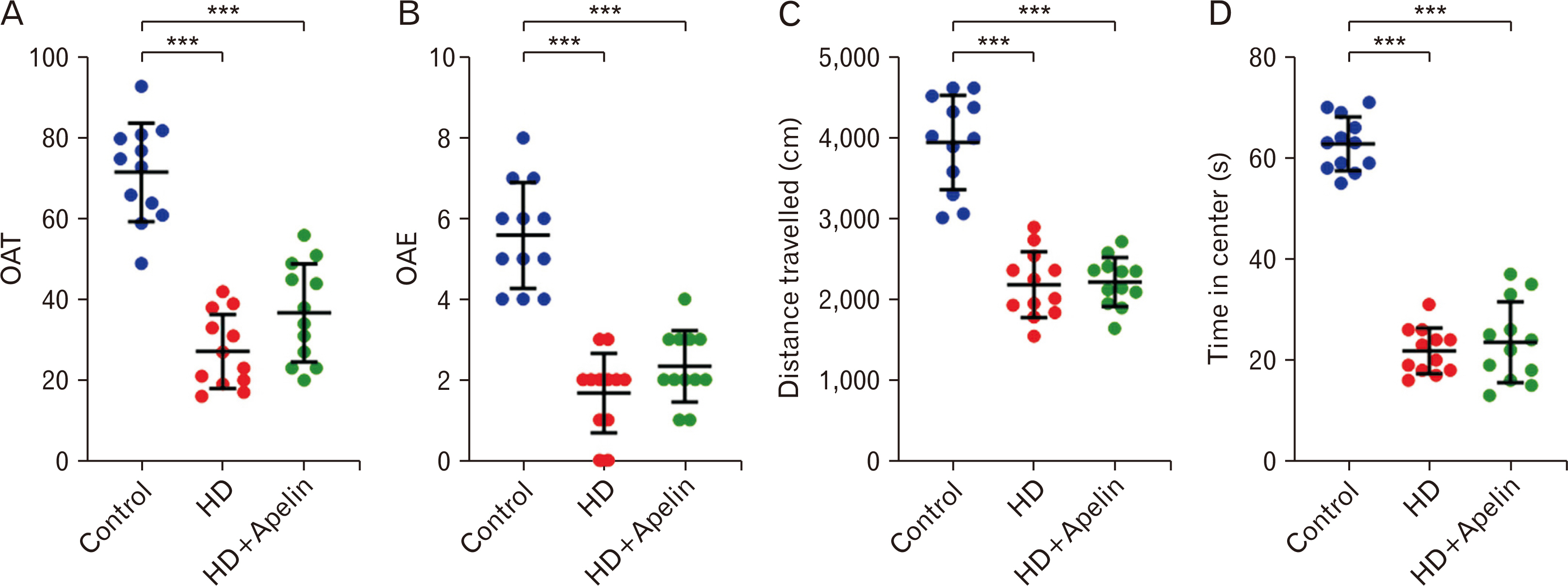
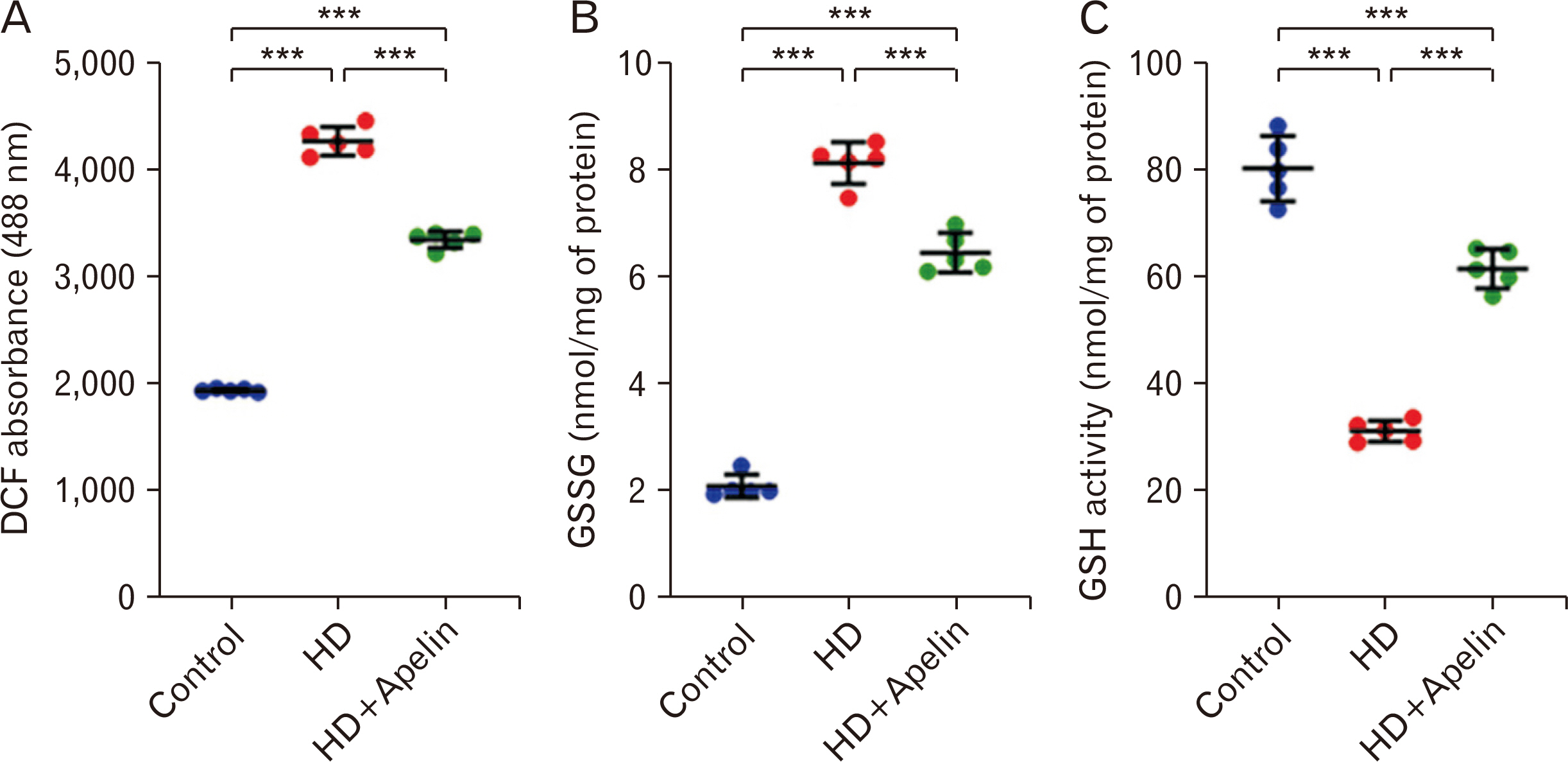
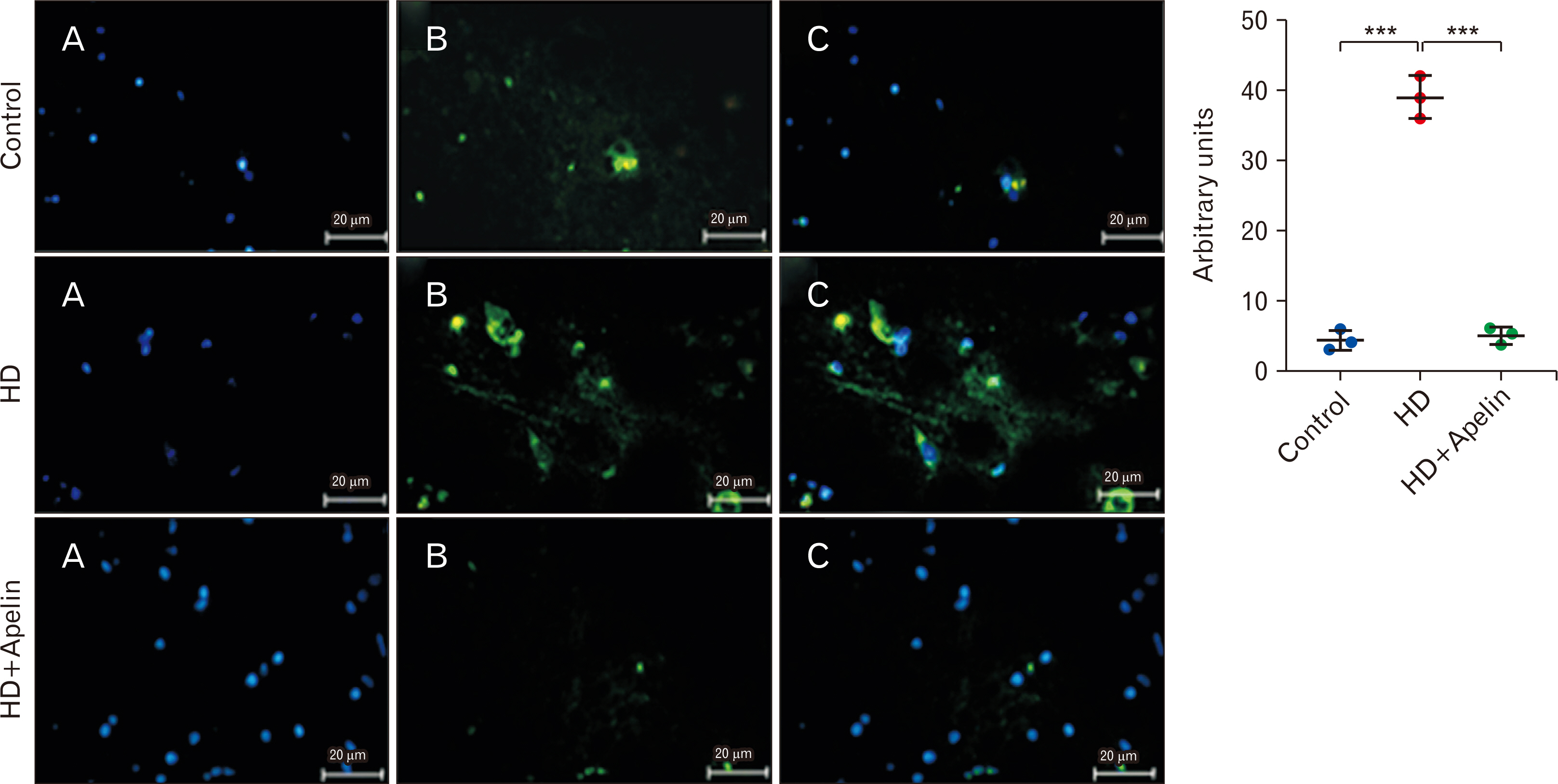
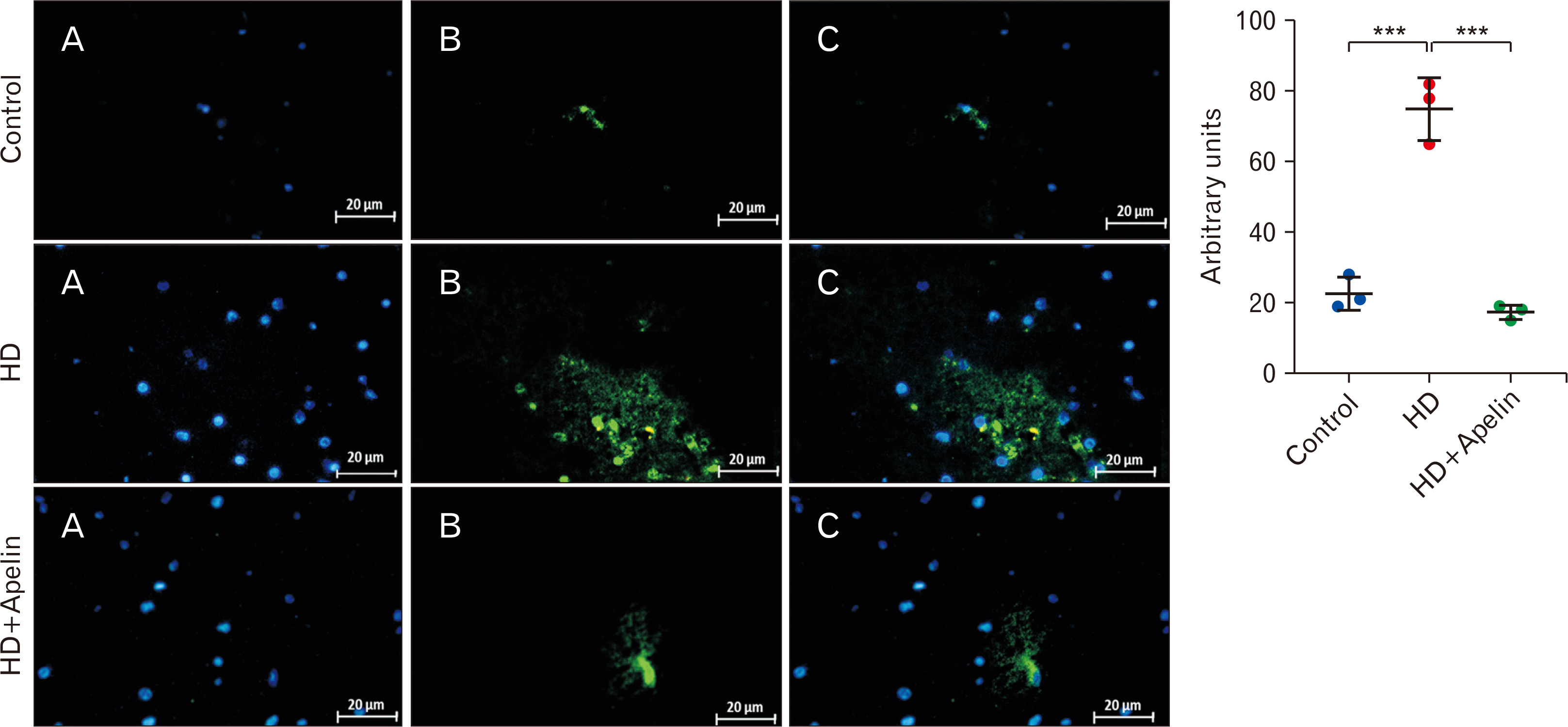
- Huntington’s disease (HD) is a hereditary condition considered by the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain, resultant in motor dysfunction and cognitive impairment. Despite current treatment modalities including pharmaceuticals and various therapies, a definitive cure remains elusive. Therefore, this study investigates the therapeutic potential effect of Apelin-13 in HD management. Thirty male Wistar rats were allocated into three groups: a control group, a group with HD, and a group with both HD and administered Apelin-13. Apelin-13 was administered continuously over a 28-day period at a dosage of around 30 mg/kg to mitigate inflammation in rats subjected to 3-NP injection within an experimental HD model. Behavioral tests, such as rotarod, electromyography (EMG), elevated plus maze, and open field assessments, demonstrated that Apelin-13 improved motor function and coordination in rats injected with 3-NP. Apelin-13 treatment significantly increased neuronal density and decreased glial cell counts compared to the control group. Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed reduced gliosis and expression of inflammatory factors in the treatment group. Moreover, Apelin-13 administration led to elevated levels of glutathione and reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in the treated group. Apelin-13 demonstrates neuroprotective effects, leading to improved movement and reduced inflammatory and fibrotic factors in the HD model.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim A, Lalonde K, Truesdell A, Gomes Welter P, Brocardo PS, Rosenstock TR, Gil-Mohapel J. 2021; New avenues for the treatment of Huntington's disease. Int J Mol Sci. 22:8363. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22168363. PMID: 34445070. PMCID: PMC8394361.2. Pringsheim T, Wiltshire K, Day L, Dykeman J, Steeves T, Jette N. 2012; The incidence and prevalence of Huntington's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord. 27:1083–91. DOI: 10.1002/mds.25075. PMID: 22692795.3. Rawlins MD, Wexler NS, Wexler AR, Tabrizi SJ, Douglas I, Evans SJ, Smeeth L. 2016; The prevalence of Huntington's disease. Neuroepidemiology. 46:144–53. DOI: 10.1159/000443738.4. Kay C, Collins JA, Wright GEB, Baine F, Miedzybrodzka Z, Aminkeng F, Semaka AJ, McDonald C, Davidson M, Madore SJ, Gordon ES, Gerry NP, Cornejo-Olivas M, Squitieri F, Tishkoff S, Greenberg JL, Krause A, Hayden MR. 2018; The molecular epidemiology of Huntington disease is related to intermediate allele frequency and haplotype in the general population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 177:346–57. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32618. PMID: 29460498.5. Liu JP, Zeitlin SO. 2017; Is Huntingtin dispensable in the adult brain? J Huntingtons Dis. 6:1–17. DOI: 10.3233/JHD-170235. PMID: 28339401. PMCID: PMC5389021.6. Ochaba J, Lukacsovich T, Csikos G, Zheng S, Margulis J, Salazar L, Mao K, Lau AL, Yeung SY, Humbert S, Saudou F, Klionsky DJ, Finkbeiner S, Zeitlin SO, Marsh JL, Housman DE, Thompson LM, Steffan JS. 2014; Potential function for the Huntingtin protein as a scaffold for selective autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 111:16889–94. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1420103111. PMID: 25385587. PMCID: PMC4250109.7. Semaka A, Kay C, Doty C, Collins JA, Bijlsma EK, Richards F, Goldberg YP, Hayden MR. 2013; CAG size-specific risk estimates for intermediate allele repeat instability in Huntington disease. J Med Genet. 50:696–703. DOI: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101796. PMID: 23896435.8. Dayalu P, Albin RL. 2015; Huntington disease: pathogenesis and treatment. Neurol Clin. 33:101–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2014.09.003. PMID: 25432725.9. Gil JM, Rego AC. 2008; Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease. Eur J Neurosci. 27:2803–20. DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06310.x.10. Cattaneo E, Zuccato C, Tartari M. 2005; Normal huntingtin function: an alternative approach to Huntington's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:919–30. DOI: 10.1038/nrn1806. PMID: 16288298.11. Nance MA. 1998; Huntington disease: clinical, genetic, and social aspects. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 11:61–70. DOI: 10.1177/089198879801100204. PMID: 9877527.12. O'Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Kennedy JL, Shi X, Petronis A, George SR, Nguyen T. 1993; A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene. 136:355–60. DOI: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90495-O. PMID: 8294032.13. Langelaan DN, Bebbington EM, Reddy T, Rainey JK. 2009; Structural insight into G-protein coupled receptor binding by apelin. Biochemistry. 48:537–48. DOI: 10.1021/bi801864b. PMID: 19123778.14. Ladeiras-Lopes R, Ferreira-Martins J, Leite-Moreira AF. 2008; The apelinergic system: the role played in human physiology and pathology and potential therapeutic applications. Arq Bras Cardiol. 90:343–9. DOI: 10.1590/S0066-782X2008000500012. PMID: 18516406.15. Niknazar S, Abbaszadeh HA, Peyvandi H, Rezaei O, Forooghirad H, Khoshsirat S, Peyvandi AA. 2019; Protective effect of [Pyr1]-apelin-13 on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hair cell-like cells derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 853:25–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.012. PMID: 30876980.16. Khoshsirat S, Abbaszadeh HA, Peyvandi AA, Heidari F, Peyvandi M, Simani L, Niknazar S. 2021; Apelin-13 prevents apoptosis in the cochlear tissue of noise-exposed rat via Sirt-1 regulation. J Chem Neuroanat. 114:101956. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2021.101956. PMID: 33831513.17. Li Y, Bai YJ, Jiang YR, Yu WZ, Shi X, Chen L, Feng J, Sun GB. 2018; Apelin-13 is an early promoter of cytoskeleton and tight junction in diabetic macular edema via PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways. Biomed Res Int. 2018:3242574. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3242574. PMID: 29850504. PMCID: PMC5904819.18. Luo H, Han L, Xu J. 2020; Apelin/APJ system: a novel promising target for neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 235:638–57. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29001. PMID: 31254280.19. Abbaszadeh HA, Tiraihi T, Delshad A, Saghedizadeh M, Taheri T, Kazemi H, Hassoun HK. 2014; Differentiation of neurosphere-derived rat neural stem cells into oligodendrocyte-like cells by repressing PDGF-α and Olig2 with triiodothyronine. Tissue Cell. 46:462–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.tice.2014.08.003. PMID: 25200619.20. Ziaeipour S, Ahrabi B, Naserzadeh P, Aliaghaei A, Sajadi E, Abbaszadeh HA, Amini A, Abdi S, Darabi S, Abdollahifar MA. 2019; Effects of Sertoli cell transplantation on spermatogenesis in azoospermic mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 52:421–34. DOI: 10.33594/000000030. PMID: 30845381.21. Darabi S, Noori-Zadeh A, Rajaei F, Abbaszadeh HA, Bakhtiyari S, Roozbahany NA. 2018; SMER28 attenuates dopaminergic toxicity mediated by 6-hydroxydopamine in the rats via modulating oxidative burdens and autophagy-related parameters. Neurochem Res. 43:2313–23. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-018-2652-2. PMID: 30288644.22. Browne SE, Beal MF. 2006; Oxidative damage in Huntington's disease pathogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:2061–73. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.2061. PMID: 17034350.23. Sorolla MA, Reverter-Branchat G, Tamarit J, Ferrer I, Ros J, Cabiscol E. 2008; Proteomic and oxidative stress analysis in human brain samples of Huntington disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:667–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.05.014. PMID: 18588971.24. O'Donnell LA, Agrawal A, Sabnekar P, Dichter MA, Lynch DR, Kolson DL. 2007; Apelin, an endogenous neuronal peptide, protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic injury. J Neurochem. 102:1905–17. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04645.x. PMID: 17767704.25. Kleinz MJ, Baxter GF. 2008; Apelin reduces myocardial reperfusion injury independently of PI3K/Akt and P70S6 kinase. Regul Pept. 146:271–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.10.002. PMID: 18022257.26. Zhuge J, Cederbaum AI. 2006; Serum deprivation-induced HepG2 cell death is potentiated by CYP2E1. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:63–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.08.012. PMID: 16337880.27. Zeng XJ, Yu SP, Zhang L, Wei L. 2010; Neuroprotective effect of the endogenous neural peptide apelin in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Exp Cell Res. 316:1773–83. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.02.005. PMID: 20152832. PMCID: PMC3155990.28. Barcia C, Ros CM, Annese V, Gómez A, Ros-Bernal F, Aguado-Yera D, Martínez-Pagán ME, de Pablos V, Fernandez-Villalba E, Herrero MT. 2011; IFN-γ signaling, with the synergistic contribution of TNF-α, mediates cell specific microglial and astroglial activation in experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis. 2:e142. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.17. PMID: 22914327. PMCID: PMC3434670.29. Bayat AH, Azimi H, Hassani Moghaddam M, Ebrahimi V, Fathi M, Vakili K, Mahmoudiasl GR, Forouzesh M, Boroujeni ME, Nariman Z, Abbaszadeh HA, Aryan A, Aliaghaei A, Abdollahifar MA. 2022; COVID-19 causes neuronal degeneration and reduces neurogenesis in human hippocampus. Apoptosis. 27:852–68. DOI: 10.1007/s10495-022-01754-9. PMID: 35876935. PMCID: PMC9310365.30. Malyszko J, Malyszko JS, Pawlak K, Wolczynski S, Mysliwiec M. 2008; Apelin, a novel adipocytokine, in relation to endothelial function and inflammation in kidney allograft recipients. Transplant Proc. 40:3466–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.06.059. PMID: 19100414.31. Yu S, Zhang Y, Li MZ, Xu H, Wang Q, Song J, Lin P, Zhang L, Liu Q, Huang QX, Wang K, Hou WK. 2012; Chemerin and apelin are positively correlated with inflammation in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:3440–4. PMID: 23044303.32. Khaksari M, Aboutaleb N, Nasirinezhad F, Vakili A, Madjd Z. 2012; Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury and cerebral edema in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 48:201–8. DOI: 10.1007/s12031-012-9808-3. PMID: 22638858.33. Wang W, McKinnie SM, Patel VB, Haddad G, Wang Z, Zhabyeyev P, Das SK, Basu R, McLean B, Kandalam V, Penninger JM, Kassiri Z, Vederas JC, Murray AG, Oudit GY. 2013; Loss of Apelin exacerbates myocardial infarction adverse remodeling and ischemia-reperfusion injury: therapeutic potential of synthetic Apelin analogues. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e000249. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000249. PMID: 23817469. PMCID: PMC3828798.34. Tiani C, Garcia-Pras E, Mejias M, de Gottardi A, Berzigotti A, Bosch J, Fernandez M. 2009; Apelin signaling modulates splanchnic angiogenesis and portosystemic collateral vessel formation in rats with portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 50:296–305. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.09.019. PMID: 19070926.35. Yoshiya S, Shirabe K, Imai D, Toshima T, Yamashita Y, Ikegami T, Okano S, Yoshizumi T, Kawanaka H, Maehara Y. 2015; Blockade of the apelin-APJ system promotes mouse liver regeneration by activating Kupffer cells after partial hepatectomy. J Gastroenterol. 50:573–82. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-014-0992-5. PMID: 25148722.36. Chen D, Lee J, Gu X, Wei L, Yu SP. 2015; Intranasal delivery of apelin-13 is neuroprotective and promotes angiogenesis after ischemic stroke in mice. ASN Neuro. 7:1759091415605114. DOI: 10.1177/1759091415605114. PMID: 26391329. PMCID: PMC4580122.37. Xin Q, Cheng B, Pan Y, Liu H, Yang C, Chen J, Bai B. 2015; Neuroprotective effects of apelin-13 on experimental ischemic stroke through suppression of inflammation. Peptides. 63:55–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.09.016. PMID: 25278489.38. O'Carroll AM, Lolait SJ, Harris LE, Pope GR. 2013; The apelin receptor APJ: journey from an orphan to a multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J Endocrinol. 219:R13–35. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-13-0227. PMID: 23943882.39. Qiu Y, Cao Y, Cao W, Jia Y, Lu N. 2020; The application of ferroptosis in diseases. Pharmacol Res. 159:104919. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104919. PMID: 32464324.40. Zhang Z, Tang J, Song J, Xie M, Liu Y, Dong Z, Liu X, Li X, Zhang M, Chen Y, Shi H, Zhong J. 2022; Elabela alleviates ferroptosis, myocardial remodeling, fibrosis and heart dysfunction in hypertensive mice by modulating the IL-6/STAT3/GPX4 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 181:130–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.020. PMID: 35122997.41. Tang M, Huang Z, Luo X, Liu M, Wang L, Qi Z, Huang S, Zhong J, Chen JX, Li L, Wu D, Chen L. 2019; Ferritinophagy activation and sideroflexin1-dependent mitochondria iron overload is involved in apelin-13-induced cardiomyocytes hypertrophy. Free Radic Biol Med. 134:445–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.052. PMID: 30731113.42. Li A, Zhao Q, Chen L, Li Z. 2023; Apelin/APJ system: an emerging therapeutic target for neurological diseases. Mol Biol Rep. 50:1639–53. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-022-08075-9. PMID: 36378421. PMCID: PMC9665010.43. Ellrichmann G, Reick C, Saft C, Linker RA. 2013; The role of the immune system in Huntington's disease. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:541259. DOI: 10.1155/2013/541259. PMID: 23956761. PMCID: PMC3727178.44. Hsiao HY, Chen YC, Chen HM, Tu PH, Chern Y. 2013; A critical role of astrocyte-mediated nuclear factor-κB-dependent inflammation in Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 22:1826–42. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddt036. PMID: 23372043.45. Hsiao HY, Chiu FL, Chen CM, Wu YR, Chen HM, Chen YC, Kuo HC, Chern Y. 2014; Inhibition of soluble tumor necrosis factor is therapeutic in Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 23:4328–44. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu151. PMID: 24698979.46. Pozniak PD, White MK, Khalili K. 2014; TNF-α/NF-κB signaling in the CNS: possible connection to EPHB2. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 9:133–41. DOI: 10.1007/s11481-013-9517-x. PMID: 24277482. PMCID: PMC3959244.47. Khoshnan A, Ko J, Watkin EE, Paige LA, Reinhart PH, Patterson PH. 2004; Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex and nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to mutant huntingtin neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 24:7999–8008. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2675-04.2004. PMID: 15371500. PMCID: PMC6729796.48. Ishimaru Y, Sumino A, Kajioka D, Shibagaki F, Yamamuro A, Yoshioka Y, Maeda S. 2017; Apelin protects against NMDA-induced retinal neuronal death via an APJ receptor by activating Akt and ERK1/2, and suppressing TNF-α expression in mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 133:34–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphs.2016.12.002. PMID: 28087150.49. Zhang H, Chen S, Zeng M, Lin D, Wang Y, Wen X, Xu C, Yang L, Fan X, Gong Y, Zhang H, Kong X. 2018; Apelin-13 administration protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:1918–32. DOI: 10.1159/000493653. PMID: 30235451.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Functional Magnetic Stimulation on the Functional Recovery in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury
- Behavioral Testing for Therapeutic Outcome Measurements in an Animal Model of Huntington's Disease
- Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients
- A Case of Huntington's Chorea