J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Sep;39(34):e255. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e255.
High-Dose Corticosteroid Use in Severe to Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Nationwide PopulationBased Matched Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Vaccine Bio Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2559201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e255
Abstract
- Background
Systemic corticosteroids have become the standard of care for severe to critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the real-world efficacy and safety outcomes associated with a higher dose of corticosteroids remain uncertain.
Methods
We conducted a nationwide, population-based, matched cohort study of severe to critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 between January 2020 and June 2021 in Korea using the National Health Information Database. Patients using systemic corticosteroids were included and high-dose corticosteroid use was defined as a daily mean prescribed dose of more than 6 mg of dexamethasone. We then employed a proportional hazard regression model to identify prognostic factors for 28-day all-cause mortality and conducted a Fine and Gray regression model to assess risk factors for developing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA).
Results
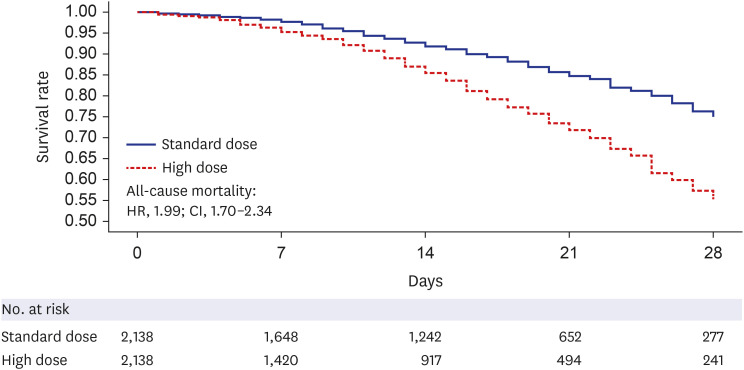
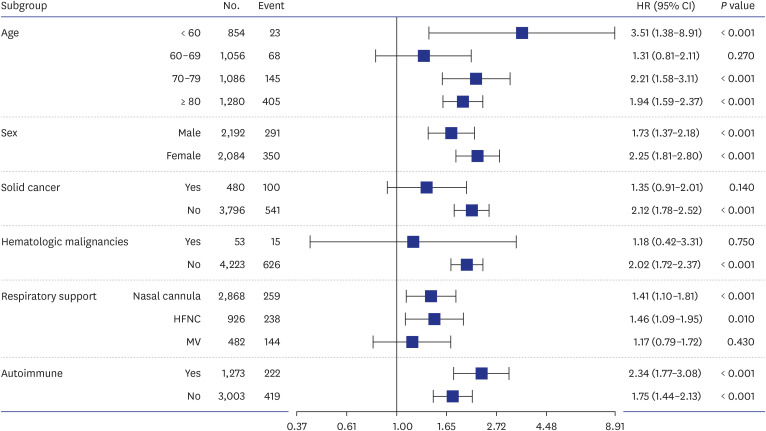
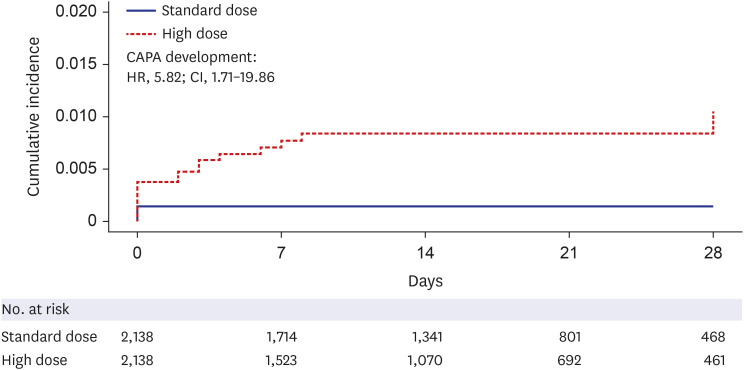
During the study period, 102,304 patients with COVID-19 were screened, 5,754 met the eligibility criteria, and 2,138 were successfully matched. The mean prescribed daily dose was 4.2 mg and 13.4 mg in the standard- and high-dose groups, respectively, and the mean duration of use was not different between the groups. High-dose corticosteroid use independently increased all-cause mortality at 28 days (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.48; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.25–1.76) and 90 days (aHR, 1.63; CI, 1.44–1.85) after admission. Subgroup analysis revealed a statistically significant elevation in the risk of mortality among patients using low-flow or high-flow nasal cannulas, with aHRs of 1.41 and 1.46, respectively. No significant impact of high-dose steroids was observed, even in patients who underwent mechanical ventilation at 28 days (aHR, 1.17; CI, 0.79–1.72). As a safety outcome, high-dose corticosteroid use showed an association with the development of CAPA (aHR, 2.97; 95% CI, 0.94–9.43).
Conclusion
Among severe to critically ill patients with COVID-19, high-dose corticosteroid use was associated with increased 28-day all-cause mortality and showed a trend toward the development of CAPA.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA. 2020; 323(20):2052–2059. PMID: 32320003.2. Park DH, Kang CK, Choe PG, Kim NJ, Park WB, Oh MD. How we have treated severe to critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(49):e353. PMID: 36536547.3. Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(8):693–704. PMID: 32678530.4. Jeronimo CM, Farias ME, Val FF, Sampaio VS, Alexandre MA, Melo GC, et al. Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): a randomized, double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(9):e373–e381. PMID: 32785710.5. Munch MW, Myatra SN, Vijayaraghavan BK, Saseedharan S, Benfield T, Wahlin RR, et al. Effect of 12 mg vs 6 mg of dexamethasone on the number of days alive without life support in adults with COVID-19 and severe hypoxemia: the COVID STEROID 2 randomized trial. JAMA. 2021; 326(18):1807–1817. PMID: 34673895.6. Pinzón MA, Ortiz S, Holguín H, Betancur JF, Cardona Arango D, Laniado H, et al. Dexamethasone vs methylprednisolone high dose for Covid-19 pneumonia. PLoS One. 2021; 16(5):e0252057. PMID: 34033648.7. Tomazini BM, Maia IS, Cavalcanti AB, Berwanger O, Rosa RG, Veiga VC, et al. Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the CoDEX randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020; 324(13):1307–1316. PMID: 32876695.8. Toroghi N, Abbasian L, Nourian A, Davoudi-Monfared E, Khalili H, Hasannezhad M, et al. Comparing efficacy and safety of different doses of dexamethasone in the treatment of COVID-19: a three-arm randomized clinical trial. Pharmacol Rep. 2022; 74(1):229–240. PMID: 34837648.9. Tan RS, Ng KT, Xin CE, Atan R, Yunos NM, Hasan MS. High-dose versus low-dose corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022; 36(9):3576–3586. PMID: 35715291.10. Abani O, Abbas A, Abbas F, Abbas J, Abbas K, Abbas M, et al. Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2023; 401(10387):1499–1507. PMID: 37060915.11. Salton F, Confalonieri P, Meduri GU, Santus P, Harari S, Scala R, et al. Prolonged low-dose methylprednisolone in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020; 7(10):ofaa421. PMID: 33072814.12. Lee R, Cho SY, Lee DG, Ahn H, Choi H, Choi SM, et al. Risk factors and clinical impact of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: Multicenter retrospective cohort study. Korean J Intern Med. 2022; 37(4):851–863. PMID: 35611611.13. Kim SH, Hong JY, Bae S, Lee H, Wi YM, Ko JH, et al. Risk Factors for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients: a nationwide, multicenter, retrospective cohort study. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(18):e134. PMID: 35535369.14. Yoon YK. Call for evidence mapping in accordance with the changing features of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Korean J Intern Med. 2022; 37(4):742–744. PMID: 35811364.15. White PL, Dhillon R, Cordey A, Hughes H, Faggian F, Soni S, et al. A national strategy to diagnose coronavirus disease 2019-associated invasive fungal disease in the intensive care unit. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 73(7):e1634–e1644. PMID: 32860682.16. Shah M, Reveles K, Moote R, Hand E, Kellogg Iii D, Attridge RL, et al. Risk of coronavirus disease 2019-associated pulmonary aspergillosis based on corticosteroid duration in intensive care patients. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023; 10(3):ofad062. PMID: 36879627.17. Ramonfaur D, Salto-Quintana JN, Aguirre-García GM, Hernández-Mata NM, Villanueva-Lozano H, Torre-Amione G, et al. Cumulative steroid dose in hospitalized patients and COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis. J Hosp Infect. 2023; 142:26–31. PMID: 37499762.18. Sari A, Ekinci O, Saraçoğlu KT, Balık R, Aslan M, Balık Y, et al. A comparison of the effects of dexamethasone and methylprednisolone, used on level-3 intensive care COVID-19 patients, on mortality: a multi-center retrospective study. J Korean Med Sci. 2023; 38(29):e232. PMID: 37489719.19. Verweij PE, Rijnders BJ, Brüggemann RJ, Azoulay E, Bassetti M, Blot S, et al. Review of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients and proposal for a case definition: an expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46(8):1524–1535. PMID: 32572532.20. Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, Khang YH, Kim HC, Park JH, et al. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open. 2017; 7(9):e016640.21. Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C. Mild or moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383(18):1757–1766. PMID: 32329974.22. Shih HI, Huang YT, Wu CJ. Disease burden and demographic characteristics of mucormycosis: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan, 2006-2017. Mycoses. 2022; 65(11):1001–1009. PMID: 35713608.23. Park JS, Choi S, Kim K, Chang J, Kim SM, Kim SR, et al. Association of particulate matter with autoimmune rheumatic diseases among adults in South Korea. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021; 60(11):5117–5126. PMID: 33560298.24. Kim YA, Lee YR, Park J, Oh IH, Kim H, Yoon SJ, et al. Socioeconomic burden of cancer in Korea from 2011 to 2015. Cancer Res Treat. 2020; 52(3):896–906. PMID: 32192276.25. Kim JY, Kim SH, Myong JP, Kim YR, Kim TS, Kim JH, et al. Outcomes of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with mitral stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73(10):1123–1131. PMID: 30871695.26. Kim MK, Han K, Kim HS, Park YM, Kwon HS, Yoon KH, et al. Cholesterol variability and the risk of mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke: a nationwide population-based study. Eur Heart J. 2017; 38(48):3560–3566. PMID: 29069458.27. Feys S, Almyroudi MP, Braspenning R, Lagrou K, Spriet I, Dimopoulos G, et al. A visual and comprehensive review on COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA). J Fungi (Basel). 2021; 7(12):1067. PMID: 34947049.28. Choi WS. Is longer duration or higher dose of steroid use effective in critical COVID-19 patients?: an area of uncertainty. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(29):e242. PMID: 35880511.29. Maskin LP, Bonelli I, Olarte GL, Palizas F Jr, Velo AE, Lurbet MF, et al. High- versus low-dose dexamethasone for the treatment of COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicenter, randomized open-label clinical trial. J Intensive Care Med. 2022; 37(4):491–499. PMID: 34898320.30. Bouadma L, Mekontso-Dessap A, Burdet C, Merdji H, Poissy J, Dupuis C, et al. High-dose dexamethasone and oxygen support strategies in intensive care unit patients with severe COVID-19 acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: the COVIDICUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2022; 182(9):906–916. PMID: 35788622.31. Chen Y, Li L. Influence of corticosteroid dose on viral shedding duration in patients with COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 72(7):1298–1300. PMID: 32588884.32. Permpalung N, Chiang TP, Massie AB, Zhang SX, Avery RK, Nematollahi S, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in mechanically ventilated patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2022; 74(1):83–91. PMID: 33693551.33. Ryu BH, Hong SI, Lim SJ, Cho Y, Hwang C, Kang H, et al. Clinical features of adult COVID-19 patients without risk factors before and after the nationwide SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (delta)-variant outbreak in Korea: experience from Gyeongsangnam-do. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(49):e341. PMID: 34931500.34. Kılınç G, Atasoy AA. Evaluation of patients treated in intensive care due to COVID-19: a retrospective study. Infect Chemother. 2022; 54(2):328–339. PMID: 35794718.35. Kim M, Yoo JR, Heo ST, Lee HR, Oh H. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe disease of coronavirus disease 2019 in a low case fatality rate region in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2021; 53(4):718–729. PMID: 34951535.36. Kim TW, Kim WY, Park S, Lee SH, Park O, Kim T, et al. Risk factors for the mortality of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a non-centralized setting: a nationwide study. J Korean Med Sci. 2024; 39(8):e75. PMID: 38442718.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How We Have Treated Severe to Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea
- Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for critically ill patients with COVID-19: a cohort study
- Experience of Treating Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients in Daegu, South Korea
- Risk factors associated with development of coinfection in critically Ill patients with COVID-19
- Characteristics of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients in Busan, Republic of Korea