Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2024 Aug;28(3):325-336. 10.14701/ahbps.24-009.
Effect of neoadjuvant transarterial chemoembolization followed by resection versus upfront liver resection on the survival of single large hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Surgery Division, Department of Surgery, Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 2ndonesian College of Digestive Surgery, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 3Indonesian Air Force Institute of Aviation Medicine, Jakarta, Indonesia
- KMID: 2558658
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.24-009
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
The efficacy of neoadjuvant transarterial chemoembolization (N−TACE) in resectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains open to debate. While N−TACE may reduce tumor size, its impact on long-term outcomes is inconclusive.
Methods
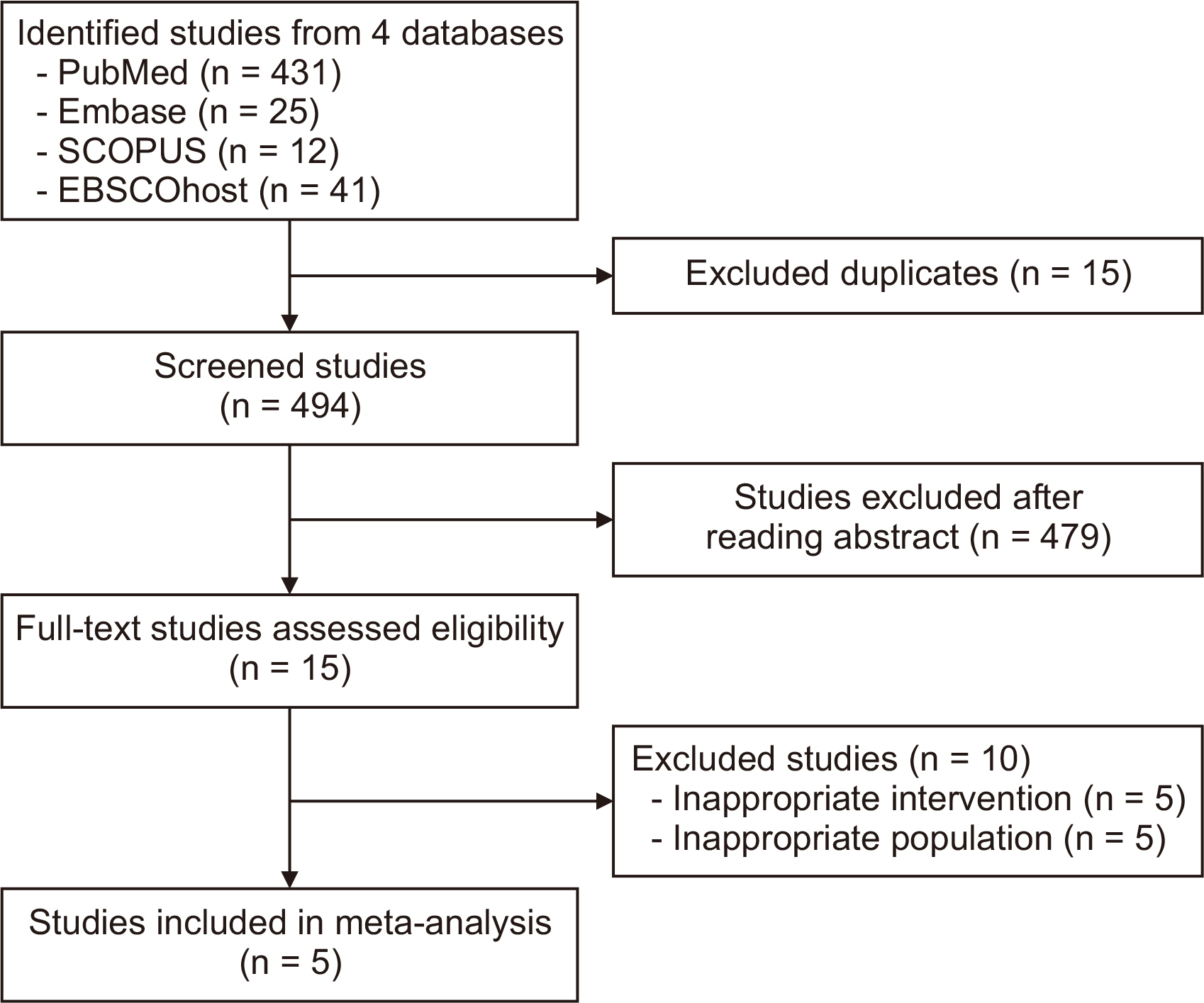
This meta-analysis reviewed studies on N−TACE before surgical resection vs. liver resection (LR) single large hepatocellular carcinoma (SLHCC) up to March 2023 from four online databases.
Results
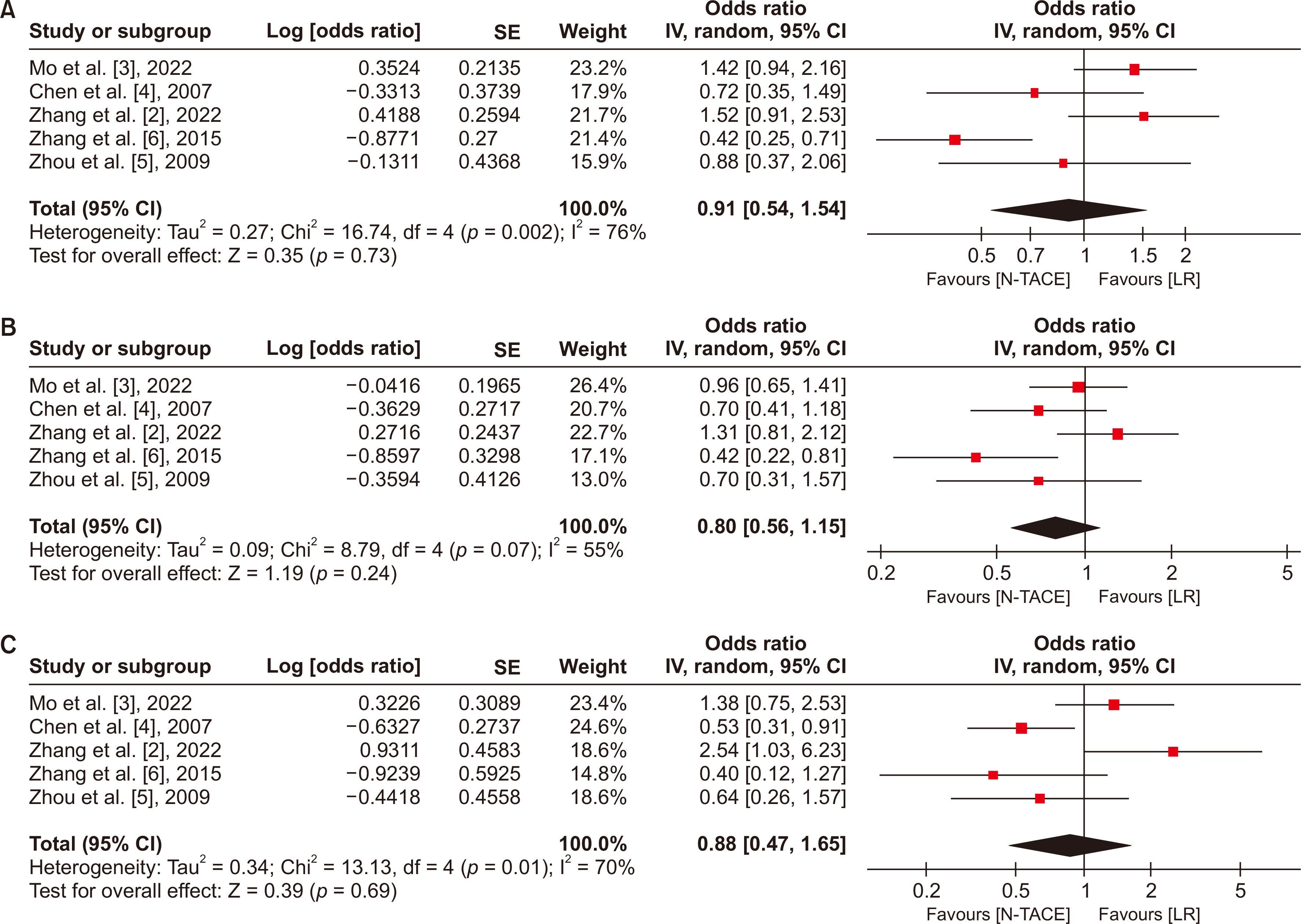
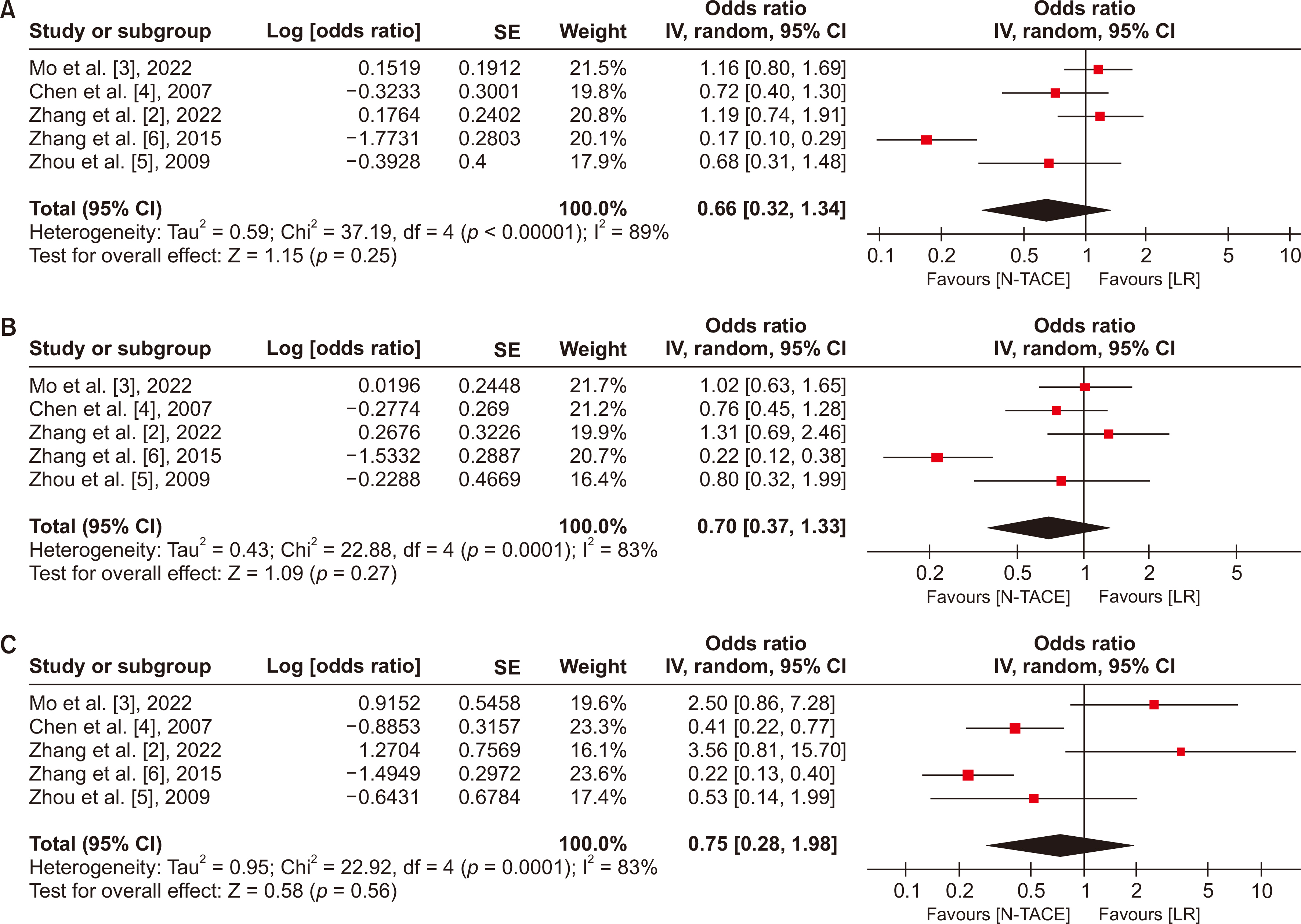
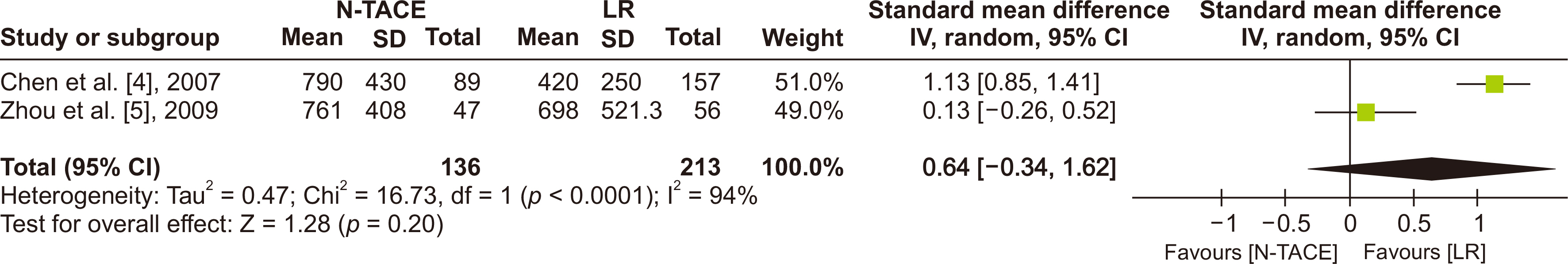
Five studies with 1,556 patients were analyzed. No significant differences between N−TACE and LR groups were observed in 1-, 3-, or 5-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). No significant differences were noted in intraoperative blood loss between groups. Subgroup analysis showed favorable 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS with combination chemotherapy N−TACE (combination group), and better 1-year OS in the LR group with single-agent chemotherapy N−TACE (single-agent group). Five-year DFS favored LR in the single-agent group, and N−TACE in the combination group.
Conclusions
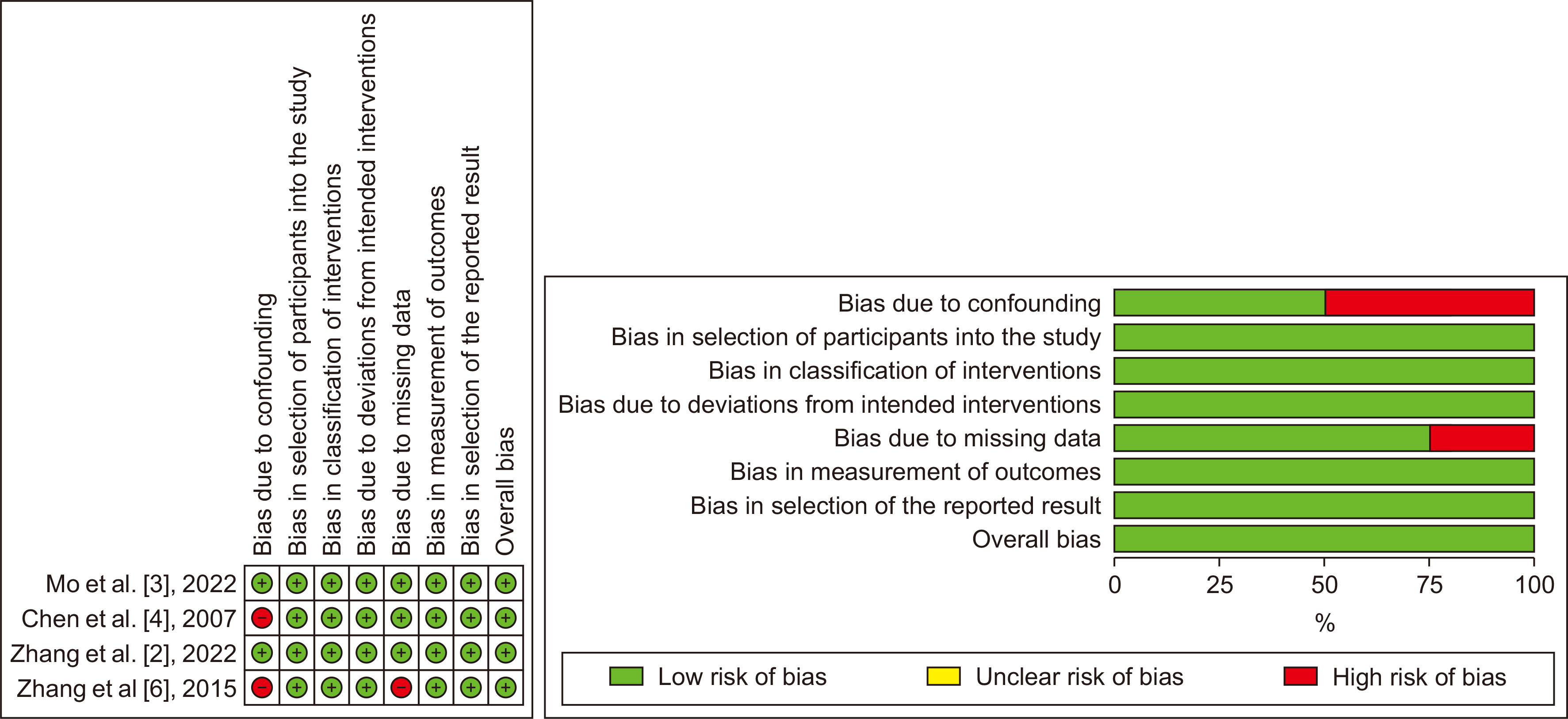
Managing SLHCC requires intricate considerations, and the treatment strategies for this challenging subgroup of HCC need to be improved. The influence of N−TACE on long-term survival depends on the specific chemotherapy regimen employed, and its impact on intraoperative blood loss in SLHCC appears limited.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Guo C, Zou X, Hong Z, Sun J, Xiao W, Sun K, et al. 2021; Preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage A/B hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: a propensity score matching analysis. HPB (Oxford). 23:1427–1438. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2021.02.006. PMID: 33715958.2. Zhang Q, Xia F, Mo A, He W, Chen J, Zhang W, et al. 2022; Guiding value of circulating tumor cells for preoperative transcatheter arterial embolization in solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center retrospective clinical study. Front Oncol. 12:839597. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.839597. PMID: 35664772. PMCID: PMC9159764.3. Mo A, Zhang Q, Xia F, Huang Z, Peng S, Cao W, et al. 2022; Preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and prognosis of patients with solitary large hepatocellular carcinomas (≥5 cm): multicenter retrospective study. Cancer Med. 12:7734–7747. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5529. PMID: 36540041. PMCID: PMC10134378.4. Chen XP, Hu DY, Zhang ZW, Zhang BX, Chen YF, Zhang WG, et al. 2007; Role of mesohepatectomy with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for large centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Surg. 24:208–213. DOI: 10.1159/000102901. PMID: 17522469.5. Zhou WP, Lai ECH, Li AJ, Fu SY, Zhou JP, Pan ZY, et al. 2009; A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for resectable large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 249:195–202. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181961c16. PMID: 19212170.6. Zhang YF, Guo RP, Zou RH, Shen JX, Wei W, Li SH, et al. 2015; Efficacy and safety of preoperative chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a prospective comparative study. Eur Radiol. 26:2078–2088. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-015-4021-8. PMID: 26396105.7. Jianyong L, Jinjing Z, Wentao W, Lunan Y, Qiao Z, Bo L, et al. 2014; Preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single center analysis. Ann Hepatol. 13:394–402. DOI: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)30846-4. PMID: 24927610.8. Tao Q, He W, Li B, Zheng Y, Zou R, Shen J, et al. 2018; Resection versus resection with preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. J Cancer. 9:2778–2785. DOI: 10.7150/jca.25033. PMID: 30123345. PMCID: PMC6096377.9. Si T, Chen Y, Ma D, Gong X, Yang K, Guan R, et al. 2016; Preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia area: a meta-analysis of random controlled trials. Scand J Gastroenterol. 51:1512–1519. DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2016.1216588. PMID: 27598831. PMCID: PMC5152561.10. Liu P, Su C, Hsu C, Hsia C, Lee YH, Huang YH, et al. 2016; Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: staging and treatment strategy. PLoS One. 11:e0155588. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155588. PMID: 27176037. PMCID: PMC4866714.11. Nishikawa H, Arimoto A, Wakasa T, Kita R, Kimura T, Osaki Y. 2013; Effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization prior to surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:151–160. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1711. PMID: 23174998.12. Cui H, Gao QQ, Li YY, Wang F. 2003; Influence of preventive effects of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Forum. 24:1–3.13. Liang L, Xing H, Zhang H, Zhong J, Li C, Lau WY, et al. 2018; Surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for BCLC intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford). 20:110–119. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.10.004. PMID: 29174493.14. Wu CC, Ho YZ, Ho WL, Wu TC, Liu TJ, P'Eng FK. 1995; Preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable large hepatocellular carcinoma: a reappraisal. Br J Surg. 82:122–126. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800820141. PMID: 7881929.15. Yamasaki S, Hasegawa H, Kinoshita H, Furukawa M, Imaoka S, Takasaki K, et al. 1996; A prospective randomized trial of the preventive effect of pre-operative transcatheter arterial embolization against recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 87:206–211. DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1996.tb03160.x. PMID: 8609071. PMCID: PMC5921067.16. Zhong JH, Ke Y, Gong WF, Xiang B De, Ma L, Ye XP, et al. 2014; Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 260:329–340. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236. PMID: 24096763.17. Min YW, Lee JH, Gwak GY, Paik YH, Lee JH, Rhee PL, et al. 2014; Long-term survival after surgical resection for huge hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with transarterial chemoembolization after propensity score matching. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:1043–1048. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12504. PMID: 24863186.18. Li C, Da M, Lun W, Han L, Jiong W, Yu J, et al. 2019; Preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for surgical resection of huge hepatocellular carcinoma (≥ 10 cm): a multicenter propensity matching analysis. Hepatol Int. 13:736–747. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09981-0. PMID: 31486964.19. Fang C, Luo R, Zhang Y, Wang J, Feng K, Liu S, et al. 2023; Hepatectomy versus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable BCLC stage A/B hepatocellular carcinoma beyond Milan criteria: a randomized clinical trial. Front Oncol. 13:1101162. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1101162. PMID: 36923427. PMCID: PMC10010190.20. Gerunda GE, Neri D, Merenda R, Barbazza F, Zangrandi F, Meduri F, et al. 2000; Role of transarterial chemoembolization before liver resection for hepatocarcinoma. Liver Transpl. 6:619–626. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2000.8312. PMID: 10980062.21. Sugo H, Futagawa S, Beppu T, Fukasawa M, Kojima K. 2003; Role of preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: relation between postoperative course and the pattern of tumor recurrence. World J Surg. 27:1295–1299. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-003-6817-y. PMID: 14574482.22. Paye F, Jagot P, Vilgrain V, Farges O, Borie D, Belghiti J. 1998; Preoperative chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study. Arch Surg. 133:767–772. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.133.7.767. PMID: 9688007.23. Luo YQ, Wang Y, Chen H, Wu MC. 2002; Influence of preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on liver resection in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 1:523–526.24. Zhou Q, Tuo F, Li R, Wang X, Wang J, Huang Z, et al. 2020; Transarterial chemoembolization combined with hepatectomy for the treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 10:578763. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.578763. PMID: 33251141. PMCID: PMC7672209.25. Hwang TL, Chen MF, Lee TY, Chen TJ, Lin DY, Liaw YF. 1987; Resection of hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial embolization. Arch Surg. 122:756–759. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400190022004. PMID: 3036038.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete Remission with Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Showed Early Recurrence following Surgical Resection
- Comparison of surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization with additional radiation therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion
- Is Transarterial Chemoembolization Only Treatment Option in Patients with Intermediate Stage of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?: in Perspectives of Surgery
- Ruptured Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cured by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Primary treatments for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm: A systematic review and network meta-analysis