Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2024 Nov;28(4):397-411. 10.14701/ahbps.24-103.
Primary treatments for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2561572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.24-103
Abstract
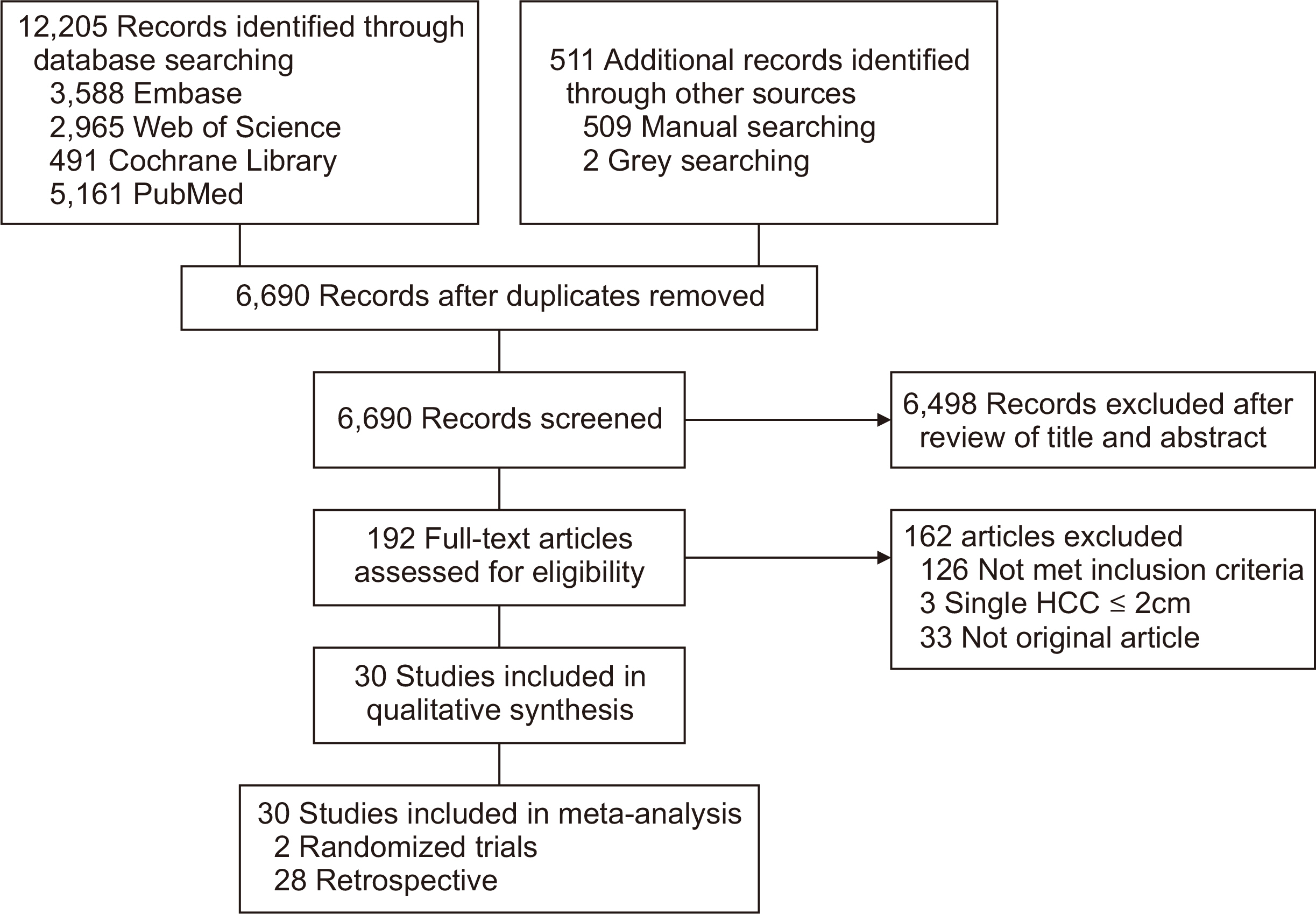
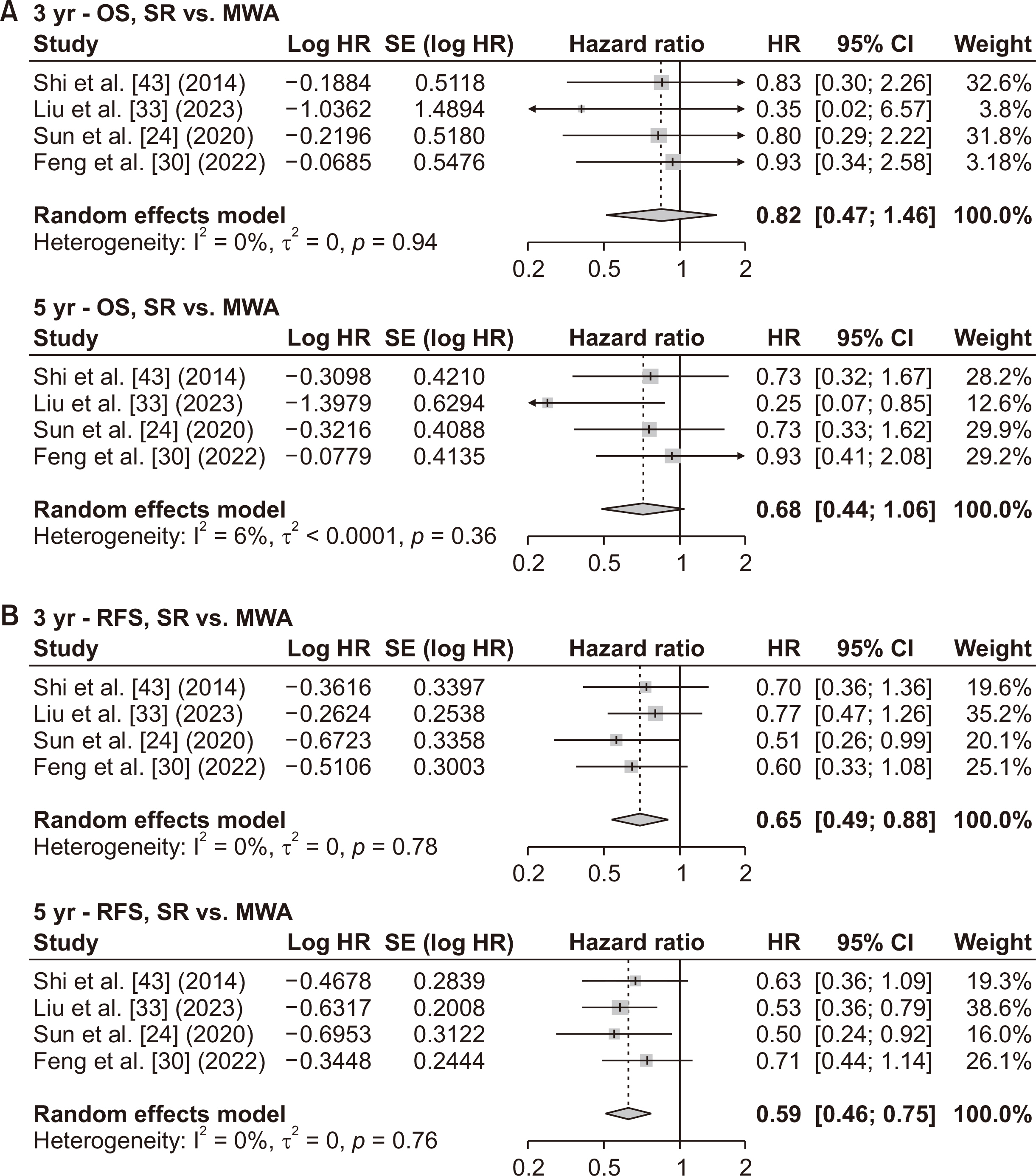
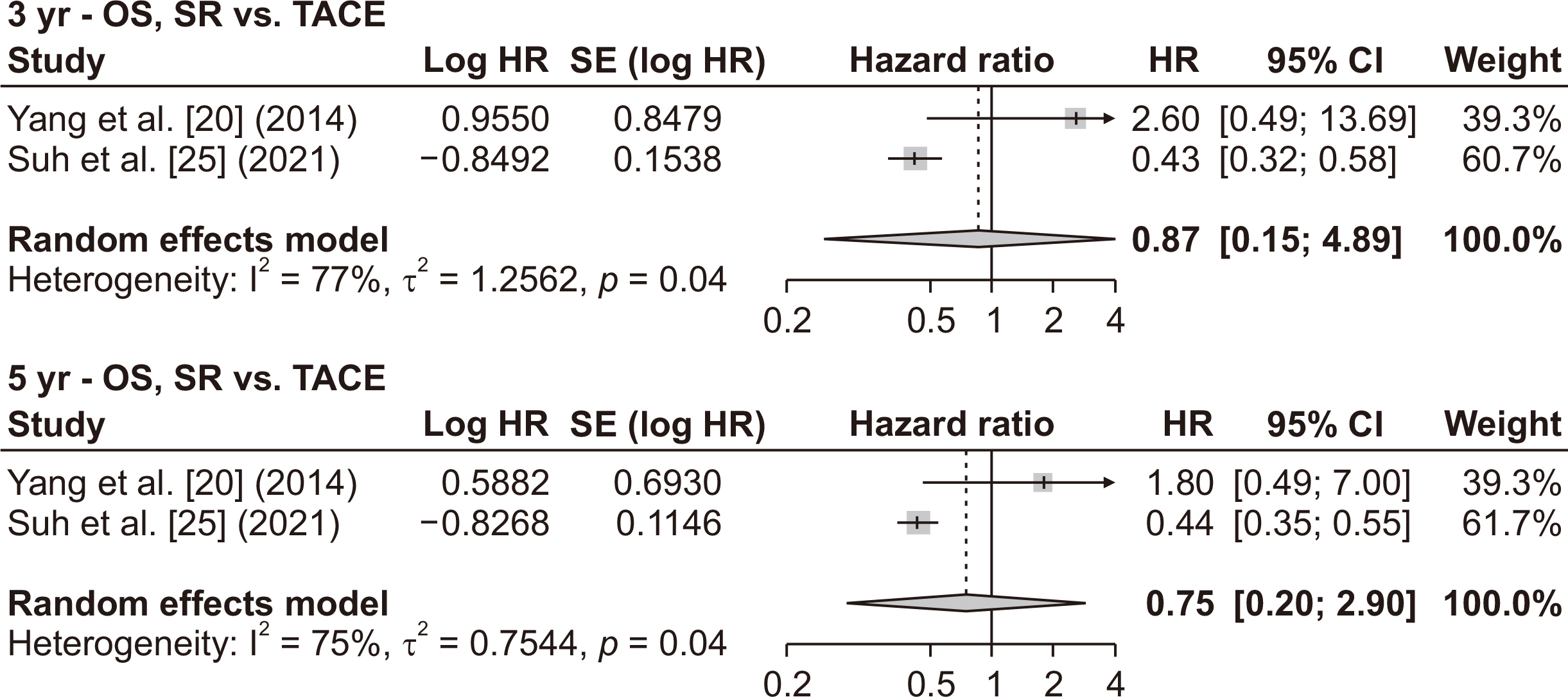
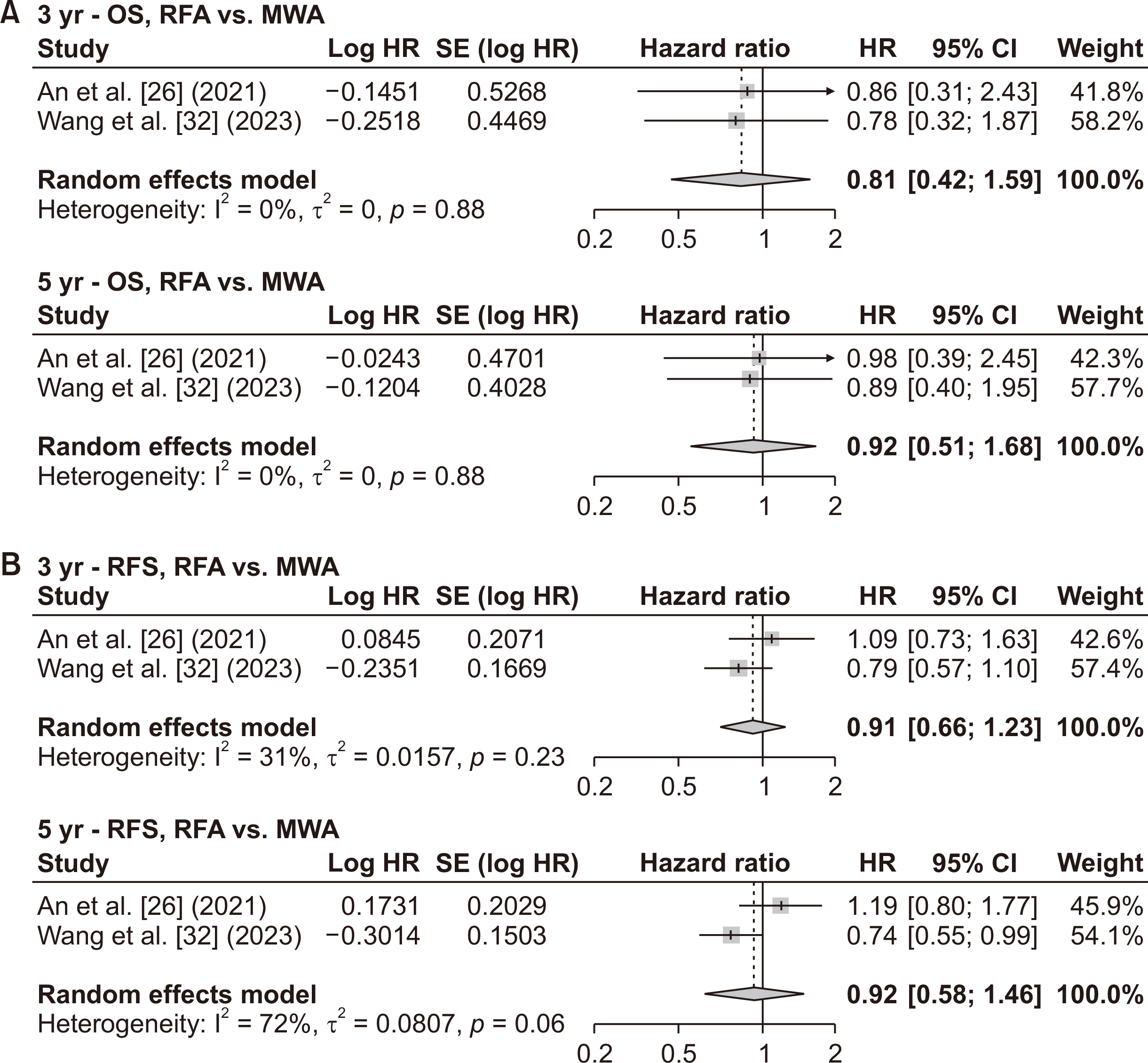
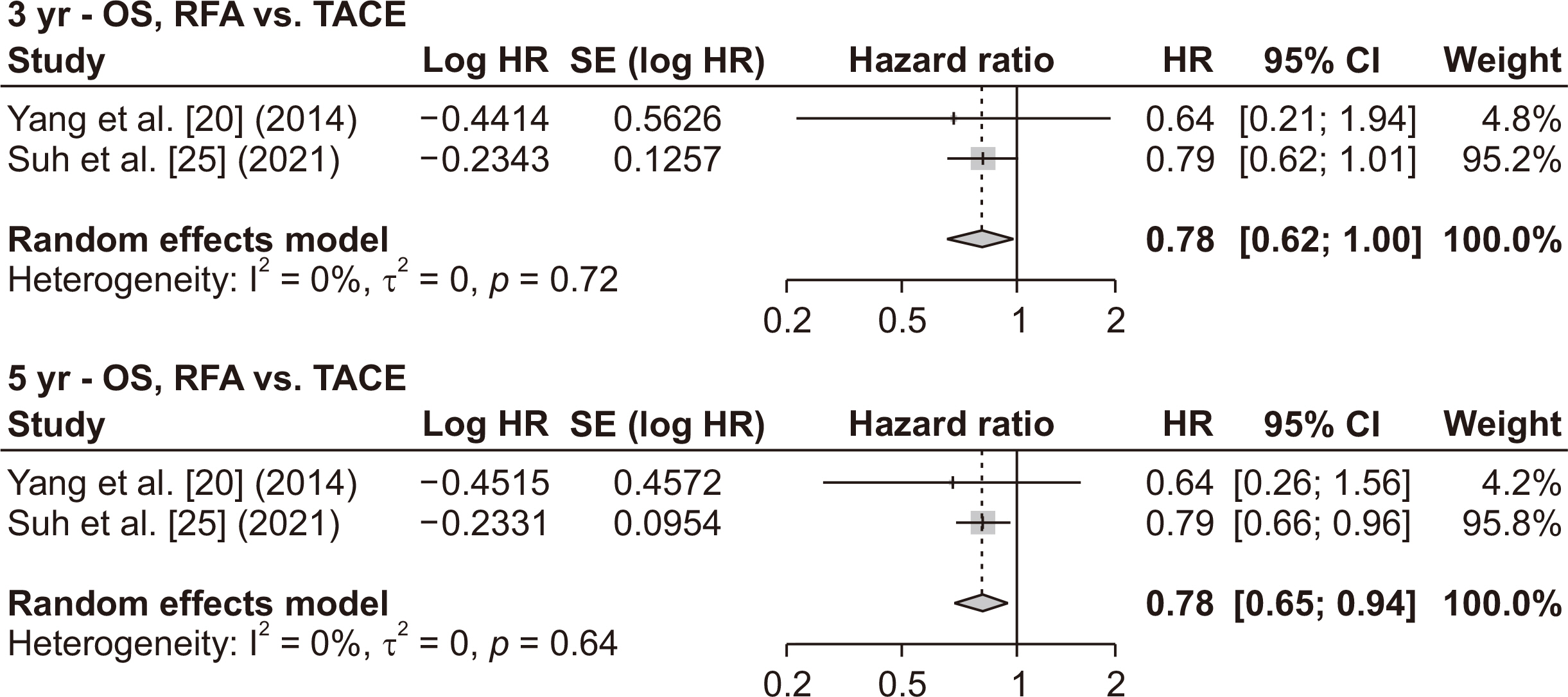
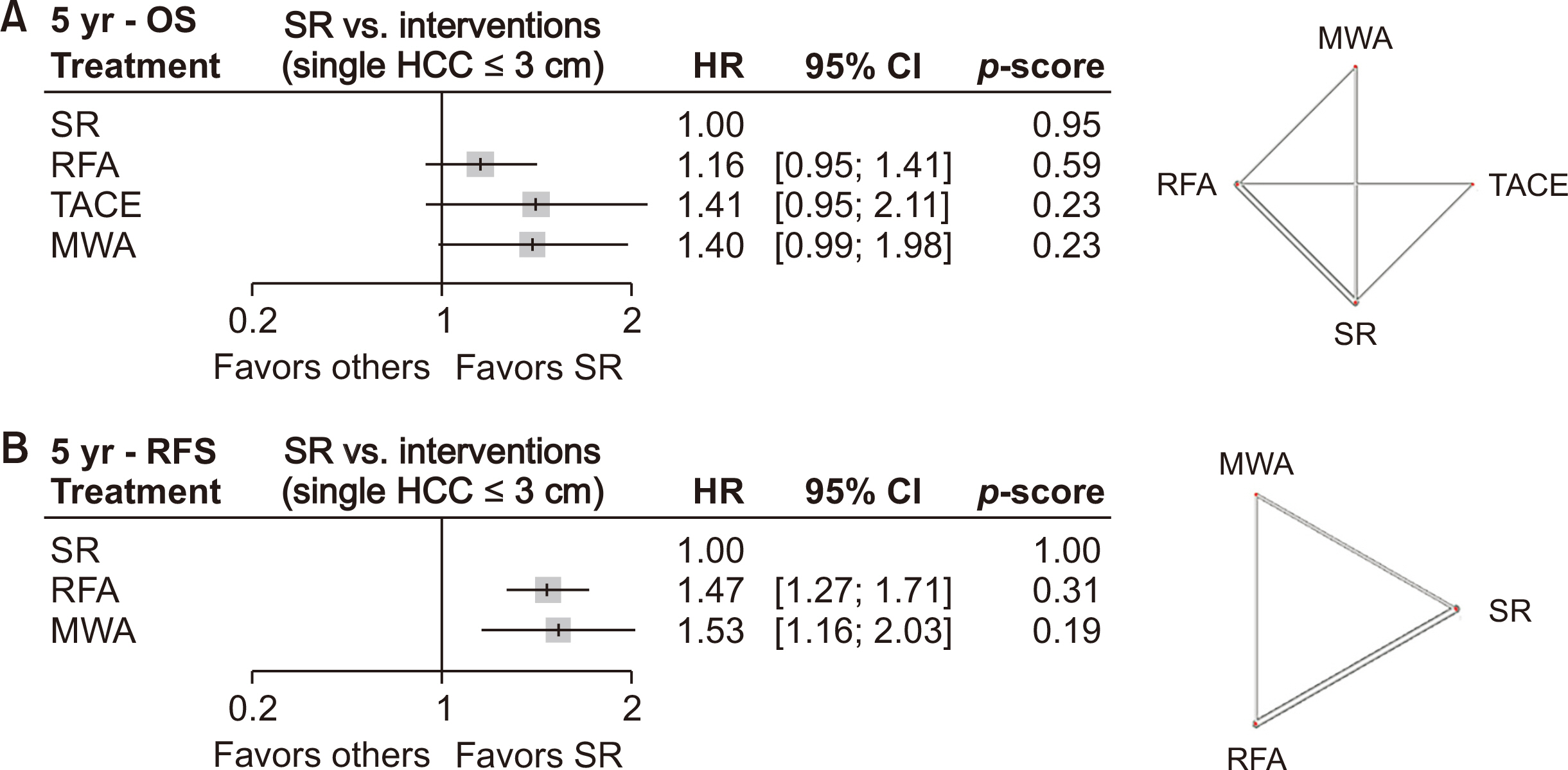
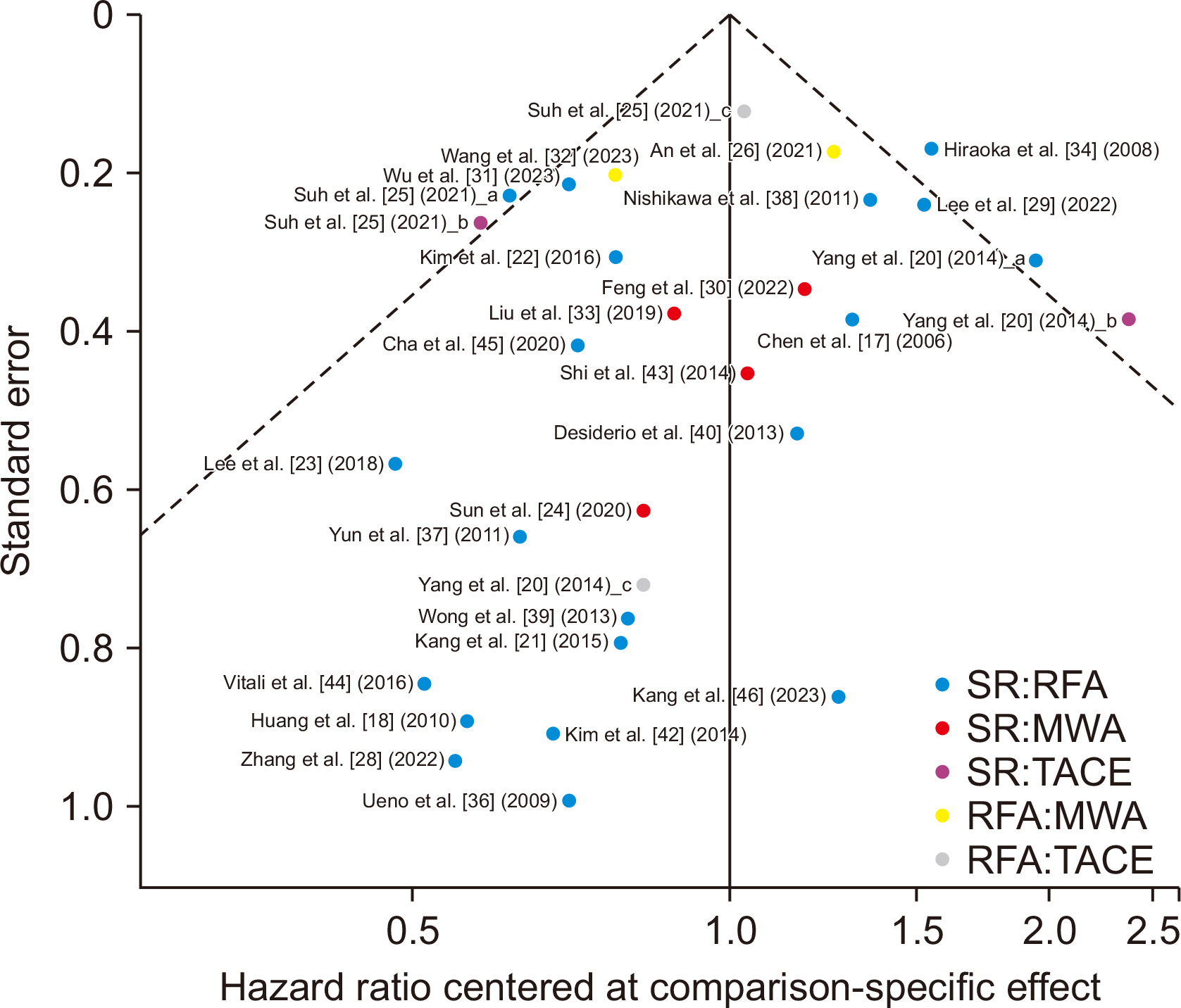
- Various treatment modalities are available for small solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), yet the optimal primary treatment strategy for tumors ≤ 3 cm remains unclear. This network meta-analysis investigates the comparative efficacy of various interventions on the long-term outcomes of patients with solitary HCC ≤ 3 cm. A systematic search of electronic databases from January 2000 to December 2023 was conducted to identify studies that compared at least two of the following treatments: surgical resection (SR), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Survival data were extracted, and pooled hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated using a frequentist network meta-analysis. A total of 30 studies, comprising 2 randomized controlled trials and 28 retrospective studies, involving 8,053 patients were analyzed. Surgical resection showed the highest overall survival benefit with a p-score of 0.95, followed by RFA at 0.59, MWA at 0.23, and TACE, also at 0.23. Moreover, SR provided the most significant recurrence-free survival advantage, with a p-score of 0.95, followed by RFA at 0.31 and MWA at 0.19. Sensitivity analyses, excluding low-quality or retrospective non-matched studies, corroborated these findings. This network meta-analysis demonstrates that SR is the most effective first-line curative treatment for single HCC ≤ 3 cm, followed by RFA in patients with preserved liver function. The limited data on MWA and TACE underscore the need for further studies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Yu HJ, He SY, Braddock M, Zhou MT, et al. 2015; Optimal adjuvant therapy for resected hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:18151–18161. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4098. PMID: 26061709. PMCID: PMC4627241.2. Tian G, Yang S, Yuan J, Threapleton D, Zhao Q, Chen F, et al. 2018; Comparative efficacy of treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 8:e021269. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-021269. PMID: 30341113. PMCID: PMC6196801.3. Yang S, Lin H, Song J. 2021; Efficacy and safety of various primary treatment strategies for very early and early hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 21:681. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02365-1. PMID: 34923980. PMCID: PMC8684647.4. Lau WY, Leung TW, Yu SC, Ho SK. 2003; Percutaneous local ablative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a review and look into the future. Ann Surg. 237:171–179. DOI: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000048443.71734.BF. PMID: 12560774. PMCID: PMC1522146.5. Shin SW, Ahn KS, Kim SW, Kim TS, Kim YH, Kang KJ. 2021; Liver resection versus local ablation therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 273:656–666. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004350. PMID: 33074898.6. Zhang T, Hu H, Jia Y, Gao Y, Hao F, Wu J, et al. 2022; Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation and surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 101:e32470. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032470. PMID: 36595979. PMCID: PMC9803499.7. Cui R, Wang XH, Ma C, Liu T, Cheng ZG, Han ZY, et al. 2019; Comparison of microwave ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for single-nodule hepatocellular carcinoma smaller than 5cm: a propensity score matching analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 11:10695–10704. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S213581. PMID: 31920380. PMCID: PMC6934117.8. Kim W, Cho SK, Shin SW, Hyun D, Lee MW, Rhim H. 2019; Combination therapy of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with TACE or RFA monotherapy. Abdom Radiol (NY). 44(6):2283–2292. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-019-01952-1. PMID: 30806742.9. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. 2019; Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 10:ED000142. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142. PMID: 31643080. PMCID: PMC10284251.10. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. 2021; The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. 88:105906. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906. PMID: 33789826.11. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. 2017; AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 358:j4008. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.j4008. PMID: 28935701. PMCID: PMC5833365.12. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. 2019; RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 366:l4898. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l4898. PMID: 31462531.13. Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, Robertson J, Peterson J, Welch V, et al. 2011. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analysis [Internet]. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute;Available from: http://www.evidencebasedpublichealth.de/download/Newcastle_Ottowa_Scale_Pope_Bruce.pdf. cited 2024 Jan 3.14. Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. 2007; Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:16. DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-16. PMID: 17555582. PMCID: PMC1920534.15. Rücker G, Schwarzer G. 2015; Ranking treatments in frequentist network meta-analysis works without resampling methods. BMC Med Res Methodol. 15:58. DOI: 10.1186/s12874-015-0060-8. PMID: 26227148. PMCID: PMC4521472.16. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons;2021.17. Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, Guo RP, Liang HH, Zhang YQ, et al. 2006; A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 243:321–328. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000201480.65519.b8. PMID: 16495695. PMCID: PMC1448947.18. Huang J, Yan L, Cheng Z, Wu H, Du L, Wang J, et al. 2010; A randomized trial comparing radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for HCC conforming to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. 252:903–912. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181efc656. PMID: 21107100.19. Pompili M, Saviano A, de Matthaeis N, Cucchetti A, Ardito F, Federico B, et al. 2013; Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J Hepatol. 59:89–97. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.009. PMID: 23523578.20. Yang HJ, Lee JH, Lee DH, Yu SJ, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, et al. 2014; Small single-nodule hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of transarterial chemoembolization, radiofrequency ablation, and hepatic resection by using inverse probability weighting. Radiology. 271:909–918. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.13131760. PMID: 24520944.21. Kang TW, Kim JM, Rhim H, Lee MW, Kim YS, Lim HK, et al. 2015; Small hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation versus nonanatomic resection--propensity score analyses of long-term outcomes. Radiology. 275:908–919. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.15141483. PMID: 25688888.22. Kim GA, Shim JH, Kim MJ, Kim SY, Won HJ, Shin YM, et al. 2016; Radiofrequency ablation as an alternative to hepatic resection for single small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br J Surg. 103:126–135. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.9960. PMID: 26572697.23. Lee S, Kang TW, Cha DI, Song KD, Lee MW, Rhim H, et al. 2018; Radiofrequency ablation vs. surgery for perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: propensity score analyses of long-term outcomes. J Hepatol. 69:70–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.02.026. PMID: 29524532.24. Sun Q, Shi J, Ren C, Du Z, Shu G, Wang Y. 2020; Survival analysis following microwave ablation or surgical resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma conforming to the Milan criteria. Oncol Lett. 19:4066–4076. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11529. PMID: 32391107. PMCID: PMC7204632.25. Suh YJ, Jin YJ, Jeong Y, Shin WY, Lee JM, Cho S, et al. 2021; Resection or ablation versus transarterial therapy for Child-Pugh A patients with a single small hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e27470. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027470. PMID: 34713824. PMCID: PMC8556049.26. An C, Li WZ, Huang ZM, Yu XL, Han YZ, Liu FY, et al. 2021; Small single perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparisons of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation by using propensity score analysis. Eur Radiol. 31:4764–4773. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07571-5. PMID: 33399908. PMCID: PMC8213545.27. Ko SE, Lee MW, Ahn S, Rhim H, Kang TW, Song KD, et al. 2022; laparoscopic hepatic resection versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinomas smaller than 3 cm: analysis of treatment outcomes using propensity score matching. Korean J Radiol. 23:615–624. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0786. PMID: 35289151. PMCID: PMC9174500.28. Zhang C, Gao R, Guo S, Ning C, Li A, Wang X, et al. 2022; Anatomic resection versus radiofrequency ablation with an ablative margin ≥ 1.0 cm for solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma measuring ≤ 3 cm: comparison of long-term outcomes using propensity score matching analysis. Eur J Radiol. 155:110498. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110498. PMID: 36049409.29. Lee J, Jin YJ, Shin SK, Kwon JH, Kim SG, Suh YJ, et al. 2022; Surgery versus radiofrequency ablation in patients with Child- Pugh class-A/single small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 28:207–218. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0294. PMID: 34814239. PMCID: PMC9013608.30. Feng H, Yang C, Xu F, Zhao Y, Jin T, Wei Z, et al. 2022; Therapeutic efficacy of microwave coagulation versus liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a propensity score matching analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 48:418–424. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.08.035. PMID: 34509336.31. Wu F, Wei C, Zhang S, Jia S, Zhang J. 2023; the efficacy of surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma: a SEER-based study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2023:1269504. DOI: 10.1155/2023/1269504. PMID: 36865983. PMCID: PMC9974275.32. Wang X, Yu H, Zhao F, Xu Y, Wang C, Liu K, et al. 2023; Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation as bridge therapy in potentially transplantable patients with single HCC ≤ 3 cm: a propensity score-matched study. Eur J Radiol. 164:110860. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.110860. PMID: 37178491.33. Liu K, Zheng H, Sui X, Liu B, Meng M, Feng Y, et al. 2023; Microwave ablation versus surgical resection for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study of long-term therapeutic outcomes. Eur Radiol. 33:1938–1948. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-09135-1. PMID: 36114849.34. Hiraoka A, Horiike N, Yamashita Y, Koizumi Y, Doi K, Yamamoto Y, et al. 2008; Efficacy of radiofrequency ablation therapy compared to surgical resection in 164 patients in Japan with single hepatocellular carcinoma smaller than 3 cm, along with report of complications. Hepatogastroenterology. 55:2171–2174.35. Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Valdegamberi A, Pachera S, Campagnaro T, D'Onofrio M, et al. 2008; Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 12:192–198. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-007-0392-8. PMID: 17999123.36. Ueno S, Sakoda M, Kubo F, Hiwatashi K, Tateno T, Baba Y, et al. 2009; Surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinomas within the Milan criteria. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 16:359–366. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-009-0069-7. PMID: 19300896.37. Yun WK, Choi MS, Choi D, Rhim HC, Joh JW, Kim KH, et al. 2011; Superior long-term outcomes after surgery in child-pugh class a patients with single small hepatocellular carcinoma compared to radiofrequency ablation. Hepatol Int. 5:722–729. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-010-9237-8. PMID: 21484104. PMCID: PMC3090548.38. Nishikawa H, Inuzuka T, Takeda H, Nakajima J, Matsuda F, Sakamoto A, et al. 2011; Comparison of percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation and surgical resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:143. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-143. PMID: 22204311. PMCID: PMC3260104.39. Wong KM, Yeh ML, Chuang SC, Wang LY, Lin ZY, Chen SC, et al. 2013; Survival comparison between surgical resection and percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for patients in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Indian J Gastroenterol. 32:253–257. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-012-0225-x. PMID: 22932964.40. Desiderio J, Trastulli S, Pasquale R, Cavaliere D, Cirocchi R, Boselli C, et al. 2013; Could radiofrequency ablation replace liver resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with compensated cirrhosis? A 5-year follow-up. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 398:55–62. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-012-1029-2. PMID: 23224564.41. Imai K, Beppu T, Chikamoto A, Doi K, Okabe H, Hayashi H, et al. 2013; Comparison between hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation as first-line treatment for solitary small-sized hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Hepatol Res. 43:853–864. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12035. PMID: 23281579.42. Kim JM, Kang TW, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Ko JS, Park JB, et al. 2014; Single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm in left lateral segment: liver resection or radiofrequency ablation? World J Gastroenterol. 20:4059–4065. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4059. PMID: 24744596. PMCID: PMC3983463.43. Shi J, Sun Q, Wang Y, Jing X, Ding J, Yuan Q, et al. 2014; Comparison of microwave ablation and surgical resection for treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas conforming to Milan criteria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:1500–1507. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12572. PMID: 24628534.44. Vitali GC, Laurent A, Terraz S, Majno P, Buchs NC, Rubbia-Brandt L, et al. 2016; Minimally invasive surgery versus percutaneous radio frequency ablation for the treatment of single small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study. Surg Endosc. 30:2301–2307. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-015-4295-6. PMID: 26534770.45. Cha DI, Song KD, Kang TW, Lee MW, Rhim H. 2020; Small masses (≤3 cm) diagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma on pre-treatment imaging: comparison of therapeutic outcomes between hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation. Br J Radiol. 93:20190719. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20190719. PMID: 31670571. PMCID: PMC6948073.46. Kang M, Cho JY, Han HS, Yoon YS, Lee HW, Lee B, et al. 2023; Comparative study of long-term outcomes of laparoscopic liver resection versus radiofrequency ablation for single small hepatocellular carcinoma located in left lateral segments of the liver. Medicina (Kaunas). 59:1063. DOI: 10.3390/medicina59061063. PMID: 37374267. PMCID: PMC10303040.47. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. 2022; BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: the 2022 update. J Hepatol. 76:681–693. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018. PMID: 34801630. PMCID: PMC8866082.48. Sonbol MB, Riaz IB, Naqvi SAA, Almquist DR, Mina S, Almasri J, et al. 2020; systemic therapy and sequencing options in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 6:e204930. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.4930. PMID: 33090186. PMCID: PMC7582230.49. Chu HH, Kim JH, Kim PN, Kim SY, Lim YS, Park SH, et al. 2019; Surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation very early-stage HCC (≤2 cm Single HCC): a propensity score analysis. Liver Int. 39:2397–2407. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14258. PMID: 31549771.50. Lin CH, Ho CM, Wu CH, Liang PC, Wu YM, Hu RH, et al. 2020; Minimally invasive surgery versus radiofrequency ablation for single subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 2 cm with compensated liver cirrhosis. Surg Endosc. 34:5566–5573. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-019-07357-x. PMID: 31993821.51. Feng Y, Wang L, Lv H, Shi T, Xu C, Zheng H, et al. 2021; Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score analysis. HPB (Oxford). 23:512–519. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.08.006. PMID: 32839089.52. Radosevic A, Quesada R, Serlavos C, Sánchez J, Zugazaga A, Sierra A, et al. 2022; Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver malignancies: a randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci Rep. 12:316. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03802-x. PMID: 35013377. PMCID: PMC8748896.53. Zheng H, Liu K, Yang Y, Liu B, Zhao X, Chen Y, et al. 2022; Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study. Eur Radiol. 32:4657–4666. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-08537-5. PMID: 35092477.54. Cho Y, Kim BH, Park JW. 2023; Overview of Asian clinical practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an Asian perspective comparison. Clin Mol Hepatol. 29:252–262. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0099. PMID: 36907570. PMCID: PMC10121305.55. Zhong C, Zhang YF, Huang JH, Xiong CM, Wang ZY, Chen QL, et al. 2018; Comparison of hepatic resection and transarterial chemoembolization for UICC stage T3 hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study. BMC Cancer. 18:643. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4557-5. PMID: 29879928. PMCID: PMC5992633.56. Signoriello S, Annunziata A, Lama N, Signoriello G, Chiodini P, De Sio I, et al. 2012; Survival after locoregional treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: a cohort study in real-world patients. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:564706. DOI: 10.1100/2012/564706. PMID: 22654628. PMCID: PMC3356712.57. Lu L, Zheng P, Wu Z, Chen X. 2021; Hepatic resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a cohort study. Front Oncol. 11:618937. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.618937. PMID: 34778022. PMCID: PMC8579001.58. Chen S, Jin H, Dai Z, Wei M, Xiao H, Su T, et al. 2019; Liver resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 8:1530–1539. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2038. PMID: 30864247. PMCID: PMC6488138.59. Fu S, Wei J, Zhang J, Dong D, Song J, Li Y, et al. 2019; selection between liver resection versus transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 10:e00070. DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000070. PMID: 31373932. PMCID: PMC6736221.60. Hsieh PM, Hsiao P, Chen YS, Yeh JH, Hung CM, Lin HY, et al. 2023; Clinical prognosis of surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for single large hepatocellular carcinoma (≥5 cm): a propensity score matching analysis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:302–310. DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12640. PMID: 36625289.61. Bogdanovic A, Bulajic P, Masulovic D, Bidzic N, Zivanovic M, Galun D. Liver resection versus transarterial chemoembolization for huge hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matched analysis. Sci Rep. 202; 11:4493. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83868-9. PMID: 33627697. PMCID: PMC7904801.62. Cai X, Wu S. 2022; Transarterial chemoembolization versus surgical resection for giant hepatocellular carcinoma under the different status of capsule: a retrospective study. Transl Cancer Res. 11:4359–4372. DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-2473. PMID: 36644188. PMCID: PMC9834591.63. Rim CH, Kim HJ, Seong J. 2019; Clinical feasibility and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Radiother Oncol. 131:135–144. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.12.005. PMID: 30773180.64. Brown AM, Kassab I, Massani M, Townsend W, Singal AG, Soydal C, et al. 2023; TACE versus TARE for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: overall and individual patient level meta analysis. Cancer Med. 12:2590–2599. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5125. PMID: 35943116. PMCID: PMC9939158.65. Pan YX, Fu YZ, Hu DD, Long Q, Wang JC, Xi M, et al. 2020; Stereotactic body radiotherapy vs. radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 10:1639. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01639. PMID: 33194569. PMCID: PMC7658324.66. Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) and National Cancer Center (NCC) Korea. 2022; 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 23:1126–1240. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0822. PMID: 36447411. PMCID: PMC9747269.67. Goh MJ, Sinn DH, Kim JM, Lee MW, Hyun DH, Yu JI, et al. 2023; Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: a Korean perspective. Clin Mol Hepatol. 29:197–205. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0404. PMID: 36603575. PMCID: PMC10121294.68. Lee MW, Lee JM, Koh YH, Chung JW. 2023; 2022 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice guidelines for local ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: what's new? Korean J Radiol. 24:10–14. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0555. PMID: 36606614. PMCID: PMC9830141.69. Ünal E, İdilman İS, Akata D, Özmen MN, Karçaaltıncaba M. 2016; Microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Interv Radiol. 22:125–132. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2015.15125. PMID: 26782155. PMCID: PMC4790063.70. Hirokawa F, Hayashi M, Miyamoto Y, Asakuma M, Shimizu T, Komeda K, et al. 2014; Outcomes and predictors of microvascular invasion of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 44:846–853. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12196. PMID: 23834279.71. Fan LF, Zhao WC, Yang N, Yang GS. Alpha-fetoprotein: the predictor of microvascular invasion in solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma and criterion for anatomic or non-anatomic hepatic resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013; 60:825–836.72. Ueno S, Kubo F, Sakoda M, Hiwatashi K, Tateno T, Mataki Y, et al. 2008; Efficacy of anatomic resection vs nonanatomic resection for small nodular hepatocellular carcinoma based on gross classification. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 15:493–500. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-007-1312-8. PMID: 18836803.73. Minami Y, Nishida N, Kudo M. 2014; Therapeutic response assessment of RFA for HCC: contrast-enhanced US, CT and MRI. World J Gastroenterol. 20:4160–4166. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160. PMID: 24764654. PMCID: PMC3989952.74. Jin YJ, Lee JW, Lee OH, Chung HJ, Kim YS, Lee JI, et al. 2014; Transarterial chemoembolization versus surgery/radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with or without microvascular invasion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:1056–1064. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12507. PMID: 24372785.75. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. 2003; Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 327:557–560. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. PMID: 12958120. PMCID: PMC192859.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concepts and emerging issues of network meta-analysis
- Overview of Network Meta-analysis for a Rheumatologist
- The use of transient elastography for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients: Editorial on “Risk assessment of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma development using vibration-controlled transient elastography: Systematic review and meta-analysis”
- Meta-epidemiology
- Loco-regional therapies competing with radiofrequency ablation in potential indications for hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis