Nutr Res Pract.
2024 Aug;18(4):451-463. 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.4.451.
Umami taste receptor suppresses cancer cachexia by regulating skeletal muscle atrophy in vivo and in vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nutritional Science and Food Management, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 03760, Korea
- 2Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
- 3Graduate Program in System Health Science and Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 03760, Korea
- KMID: 2558485
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2024.18.4.451
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
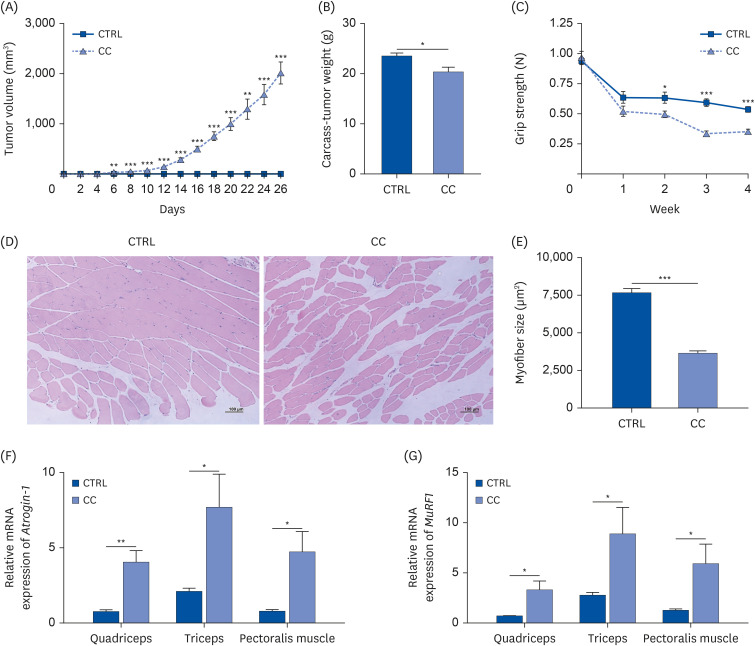
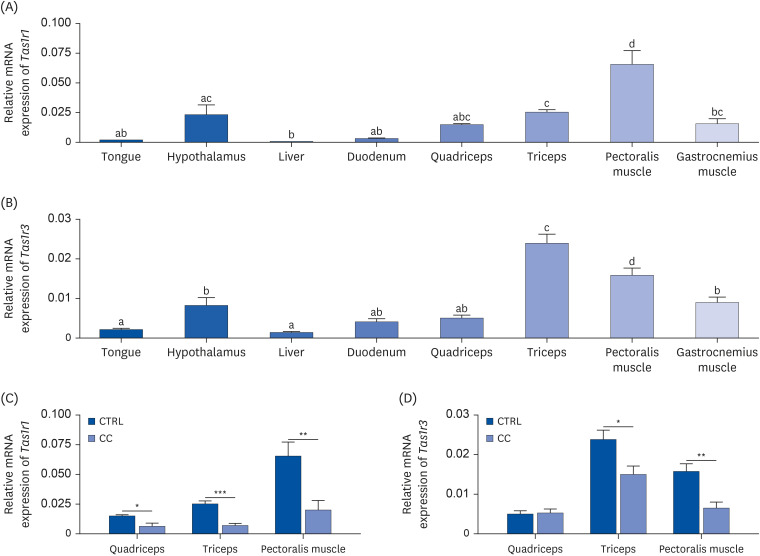
The umami taste receptor (TAS1R1/TAS1R3) is endogenously expressed in skeletal muscle and is involved in myogenesis; however, there is a lack of evidence about whether the expression of the umami taste receptor is involved in muscular diseases. This study aimed to elucidate the effects of the umami taste receptor and its mechanism on muscle wasting in cancer cachexia using in vivo and in vitro models.
MATERIALS/METHODS
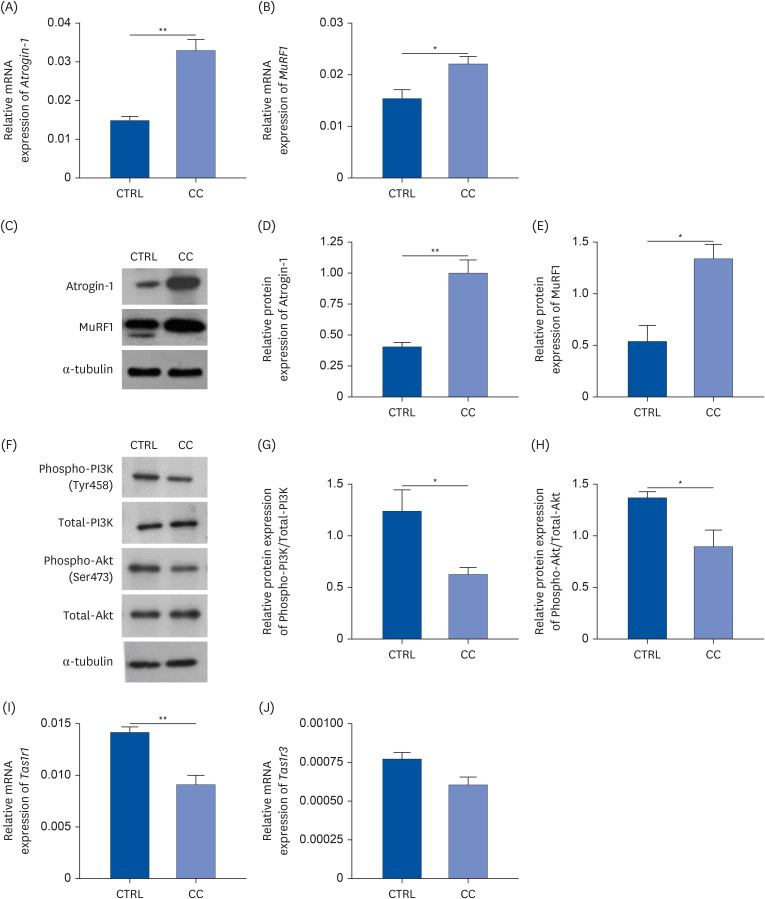
The Lewis lung carcinoma-induced cancer cachexia model was used in vivo and in vitro, and the expressions of umami taste receptor and muscle atrophy-related markers, muscle atrophy F-box protein, and muscle RING-finger protein-1 were analyzed.
RESULTS
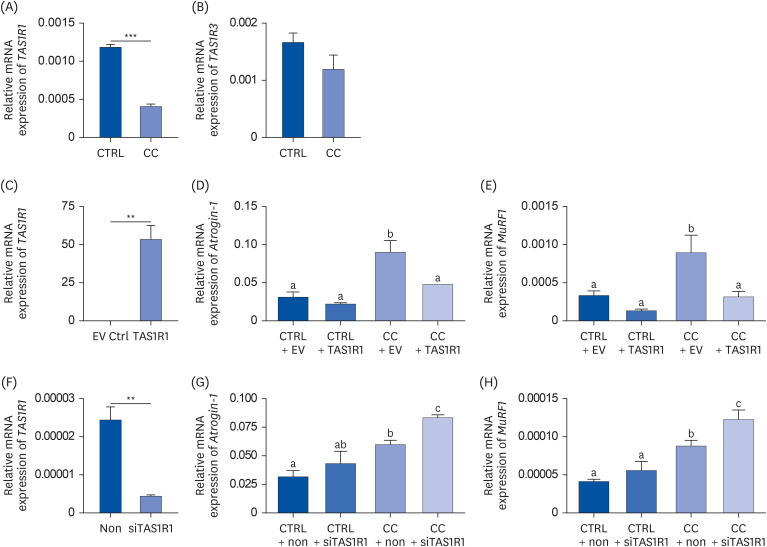
Results showed that TAS1R1 was significantly downregulated in vivo and in vitro under the muscle wasting condition. Moreover, overexpression of TAS1R1 in vitro in the human primary cell model protected the cells from muscle atrophy, and knockdown of TAS1R1 using siRNA exacerbated muscle atrophy.
CONCLUSION
Taken together, the umami taste receptor exerts protective effects on muscle-wasting conditions by restoring dysregulated muscle atrophy in cancer cachexia. In conclusion, this result provided evidence that the umami taste receptor exerts a therapeutic anti-cancer cachexia effect by restoring muscle atrophy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, Jatoi A, Loprinzi C, MacDonald N, Mantovani G, et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:489–495. PMID: 21296615.
Article2. Kasvis P, Vigano M, Vigano A. Health-related quality of life across cancer cachexia stages. Ann Palliat Med. 2019; 8:33–42. PMID: 30525763.3. Dodson S, Baracos VE, Jatoi A, Evans WJ, Cella D, Dalton JT, Steiner MS. Muscle wasting in cancer cachexia: clinical implications, diagnosis, and emerging treatment strategies. Annu Rev Med. 2011; 62:265–279. PMID: 20731602.
Article4. Balagopal P, Ljungqvist O, Nair KS. Skeletal muscle myosin heavy-chain synthesis rate in healthy humans. Am J Physiol. 1997; 272:E45–E50. PMID: 9038850.
Article5. Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, et al. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science. 2001; 294:1704–1708. PMID: 11679633.
Article6. Yuan L, Han J, Meng Q, Xi Q, Zhuang Q, Jiang Y, Han Y, Zhang B, Fang J, Wu G. Muscle-specific E3 ubiquitin ligases are involved in muscle atrophy of cancer cachexia: an in vitro and in vivo study. Oncol Rep. 2015; 33:2261–2268. PMID: 25760630.
Article7. Adams V, Gußen V, Zozulya S, Cruz A, Moriscot A, Linke A, Labeit S. Small-molecule chemical knockdown of MuRF1 in melanoma bearing mice attenuates tumor cachexia associated myopathy. Cells. 2020; 9:2272. PMID: 33050629.8. Moro T, Ebert SM, Adams CM, Rasmussen BB. Amino acid sensing in skeletal muscle. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 27:796–806. PMID: 27444066.
Article9. Wauson EM, Zaganjor E, Lee AY, Guerra ML, Ghosh AB, Bookout AL, Chambers CP, Jivan A, McGlynn K, Hutchison MR, et al. The G protein-coupled taste receptor T1R1/T1R3 regulates mTORC1 and autophagy. Mol Cell. 2012; 47:851–862. PMID: 22959271.
Article10. Wauson EM, Lorente-Rodríguez A, Cobb MH. Minireview: nutrient sensing by G protein-coupled receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 2013; 27:1188–1197. PMID: 23820899.
Article11. Shirakawa T, Toyono T, Inoue A, Matsubara T, Kawamoto T, Kokabu S. Factors regulating or regulated by myogenic regulatory factors in skeletal muscle stem cells. Cells. 2022; 11:1493. PMID: 35563799.
Article12. Kokabu S, Lowery JW, Toyono T, Seta Y, Hitomi S, Sato T, Enoki Y, Okubo M, Fukushima Y, Yoda T. Muscle regulatory factors regulate T1R3 taste receptor expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 468:568–573. PMID: 26545778.13. Obikane Y, Toyono T, Kokabu S, Matsuyama K, Kataoka S, Nakatomi M, Hosokawa R, Seta Y. Myogenic differentiation 1 and transcription factor 12 activate the gene expression of mouse taste receptor type 1 member 1. J Oral Biosci. 2021; 63:420–428. PMID: 34492379.
Article14. Carlsson G, Gullberg B, Hafström L. Estimation of liver tumor volume using different formulas - an experimental study in rats. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1983; 105:20–23. PMID: 6833336.
Article15. Ahn SR, An JH, Song HS, Park JW, Lee SH, Kim JH, Jang J, Park TH. Duplex bioelectronic tongue for sensing umami and sweet tastes based on human taste receptor nanovesicles. ACS Nano. 2016; 10:7287–7296. PMID: 27327579.
Article16. Dalesio NM, Barreto Ortiz SF, Pluznick JL, Berkowitz DE. Olfactory, taste, and photo sensory receptors in non-sensory organs: it just makes sense. Front Physiol. 2018; 9:1673. PMID: 30542293.
Article17. Li X, Staszewski L, Xu H, Durick K, Zoller M, Adler E. Human receptors for sweet and umami taste. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99:4692–4696. PMID: 11917125.18. Kokabu S, Lowery JW, Toyono T, Sato T, Yoda T. On the emerging role of the taste receptor type 1 (T1R) family of nutrient-sensors in the musculoskeletal system. Molecules. 2017; 22:469. PMID: 28294983.
Article19. Rask-Andersen M, Almén MS, Schiöth HB. Trends in the exploitation of novel drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011; 10:579–590. PMID: 21804595.
Article20. Xu H, Staszewski L, Tang H, Adler E, Zoller M, Li X. Different functional roles of T1R subunits in the heteromeric taste receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:14258–14263. PMID: 15353592.
Article21. Schiaffino S, Dyar KA, Ciciliot S, Blaauw B, Sandri M. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013; 280:4294–4314. PMID: 23517348.
Article22. Rommel C, Bodine SC, Clarke BA, Rossman R, Nunez L, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ. Mediation of IGF-1-induced skeletal myotube hypertrophy by PI(3)K/Akt/mTOR and PI(3)K/Akt/GSK3 pathways. Nat Cell Biol. 2001; 3:1009–1013. PMID: 11715022.23. Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C, Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH, Goldberg AL. Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell. 2004; 117:399–412. PMID: 15109499.
Article