Ann Lab Med.
2024 Jul;44(4):371-374. 10.3343/alm.2023.0426.
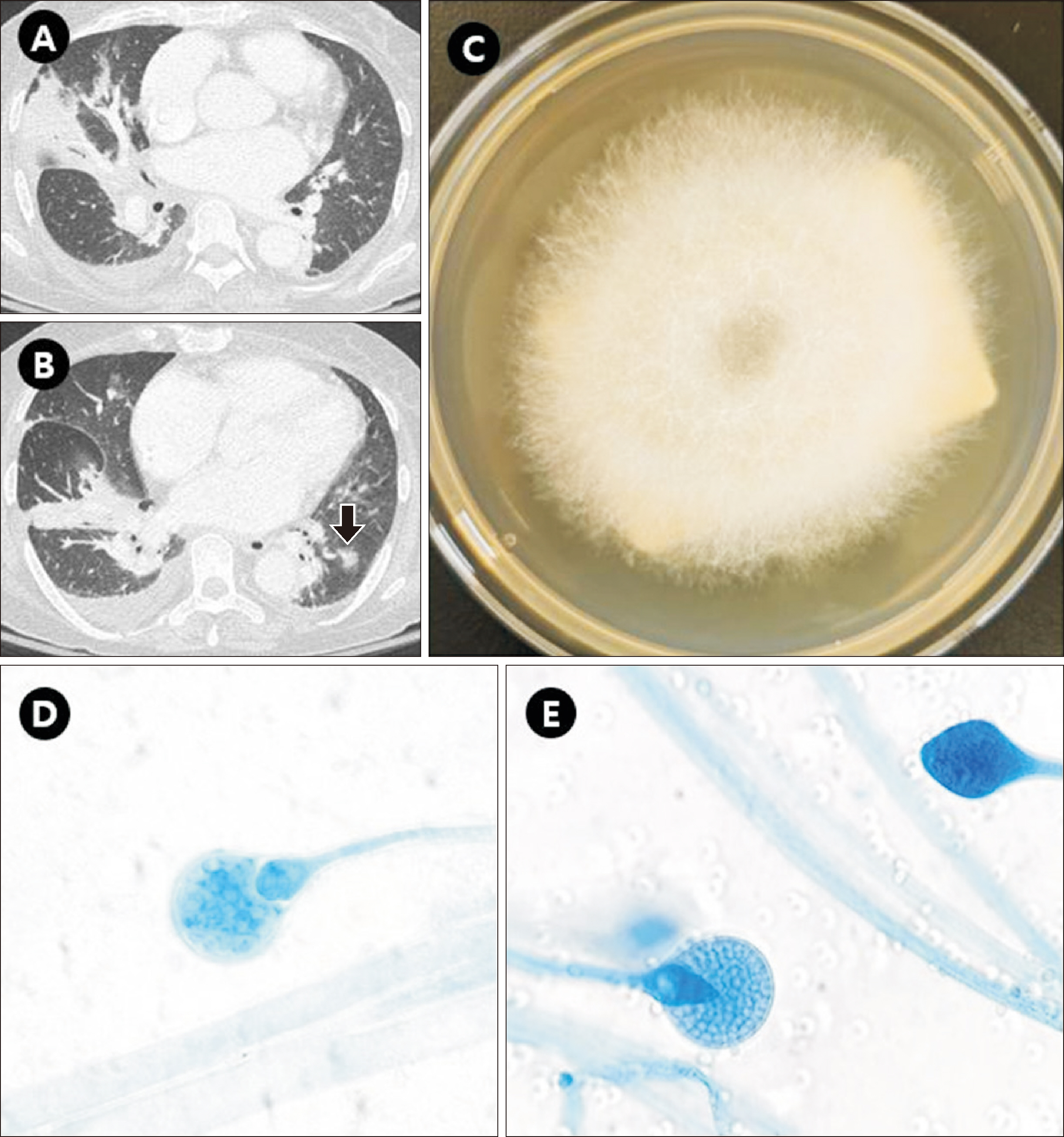
The First Case of Pulmonary Mucormycosis Caused by Lichtheimia ornata
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Hematology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2557938
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0426
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Skiada A, Pagano L, Groll A, Zimmerli S, Dupont B, Lagrou K, et al. 2011; Zygomycosis in Europe: analysis of 230 cases accrued by the registry of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Working Group on Zygomycosis between 2005 and 2007. Clin Microbiol Infect. 17:1859–67. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03456.x. PMID: 21199154.
Article2. Alvarez E, Sutton DA, Cano J, Fothergill AW, Stchigel A, Rinaldi MG, et al. 2009; Spectrum of zygomycete species identified in clinically significant specimens in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 47:1650–6. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00036-09. PMID: 19386856. PMCID: PMC2691065.
Article3. Schwartze VU, Hoffmann K, Nyilasi I, Papp T, Vagvolgyi C, de Hoog S, et al. 2012; Lichtheimia species exhibit differences in virulence potential. PLoS One. 7:e40908. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040908. PMID: 22911715. PMCID: PMC3401187. PMID: 076d85624f3d47cea894630880f1a61c.4. Pan J, Tsui C, Li M, Xiao K, de Hoog GS, Verweij PE, et al. 2020; First case of rhinocerebral mucormycosis caused by Lichtheimia ornata, with a review of Lichtheimia infections. Mycopathologia. 185:555–67. DOI: 10.1007/s11046-020-00451-y. PMID: 32388712.
Article5. Chowdhary A, Gupta N, Wurster S, Kumar R, Mohabir JT, Tatavarthy S, et al. 2023; Multimodal analysis of the COVID-19-associated mucormycosis outbreak in Delhi, India indicates the convergence of clinical and environmental risk factors. Mycoses. 66:515–26. DOI: 10.1111/myc.13578. PMID: 36790120.
Article6. Tissot F, Agrawal S, Pagano L, Petrikkos G, Groll AH, Skiada A, et al. 2017; ECIL-6 guidelines for the treatment of invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis and mucormycosis in leukemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Haematologica. 102:433–44. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.152900. PMID: 28011902. PMCID: PMC5394968.
Article7. CLSI. 2017. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi. 3rd ed. M38-ED3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA: DOI: 10.1201/9781420014495-15.8. CLSI. 2018. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by targeted DNA sequencing. 2nd ed. MM18-ED2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:9. Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Cuesta I, Walther G, Cuenca-Estrella M, Rodriguez-Tudela JL. 2010; Antifungal susceptibility profile of human-pathogenic species of Lichtheimia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 54:3058–60. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01270-09. PMID: 20421405. PMCID: PMC2897292.
Article10. Subcommittee on antifungal susceptibility testing of the ESCMID. 2008; EUCAST technical note on the method for the determination of broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentrations of antifungal agents for conidia-forming moulds. Clin Microbiol Infect. 14:982–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02086.x. PMID: 18828858.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Angioinvasive Mucormycosis Mimicking Mass and Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A Case Report
- A Case of Pulmonary Mucormycosis without Obvious Predisposing Factors
- Pulmonary mucormycosis with an appearance of consolidation
- Pulmonary and Endobronchial Mucormycosis in a Diabetic Patient: A Case Report
- Pulmonary Mucormycosis Treated Successfully with Posaconazole as Salvage Therapy