J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2024 Jun;26(2):152-162. 10.7461/jcen.2023.E2023.03.002.
Intracranial stenting compared to medical treatment alone for intracranial atherosclerosis patients: An updated meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Neuroendovascular Program, Massachusetts General Hospital & Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA, USA
- 2Neurovascular Centre, Departments of Medical Imaging & Surgery, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre and St. Michael’s Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto ON, Canada
- 3Neurointerventional Program, Departments of Medical Imaging & Clinical Neurological Sciences, London Health Sciences Centre, Western University, London ON, Canada
- 4Nested Knowledge, Department of Neuroradiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN, USA
- KMID: 2556977
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2023.E2023.03.002
Abstract
Objective
Stroke is the second-leading cause of death globally. Intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS) represents 10-15% of ischemic strokes in Western countries and up to 47% in Asian countries. Patients with ICAS have an especially high risk of stroke recurrence. The aim of this meta-analysis is to reassess recurrent stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), and other outcomes with stenting versus best medical management for symptomatic ICAS.
Methods
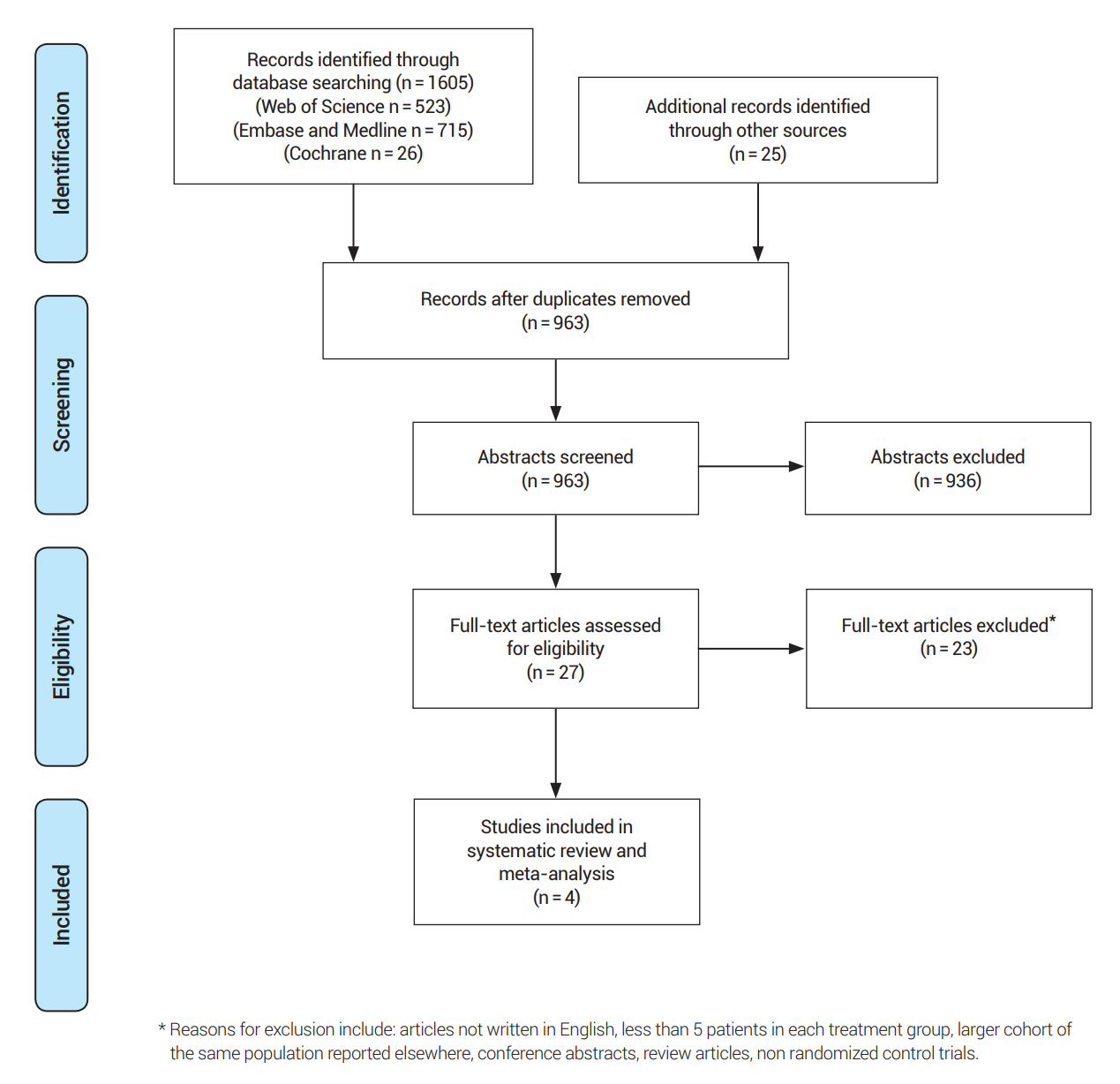
The search protocol was developed a priori according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The OVID Medline, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched from inception to August 14th, 2022.
Results
This Meta-analysis Included Four Randomized Controlled Trials (Rcts), With A Total Number Of 991 Patients. The Mean Age Of Participants Was 57 Years. The Total Number Of Intracranial Stenting Patients Was 495, And The Number Of Medical Treatment Patients Was 496. The Included Studies Were Published Between 2011 And 2022. Two Studies Were Conducted In The Usa, And The Other Two In China. All Included Studies Compared Intracranial Stenting To Medical Treatment For Icas.
Conclusions
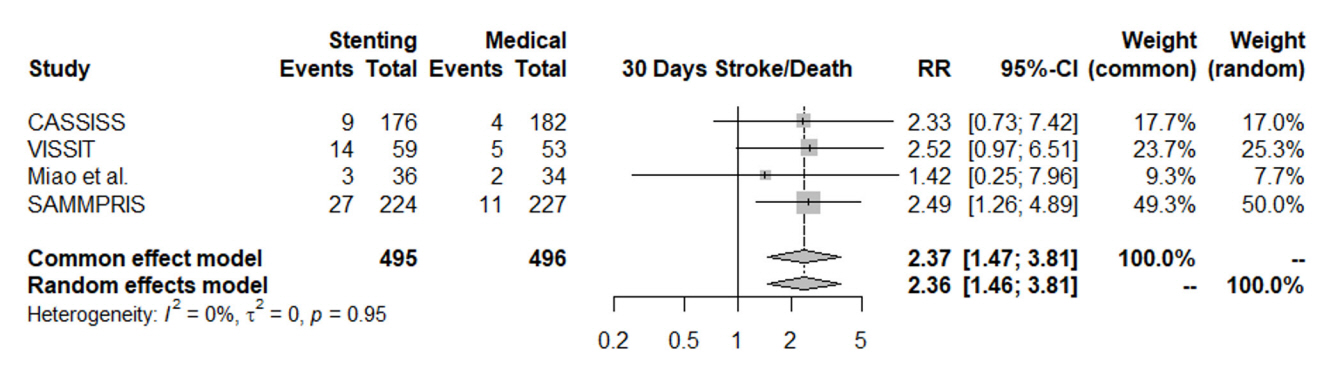
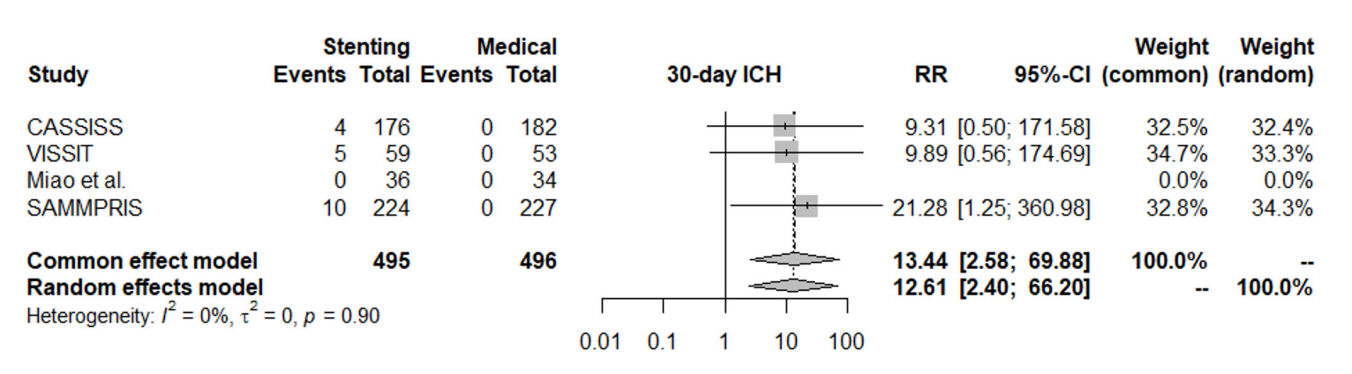
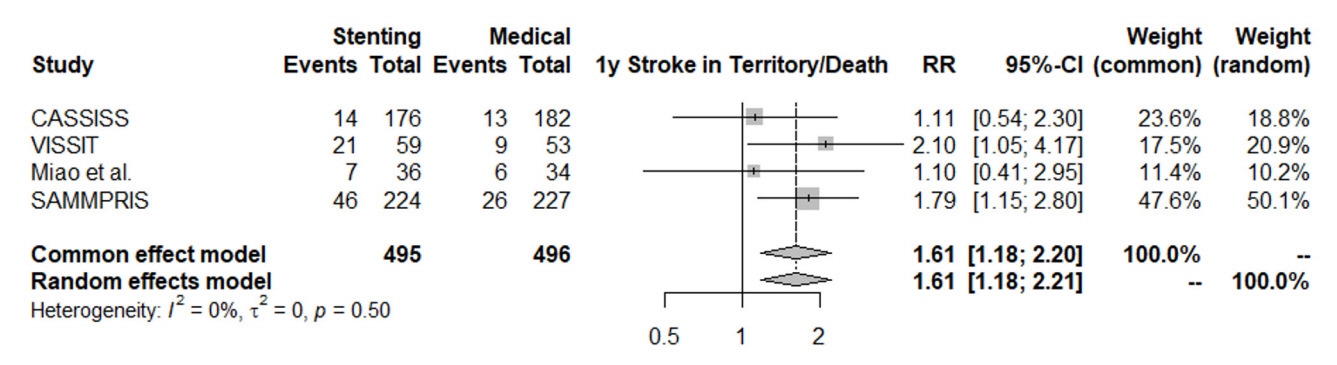
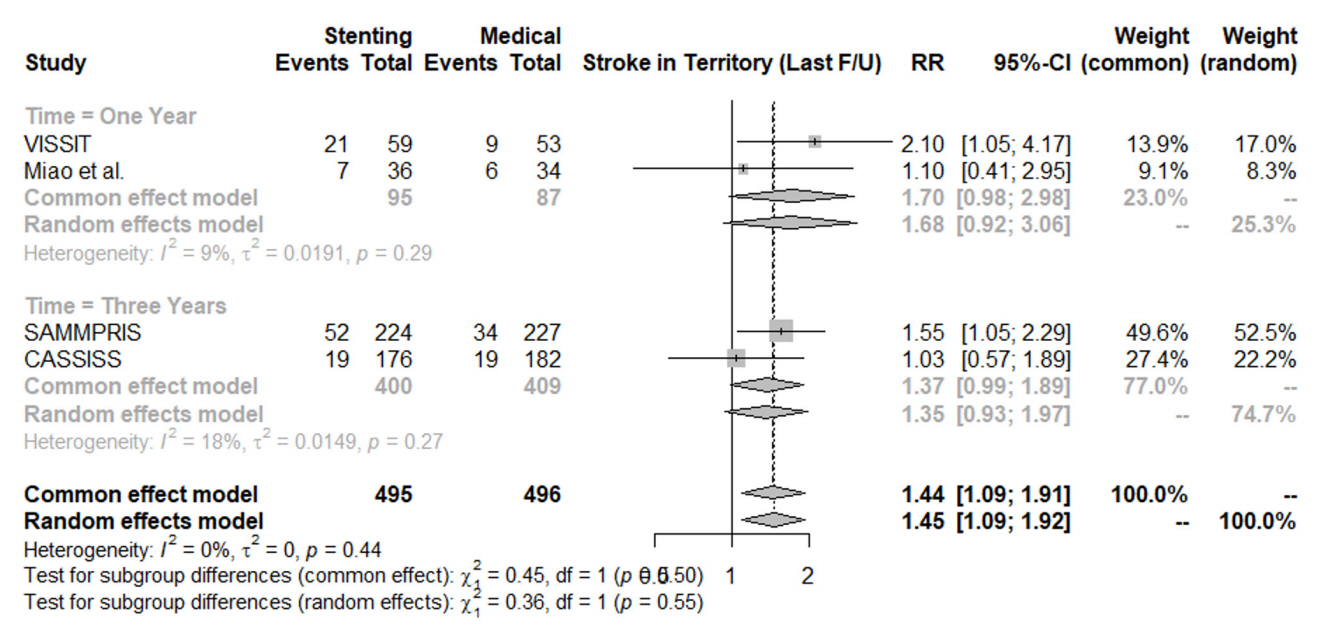
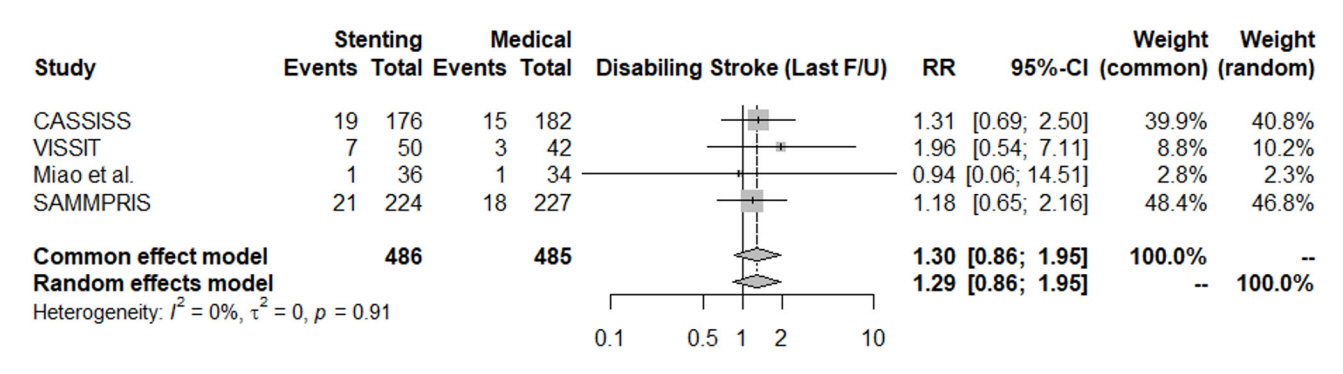
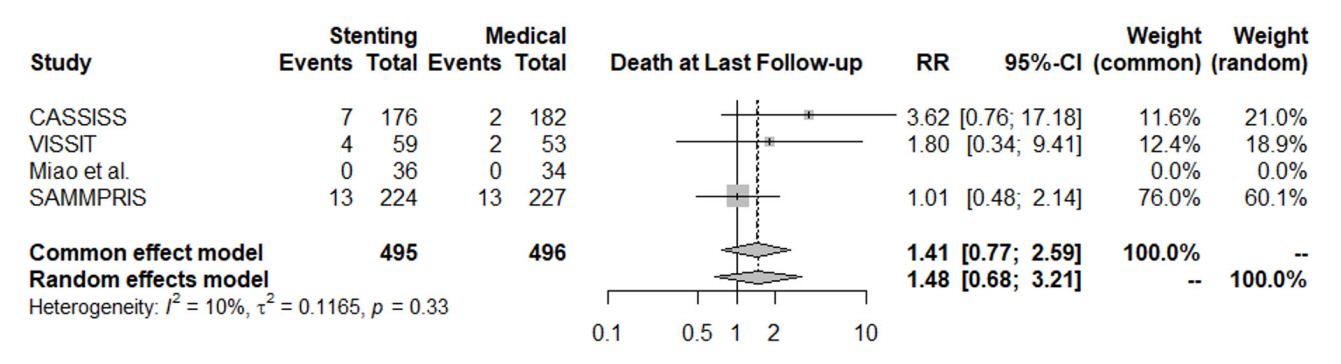
In patients with ischemic stroke due to symptomatic severe intracranial atherosclerosis, the rate of 30-day ischemic stroke, 30-day intracerebral hemorrhage, one-year stroke in territory or mortality favored the medical treatment alone without intracranial stenting. The risk of same-territory stroke at last follow-up, disabling stroke at last follow-up, and mortality did not significantly favor either group. Intracranial stenting for atherosclerosis did not result in significant benefit over medical treatment.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abou-Chebl A. Intracranial stenting with Wingspan: Still awaiting a safe landing. Stroke. 2011; Jul. 42(7):1809–11.2. Alexander MJ, Zauner A, Chaloupka JC, Baxter B, Callison RC, Gupta R, et al. WEAVE trial: Final results in 152 on-label patients. Stroke. 2019; Apr. 50(4):889–94.3. Arenillas JF. Intracranial atherosclerosis: Current concepts. Stroke. 2011; Jan. 42(1 Suppl):S20–3.4. Bose A, Hartmann M, Henkes H, Liu HM, Teng MM, Szikora I, et al. A novel, self-expanding, nitinol stent in medically refractory intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses: The Wingspan study. Stroke. 2007; May. 38(5):1531–7.
Article5. Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Derdeyn CP, Turan TN, Fiorella D, Lane BF, et al. Stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2011; Sep. 365(11):993–1003.6. Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, Frankel MR, et al. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; Mar. 352(13):1305–16.
Article7. Derdeyn CP, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Fiorella D, Turan TN, Janis LS, et al. Aggressive medical treatment with or without stenting in high-risk patients with intracranial artery stenosis (SAMMPRIS): The final results of a randomised trial. Lancet. 2014; Jan. 383(9914):333–41.
Article8. Derdeyn CP, Fiorella D, Lynn MJ, Rumboldt Z, Cloft HJ, Gibson D, et al. Mechanisms of stroke after intracranial angioplasty and stenting in the SAMMPRIS trial. Neurosurgery. 2013; May. 72(5):777–95. discussion 795.
Article9. Fiorella D, Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, et al. US multicenter experience with the wingspan stent system for the treatment of intracranial atheromatous disease: Periprocedural results. Stroke. 2007; Mar. 38(3):881–7.
Article10. Gao P, Wang D, Zhao Z, Cai Y, Li T, Shi H, et al. Multicenter prospective trial of stent placement in patients with symptomatic high-grade intracranial stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; Jul. 37(7):1275–80.
Article11. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021; Oct. 20(10):795–820.12. Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK. Large artery intracranial occlusive disease: A large worldwide burden but a relatively neglected frontier. Stroke. 2008; Aug. 39(8):2396–9.13. Kurre W, Berkefeld J, Brassel F, Brüning R, Eckert B, Kamek S, et al. In-hospital complication rates after stent treatment of 388 symptomatic intracranial stenoses: Results from the INTRASTENT multicentric registry. Stroke. 2010; Mar. 41(3):494–8.
Article14. Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J, Jiang C, Zhu Q, Chen K, et al. Thirty-day outcome of a multicenter registry study of stenting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China. Stroke. 2015; Oct. 46(10):2822–9.
Article15. Nahab F, Lynn MJ, Kasner SE, Alexander MJ, Klucznik R, Zaidat OO, et al. Risk factors associated with major cerebrovascular complications after intracranial stenting. Neurology. 2009; Jun. 72(23):2014–9.
Article16. Romano JG, Prabhakaran S, Nizam A, Feldmann E, Sangha R, Cotsonis G, et al. Infarct recurrence in intracranial atherosclerosis: Results from the MyRIAD study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021; Feb. 30(2):105504.
Article17. Turan TN, Zaidat OO, Gronseth GS, Chimowitz MI, Culebras A, Furlan AJ, et al. Stroke prevention in symptomatic large artery intracranial atherosclerosis practice advisory: Report of the AAN guideline subcommittee. Neurology. 2022; Mar. 98(12):486–98.
Article18. Wabnitz AM, Derdeyn CP, Fiorella DJ, Lynn MJ, Cotsonis GA, Liebeskind DS, et al. Hemodynamic markers in the anterior circulation as predictors of recurrent stroke in patients with intracranial stenosis. Stroke. 2019; Jan. 50(1):143–7.
Article19. Wang T, Luo J, Wang X, Yang K, Jadhav V, Gao P, et al. Endovascular therapy versus medical treatment for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020; Aug. 8(8):CD013267.
Article20. Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L, Soo YO, Pu Y, Pan Y, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of symptomatic intracranial large artery stenoses and occlusions in China: the Chinese Intracranial Atherosclerosis (CICAS) Study. Stroke. 2014; Mar. 45(3):663–9.21. Boden-Albala B, Wang C, Elkind MS, Rundek T, Wright CB, et al. Ischemic stroke subtype incidence among whites, blacks, and Hispanics: the Northern Manhattan Study. Circulation. 2005; Mar. 111(10):1327–31.22. Yu SC, Leung TW, Lee KT, Wong LK. Learning curve of Wingspan stenting for intracranial atherosclerosis: Single-center experience of 95 consecutive patients. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; Apr. 6(3):212–8.
Article23. Yu Y, Wang T, Yang K, Zhang X, Yu SCH, Luo J, et al. Timing and outcomes of intracranial stenting in the post-SAMMPRIS era: A systematic review. Front Neurol. 2021; Feb. 12:637632.
Article24. Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF, Woodward BK, Wang Z, Killer-Oberpfalzer M, Wakhloo A, et al. Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: The VISSIT randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015; Mar. 313(12):1240–8.
Article25. Zaidat OO, Klucznik R, Alexander MJ, Chaloupka J, Lutsep H, Barnwell S, et al. The NIH registry on use of the Wingspan stent for symptomatic 70-99% intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology. 2008; Apr. 70(17):1518–24.
Article26. Zhang Y, Sun Y, Li X, Liu T, Liu P, Wang H, et al. Early versus delayed stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic artery stenosis with ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020; Mar. 12(3):274–8.
Article27. Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019; Sep. 394(10204):1145–58.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease; Current Options for Surgical or Medical Treatment
- Angioplasty, Stenting and Other Potential Treatments of Atherosclerotic Stenosis of the Intracranial Arteries: Past, Present and Future
- Guideline for Intracranial Stenting of Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis: Preliminary Report
- Association of Metabolic Syndrome and C-reactive Protein Levels with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stroke
- Intracranial Atherosclerosis: From Microscopy to High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging