Neonatal Med.
2024 May;31(2):24-30. 10.5385/nm.2024.31.2.24.
Bronchoscopic Evaluations in Preterm Infants with Moderate to Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2024.31.2.24
Abstract
- Purpose
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease that primarily affects premature infants receiving mechanical ventilation and oxygen therapy. Severe BPD leads to long-term respiratory complications, including lung tissue damage, vascular abnormalities, and airway diseases. This study aimed to investigate bronchoscopy findings and characteristics in patients with moderate-to-severe BPD, and to investigate BPD-associated airway diseases.
Methods
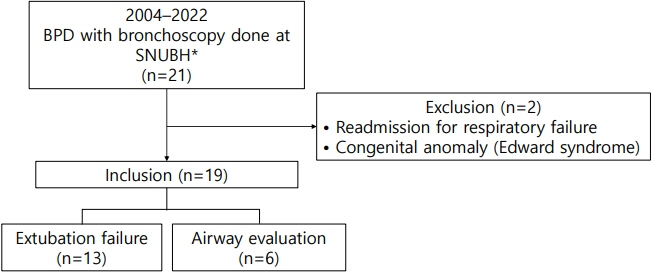
A retrospective study of preterm infants diagnosed with moderate-to-severe BPD who underwent bronchoscopic evaluation in the neonatal intensive care unit at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital between 2004 and December 2022 was conducted.
Results
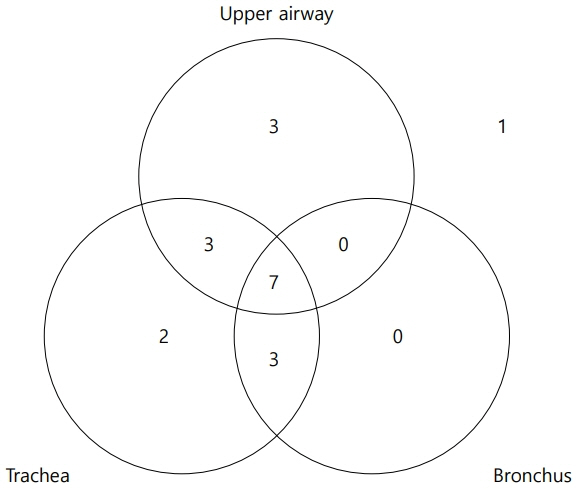
Nineteen patients with a mean gestational age of 28.0±1.6 weeks and mean birth weight of 960.5±271.0 g were included in the study. Among these 19 patients, 18 were diagnosed with severe BPD. Tracheobronchomalacia, laryngomalacia, and subglottic stenosis were observed in 63.2%, 52.6%, and 36.8% of patients, respectively. Tracheostomy was performed in nine of the 19 patients (47.4%); five were discharged without requiring tracheostomy following surgical or medical interventions.
Conclusion
Tracheobronchomalacia, laryngomalacia, and subglottic stenosis were common in patients with moderate or severe BPD who underwent bronchoscopic evaluations, of which 50% required tracheostomy. Our study findings provide valuable insights into the pathophysiology of BPD-associated airway diseases and may inform future clinical management strategies for patients with BPD.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah PS, Sankaran K, Aziz K, Allen AC, Seshia M, Ohlsson A, et al. Outcomes of preterm infants <29 weeks gestation over 10-year period in Canada: a cause for concern? J Perinatol. 2012; 32:132–8.
Article2. Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Walsh MC, Carlo WA, Shankaran S, et al. Trends in care practices, morbidity, and mortality of extremely preterm neonates, 1993-2012. JAMA. 2015; 314:1039–51.
Article3. Costeloe KL, Hennessy EM, Haider S, Stacey F, Marlow N, Draper ES. Short term outcomes after extreme preterm birth in England: comparison of two birth cohorts in 1995 and 2006 (the EPICure studies). BMJ. 2012; 345:e7976.
Article4. McCubbin M, Frey EE, Wagener JS, Tribby R, Smith WL. Large airway collapse in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1989; 114:304–7.
Article5. Downing GJ, Kilbride HW. Evaluation of airway complications in high-risk preterm infants: application of flexible fiberoptic airway endoscopy. Pediatrics. 1995; 95:567–72.
Article6. Miller RW, Woo P, Kellman RK, Slagle TS. Tracheobronchial abnormalities in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1987; 111:779–82.
Article7. Cohn RC, Kercsmar C, Dearborn D. Safety and efficacy of flexible endoscopy in children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1988; 142:1225–8.
Article8. Wu KY, Jensen EA, White AM, Wang Y, Biko DM, Nilan K, et al. Characterization of disease phenotype in very preterm infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020; 201:1398–406.
Article9. Bamat NA, Zhang H, McKenna KJ, Morris H, Stoller JZ, Gibbs K. The clinical evaluation of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neoreviews. 2020; 21:e442–53.
Article10. Hysinger EB, Friedman NL, Padula MA, Shinohara RT, Zhang H, Panitch HB, et al. Tracheobronchomalacia is associated with increased morbidity in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017; 14:1428–35.
Article11. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1723–9.
Article12. Jensen EA, Dysart K, Gantz MG, McDonald S, Bamat NA, Keszler M, et al. The diagnosis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very preterm infants: an evidence-based approach. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019; 200:751–9.
Article13. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–34.
Article14. Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg. 1978; 187:1–7.
Article15. Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002; 110(2 Pt 1):285–91.
Article16. Windsor AM, Kiell EP, Sobol SE. Predictors of the need for tracheostomy in the neonatal intensive care unit. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; 135:110122.
Article17. Walner DL, Loewen MS, Kimura RE. Neonatal subglottic stenosis: incidence and trends. Laryngoscope. 2001; 111:48–51.18. Annesi CA, Levin JC, Litt JS, Sheils CA, Hayden LP. Long-term respiratory and developmental outcomes in children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia and history of tracheostomy. J Perinatol. 2021; 41:2645–50.
Article19. Soong WJ, Tsao PC, Yang CF, Lee YS, Lin CH, Chen CH. Flexible endoscopy with non-invasive ventilation enables clinicians to assess and manage infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Front Pediatr. 2022; 10:837329.
Article20. Bush D, Juliano C, Bowler S, Tiozzo C. Development and disorders of the airway in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Children (Basel). 2023; 10:1127.
Article21. Pereira KD, Smith SL, Henry M. Failed extubation in the neonatal intensive care unit. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 71:1763–6.
Article22. Venkatesan NN, Pine HS, Underbrink M. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013; 60:865–78.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Positive Ureaplasma in Gastric Fluid with Clinical Features in Preterm Infants
- Changes in the Incidence of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia among Preterm Infants in a Single Center over 10 Years
- Optimal Ventilatory Strategies in Preterm Infants: Permissive Hypercapnia
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?