Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2024 May;17(2):137-146. 10.21053/ceo.2023.00089.
Treatment Outcomes of Olfactory Neuroblastoma: A Multicenter Study by the Korean Sinonasal Tumor and Skull Base Surgery Study Group
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 5Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 6Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
- 7Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- 8Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 9Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 10Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 11Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2023.00089
Abstract
Objectives
. Due to the rarity of olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB), there is ongoing debate about optimal treatment strategies, especially for early-stage or locally advanced cases. Therefore, our study aimed to explore experiences from multiple centers to identify factors that influence the oncological outcomes of ONB.
Methods
. We retrospectively analyzed 195 ONB patients treated at nine tertiary hospitals in South Korea between December 1992 and December 2019. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to evaluate oncological outcomes, and a Cox proportional hazards regression model was employed to analyze prognostic factors for survival outcomes. Furthermore, we conducted 1:1 nearest-neighbor matching to investigate differences in clinical outcomes according to the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Results
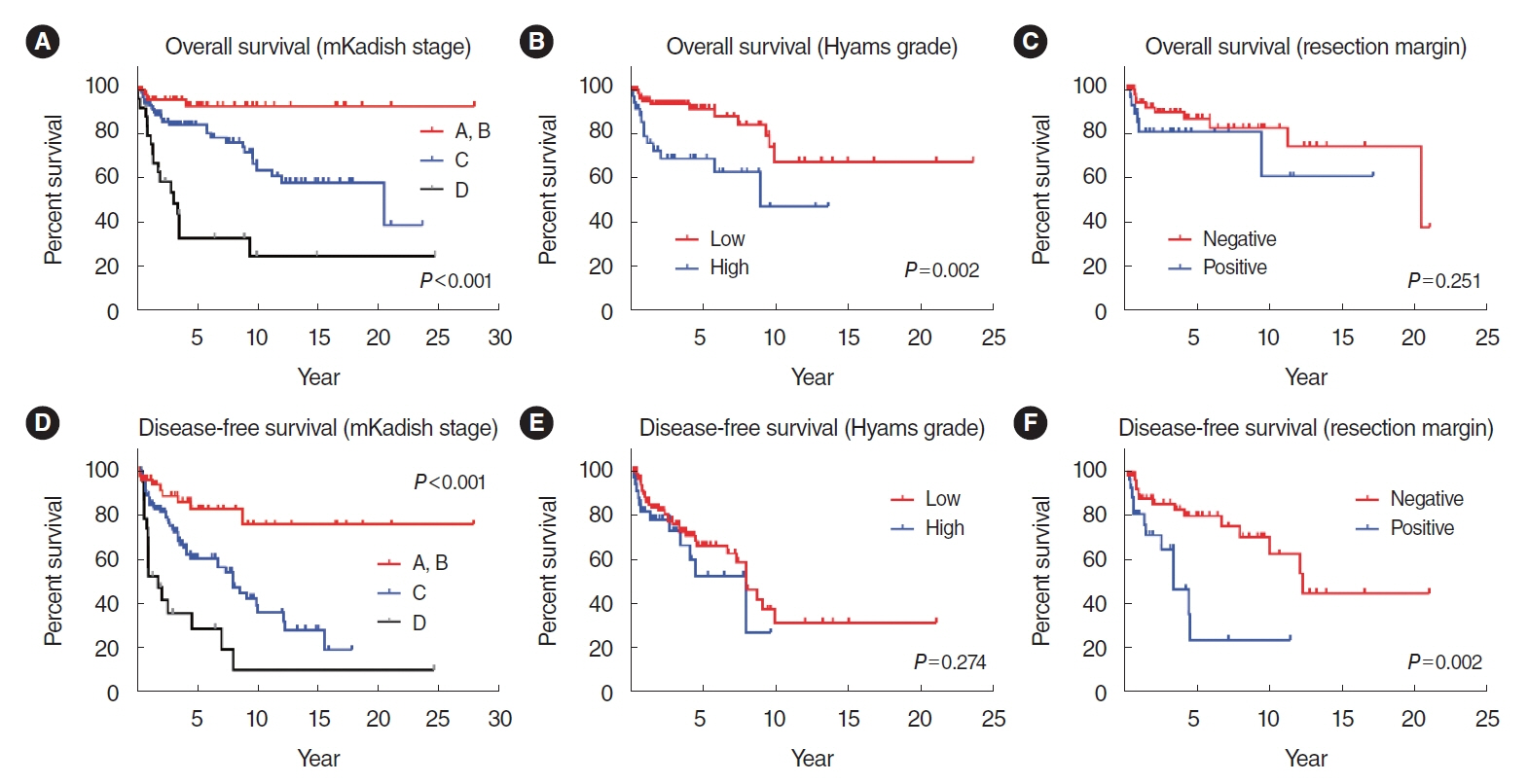
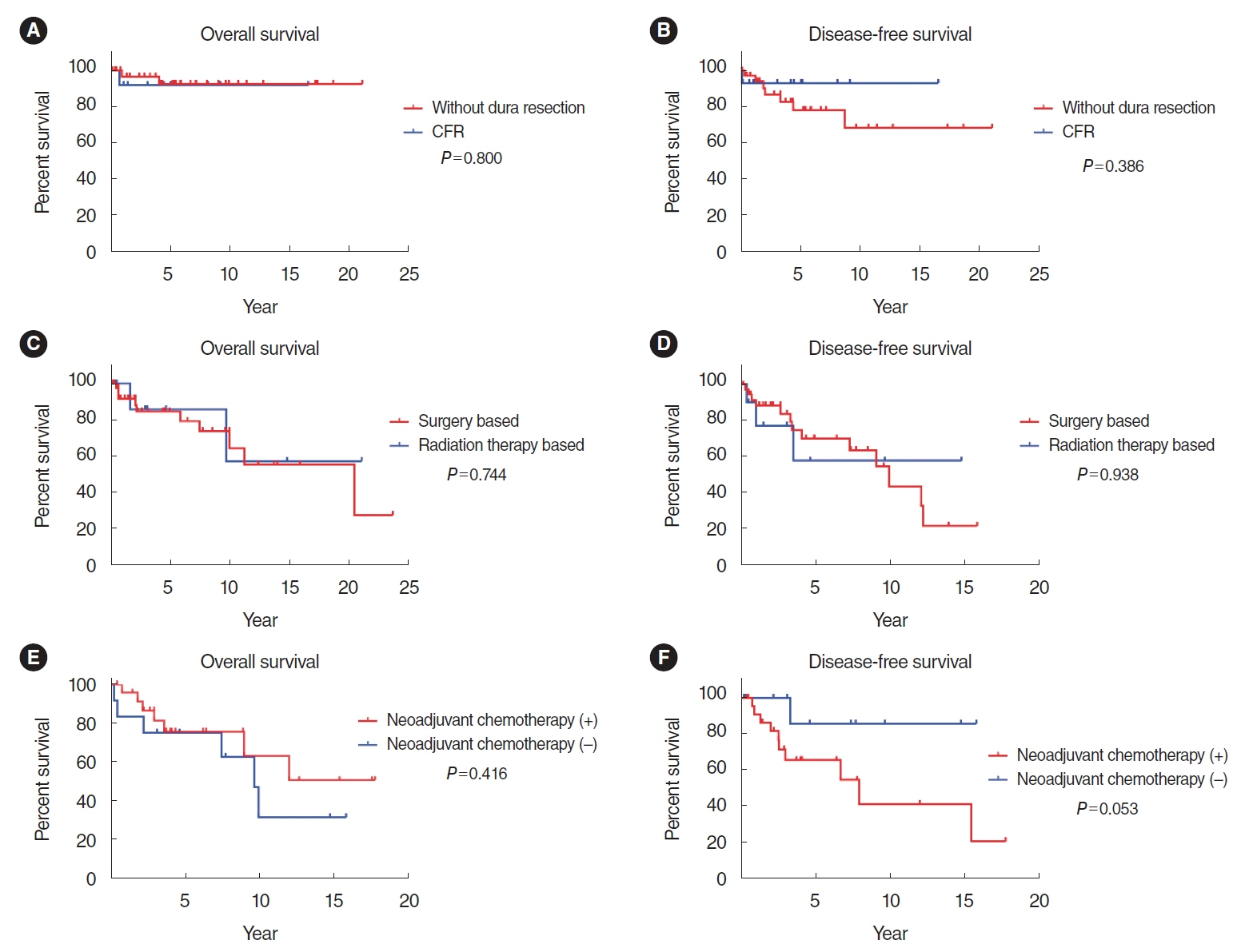
. In our cohort, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate was 78.6%, and the 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate was 62.4%. The Cox proportional hazards model revealed that the modified Kadish (mKadish) stage and Dulguerov T status were significantly associated with DFS, while the mKadish stage and Hyams grade were identified as prognostic factors for OS. The subgroup analyses indicated a trend toward improved 5-year DFS with dural resection in mKadish A and B cases, even though the result was statistically insignificant. Induction chemotherapy did not provide a survival benefit in this study after matching for the mKadish stage and nodal status.
Conclusion
. Clinical staging and pathologic grading are important prognostic factors in ONB. Dural resection in mKadish A and B did not show a significant survival benefit. Similarly, induction chemotherapy also did not show a survival benefit, even after stage matching.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arnold MA, Farnoosh S, Gore MR. Comparing Kadish and modified Dulguerov staging systems for olfactory neuroblastoma: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020; Sep. 163(3):418–27.
Article2. Marinelli JP, Janus JR, Van Gompel JJ, Link MJ, Moore EJ, Van Abel KM, et al. Dural invasion predicts the laterality and development of neck metastases in esthesioneuroblastoma. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2018; Oct. 79(5):495–500.
Article3. Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Rhys-Evans PH. Contemporary clinical commentary: esthesioneuroblastoma: an update on management of the neck. Laryngoscope. 2003; Nov. 113(11):1935–8.
Article4. Kumar M, Fallon RJ, Hill JS, Davis MM. Esthesioneuroblastoma in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002; 24(6):482–7.
Article5. Ow TJ, Bell D, Kupferman ME, Demonte F, Hanna EY. Esthesioneuroblastoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2013; Jan. 24(1):51–65.
Article6. Schmidt C, Potter N, Porceddu S, Panizza B. Olfactory neuroblastoma: 14-year experience at an Australian tertiary centre and the role for longer-term surveillance. J Laryngol Otol. 2017; Jul. 131(S2):S29–34.
Article7. Hirose T, Scheithauer BW, Lopes MB, Gerber HA, Altermatt HJ, Harner SG, et al. Olfactory neuroblastoma. An immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and flow cytometric study. Cancer. 1995; Jul. 76(1):4–19.
Article8. Kadish S, Goodman M, Wang CC. Olfactory neuroblastoma: a clinical analysis of 17 cases. Cancer. 1976; Mar. 37(3):1571–6.
Article9. Morita A, Ebersold MJ, Olsen KD, Foote RL, Lewis JE, Quast LM. Esthesioneuroblastoma: prognosis and management. Neurosurgery. 1993; May. 32(5):706–14.10. Dulguerov P, Calcaterra T. Esthesioneuroblastoma: the UCLA experience 1970-1990. Laryngoscope. 1992; Aug. 102(8):843–9.
Article11. Hyams VJ, Batsakis JG, Michaels L. Tumors of the upper respiratory tract and ear. 2nd ed. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1988.12. Su SY, Bell D, Ferrarotto R, Phan J, Roberts D, Kupferman ME, et al. Outcomes for olfactory neuroblastoma treated with induction chemotherapy. Head Neck. 2017; Aug. 39(8):1671–9.
Article13. Miller KC, Marinelli JP, Janus JR, Chintakuntlawar AV, Foote RL, Link MJ, et al. Induction therapy prior to surgical resection for patients presenting with locally advanced esthesioneuroblastoma. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021; Jul. 82(Suppl 3):e131–7.
Article14. Broich G, Pagliari A, Ottaviani F. Esthesioneuroblastoma: a general review of the cases published since the discovery of the tumour in 1924. Anticancer Res. 1997; 17(4A):2683–706.15. Dulguerov P, Allal AS, Calcaterra TC. Esthesioneuroblastoma: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol. 2001; Nov. 2(11):683–90.
Article16. Gruber G, Laedrach K, Baumert B, Caversaccio M, Raveh J, Greiner R. Esthesioneuroblastoma: irradiation alone and surgery alone are not enough. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; Oct. 54(2):486–91.
Article17. Diaz EM, Johnigan RH, Pero C, El-Naggar AK, Roberts DB, Barker JL, et al. Olfactory neuroblastoma: the 22-year experience at one comprehensive cancer center. Head Neck. 2005; Feb. 27(2):138–49.
Article18. Jethanamest D, Morris LG, Sikora AG, Kutler DI. Esthesioneuroblastoma: a population-based analysis of survival and prognostic factors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; Mar. 133(3):276–80.19. Van Gompel JJ, Giannini C, Olsen KD, Moore E, Piccirilli M, Foote RL, et al. Long-term outcome of esthesioneuroblastoma: hyams grade predicts patient survival. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2012; Oct. 73(5):331–6.
Article20. Capelle L, Krawitz H. Esthesioneuroblastoma: a case report of diffuse subdural recurrence and review of recently published studies. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2008; Feb. 52(1):85–90.
Article21. Bachar G, Goldstein DP, Shah M, Tandon A, Ringash J, Pond G, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma: the Princess Margaret Hospital experience. Head Neck. 2008; Dec. 30(12):1607–14.
Article22. Prasad KC, Kumar A, Prasad SC, Jain D. Endoscopic-assisted excision of esthesioneuroblastoma. J Craniofac Surg. 2007; Sep. 18(5):1034–8.
Article23. Fitzek MM, Thornton AF, Varvares M, Ancukiewicz M, Mcintyre J, Adams J, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the sinonasal tract: results of a prospective study incorporating chemotherapy, surgery, and combined proton-photon radiotherapy. Cancer. 2002; May. 94(10):2623–34.24. Eich HT, Hero B, Staar S, Micke O, Seegenschmiedt H, Mattke A, et al. Multimodality therapy including radiotherapy and chemotherapy improves event-free survival in stage C esthesioneuroblastoma. Strahlenther Onkol. 2003; Apr. 179(4):233–40.
Article25. Bradley PJ, Jones NS, Robertson I. Diagnosis and management of esthesioneuroblastoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; Apr. 11(2):112–8.
Article26. Kim HJ, Kim CH, Lee BJ, Chung YS, Kim JK, Choi YS, et al. Surgical treatment versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy as an initial treatment modality in advanced olfactory neuroblastoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2007; Dec. 34(4):493–8.
Article27. Rimmer J, Lund VJ, Beale T, Wei WI, Howard D. Olfactory neuroblastoma: a 35-year experience and suggested follow-up protocol. Laryngoscope. 2014; Jul. 124(7):1542–9.
Article28. McMillan RA, Van Gompel JJ, Link MJ, Moore EJ, Price DL, Stokken JK, et al. Long-term oncologic outcomes in esthesioneuroblastoma: an institutional experience of 143 patients. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022; Dec. 12(12):1457–67.
Article29. Sun M, Wang K, Qu Y, Zhang J, Zhang S, Chen X, et al. Long-term analysis of multimodality treatment outcomes and prognosis of esthesioneuroblastomas: a single center results of 138 patients. Radiat Oncol. 2020; Sep. 15(1):219.
Article30. Choby G, Geltzeiler M, Almeida JP, Champagne PO, Chan E, Ciporen J, et al. Multicenter survival analysis and application of an olfactory neuroblastoma staging modification incorporating Hyams grade. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023; Sep. 149(9):837–44.
Article31. Ketcham AS, Wilkins RH, Vanburen JM, Smith RR. A combined intracranial facial approach to the paranasal sinuses. Am J Surg. 1963; Nov. 106:698–703.
Article32. Mays AC, Bell D, Ferrarotto R, Phan J, Roberts D, Fuller CD, et al. Early stage olfactory neuroblastoma and the impact of resecting dura and olfactory bulb. Laryngoscope. 2018; Jun. 128(6):1274–80.
Article33. Hanna E, DeMonte F, Ibrahim S, Roberts D, Levine N, Kupferman M. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal cancers with and without craniotomy: oncologic results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; Dec. 135(12):1219–24.
Article34. Geltzeiler M, Choby GW, Ji KS, JessMace C, Almeida JP, de Almeida J, et al. Radiographic predictors of occult intracranial involvement in olfactory neuroblastoma patients. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023; Oct. 13(10):1876–88.
Article35. Thompson LD. Olfactory neuroblastoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2009; Sep. 3(3):252–9.
Article36. Ozsahin M, Gruber G, Olszyk O, Karakoyun-Celik O, Pehlivan B, Azria D, et al. Outcome and prognostic factors in olfactory neuroblastoma: a rare cancer network study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; Nov. 78(4):992–7.
Article37. Bhattacharyya N, Thornton AF, Joseph MP, Goodman ML, Amrein PC. Successful treatment of esthesioneuroblastoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma with combined chemotherapy and proton radiation: results in 9 cases. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; Jan. 123(1):34–40.
Article38. Saade RE, Hanna EY, Bell D. Prognosis and biology in esthesioneuroblastoma: the emerging role of Hyams grading system. Curr Oncol Rep. 2015; Jan. 17(1):423.
Article39. Loy AH, Reibel JF, Read PW, Thomas CY, Newman SA, Jane JA, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma: continued follow-up of a single institution’s experience. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; Feb. 132(2):134–8.40. Platek ME, Merzianu M, Mashtare TL, Popat SR, Rigual NR, Warren GW, et al. Improved survival following surgery and radiation therapy for olfactory neuroblastoma: analysis of the SEER database. Radiat Oncol. 2011; Apr. 6:41.
Article41. Ow TJ, Hanna EY, Roberts DB, Levine NB, El-Naggar AK, Rosenthal DI, et al. Optimization of long-term outcomes for patients with esthesioneuroblastoma. Head Neck. 2014; Apr. 36(4):524–30.
Article42. Patil VM, Joshi A, Noronha V, Sharma V, Zanwar S, Dhumal S, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced and borderline resectable nonsquamous sinonasal tumors (esthesioneuroblastoma and sinonasal tumor with neuroendocrine differentiation). Int J Surg Oncol. 2016; 2016:6923730.
Article43. Kim DW, Jo YH, Kim JH, Wu HG, Rhee CS, Lee CH, et al. Neoadjuvant etoposide, ifosfamide, and cisplatin for the treatment of olfactory neuroblastoma. Cancer. 2004; Nov. 101(10):2257–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Metastasis from Olfactory Neuroblastoma: A Report of 2 Cases
- A Case of Primary Olfactory Neuroblastoma of the Sphenoid Sinus
- Endoscopic Versus Traditional Craniofacial Resection for Patients with Sinonasal Tumors Involving the Anterior Skull Base
- Case report of olfactory neuroblastoma
- The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion with olfactory neuroblastoma: A case report