J Pathol Transl Med.
2024 May;58(3):127-133. 10.4132/jptm.2024.03.11.
The spectrum of microvascular patterns in adult diffuse glioma and their correlation with tumor grade
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Pathology and Lab Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhopal, India
- 2Departments of Neurosurgery, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhopal, India
- KMID: 2555538
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.11
Abstract
- Background
Primary brain tumors constitute the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Among them, adult diffuse gliomas are the most common type, affecting the cerebral hemispheres and displaying a diffuse infiltrative pattern of growth in the surrounding neuropil that accounts for about 80% of all primary intracranial tumors. The hallmark feature of gliomas is blood vessel proliferation, which plays an important role in tumor growth, tumor biological behavior, and disease outcome. High-grade gliomas exhibit increased vascularity, the worst prognosis, and lower survival rates. Several angiogenic receptors and factors are upregulated in glioblastomas and stimulate angiogenesis signaling pathways by means of activating oncogenes and/or down-regulating tumor-suppressor genes. Existing literature has emphasized that different microvascular patterns (MVPs) are displayed in different subtypes of adult diffuse gliomas.
Methods
We examined the distribution and biological characteristics of different MVPs in 50 patients with adult diffuse gliomas. Haematoxylin and eosin staining results, along with periodic acid–Schiff and CD34 dual-stained sections, were examined to assess the vascular patterns and correlate with different grades of diffuse glioma.
Results
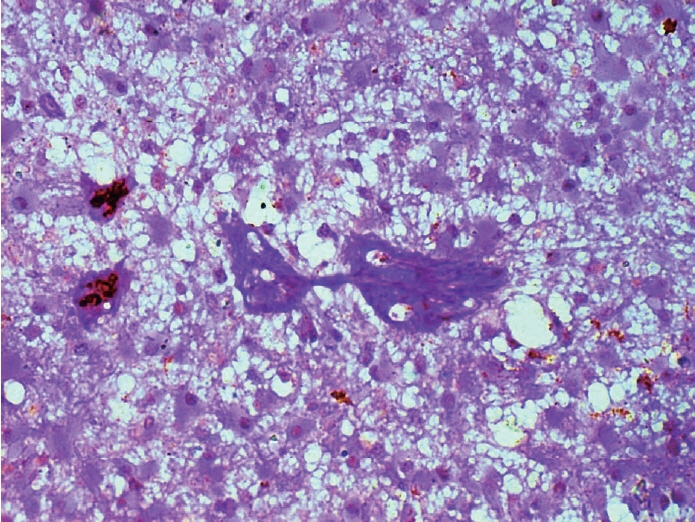
The present observational study on adult diffuse glioma evaluated tumor grade and MVPs. Microvascular sprouting was the most common pattern, while a bizarre pattern (type 2) was associated with the presence of a high-grade glioma. Vascular mimicry was observed in 6% of cases, all of which were grade 4 gliomas.
Conclusions
This study supplements the role of neo-angiogenesis and aberrant vasculature patterns in the grading and progression of adult diffuse gliomas, which can be future targets for planning treatment strategies.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jiang H, Zhang Z, Ren X, Zeng W, Wang J, Lin S. Tumor cell-specific chromosomal abnormality in the vascular endothelial cells of anaplastic oligodendroglioma. J Neurosurg. 2016; 125:995–1001.
Article2. Ostrom QT, Patil N, Cioffi G, Waite K, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2013-2017. Neuro Oncol. 2020; 22:iv1–96.
Article3. Onizuka H, Masui K, Komori T. Diffuse gliomas to date and beyond 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Int J Clin Oncol. 2020; 25:997–1003.
Article4. Gupta A, Dwivedi T. A simplified overview of World Health Organization classification update of central nervous system tumors 2016. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2017; 8:629–41.
Article5. Kong X, Guan J, Ma W, et al. CD34 Over-expression is associated with gliomas’ higher WHO grade. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e2830.
Article6. Meng FW, Liu FS, Liu WH, Li L, Jie LL. Formation of new lymphatic vessels in glioma: an immunohistochemical analysis. Neuropathology. 2020; 40:215–23.
Article7. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumors, central nervous system tumors. 5th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2021. p. 7–14.8. Hardee ME, Zagzag D. Mechanisms of glioma-associated neovascularization. Am J Pathol. 2012; 181:1126–41.
Article9. Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, et al. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992; 84:1875–87.
Article10. Huettner C, Czub S, Kerkau S, Roggendorf W, Tonn JC. Interleukin 10 is expressed in human gliomas in vivo and increases glioma cell proliferation and motility in vitro. Anticancer Res. 1997; 17:3217–24.11. Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, et al. Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science. 1999; 284:1994–8.
Article12. Wang FY, Li XJ. Angiogenesis in glioma. Glioma. 2018; 1:43–9.
Article13. Fox SB, Harris AL. Histological quantitation of tumour angiogenesis. APMIS. 2004; 112:413–30.
Article14. Loureiro LV, Neder L, Callegaro-Filho D, de Oliveira Koch L, Stavale JN, Malheiros SM. The immunohistochemical landscape of VEGF family and its receptors in glioblastomas. Surg Exp Pathol. 2020; 3:9.15. Yue WY, Chen ZP. Does vasculogenic mimicry exist in astrocytoma? J Histochem Cytochem. 2005; 53:997–1002.
Article16. Jha K, Pant I, Singh R, Bansal AK, Chaturvedi S. Assessment of microvascular patterns and density in glioblastoma and their correlation with matrix metalloproteinase-9, p53, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and Ki-67. Glioma. 2018; 1:201–7.
Article17. Chen L, Lin ZX, Lin GS, et al. Classification of microvascular patterns via cluster analysis reveals their prognostic significance in glioblastoma. Hum Pathol. 2015; 46:120–8.
Article18. Seyedmirzaei H, Shobeiri P, Turgut M, Hanaei S, Rezaei N. VEGF levels in patients with glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Neurosci. 2021; 32:191–202.
Article19. Schneider T, Mawrin C, Scherlach C, Skalej M, Firsching R. Gliomas in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010; 107:799–807.
Article20. Sharma S, Sharma MC, Sarkar C. Morphology of angiogenesis in human cancer: a conceptual overview, histoprognostic perspective and significance of neoangiogenesis. Histopathology. 2005; 46:481–9.
Article21. Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P, Folkman J. Clinical application of antiangiogenic therapy: microvessel density, what it does and doesn’t tell us. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94:883–93.
Article22. Bar EE. Glioblastoma, cancer stem cells and hypoxia. Brain Pathol. 2011; 21:119–29.
Article23. Mahzouni P, Mohammadizadeh F, Mougouei K, Moghaddam NA, Chehrei A, Mesbah A. Determining the relationship between “microvessel density” and different grades of astrocytoma based on immunohistochemistry for “factor VIII-related antigen” (von Willebrand factor) expression in tumor microvessels. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2010; 53:605–10.
Article24. Gunsilius E, Duba HC, Petzer AL, et al. Evidence from a leukaemia model for maintenance of vascular endothelium by bone-marrow-derived endothelial cells. Lancet. 2000; 355:1688–91.
Article25. Rojiani AM, Dorovini-Zis K. Glomeruloid vascular structures in glioblastoma multiforme: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Neurosurg. 1996; 85:1078–84.
Article26. Preusser M, Heinzl H, Gelpi E, et al. Histopathologic assessment of hot-spot microvessel density and vascular patterns in glioblastoma: Poor observer agreement limits clinical utility as prognostic factors: a translational research project of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group. Cancer. 2006; 107:162–70.
Article27. Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, et al. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 1999; 155:739–52.
Article28. Liu XM, Zhang QP, Mu YG, et al. Clinical significance of vasculogenic mimicry in human gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2011; 105:173–9.
Article29. Wang SY, Ke YQ, Lu GH, et al. Vasculogenic mimicry is a prognostic factor for postoperative survival in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2013; 112:339–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hemorrhagic Recurrence in Diffuse Astrocytoma without Malignant Transformation
- Intracranial Undifferentiated Sarcoma Arising from a Low-Grade Glioma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Chordoid Glioma: an Uncommon Tumor of the Third Ventricle
- Molecular Culprits Generating Brain Tumor Stem Cells
- Combined Treatment With Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy for Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Mutant Brainstem Glioma in Adult: A Case Report