J Rhinol.
2024 Mar;31(1):8-16. 10.18787/jr.2024.00007.
Does Desmopressin Reduce Intraoperative Bleeding in Patients Who Undergo Nasal Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Bucheon Saint Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul Saint Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2554085
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2024.00007
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
This study aimed to determine the efficacy of prophylactic desmopressin administered via the intranasal or intravenous route in reducing intraoperative bleeding during nasal surgery. We conducted a meta-analysis of the relevant literature to investigate the role of preoperative desmopressin in minimizing bleeding complications associated with nasal surgery.
Methods
We screened the relevant literature published before February 2023. Nine articles that compared the perioperative use of desmopressin (treatment) with a placebo or no treatment (control) were included. The analyzed outcomes were intraoperative bleeding during nasal surgery and postoperative morbidity.
Results
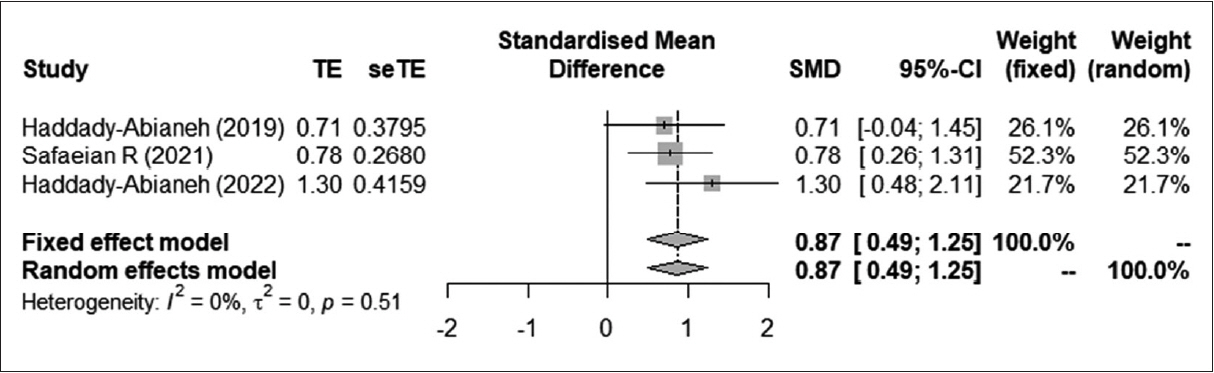
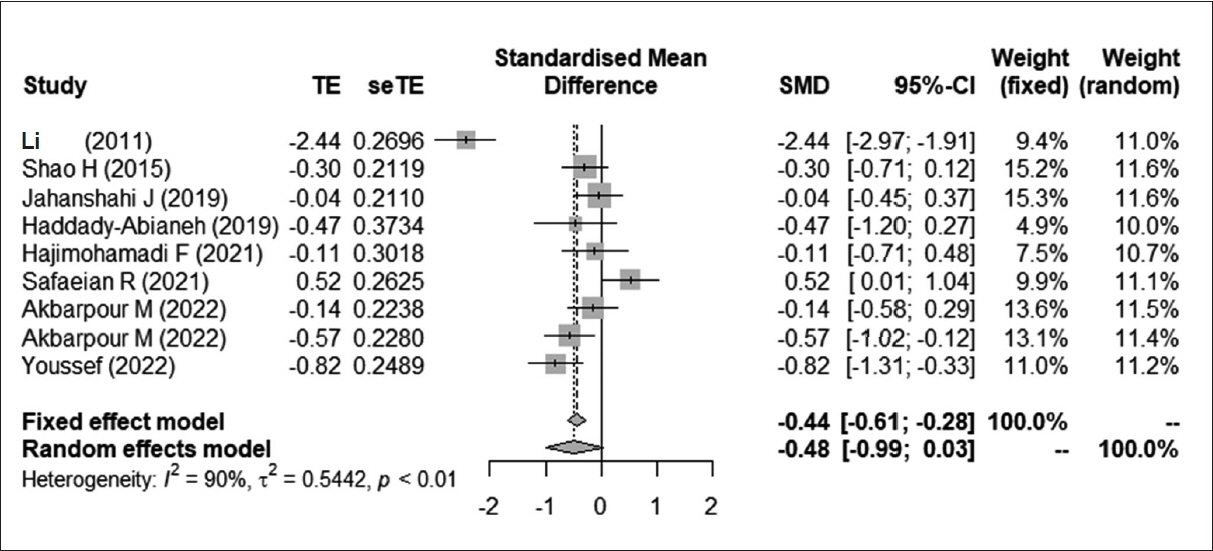
The treatment group showed significant improvements in intraoperative bleeding, the surgical field, and surgeon satisfaction compared to the control group. However, the prophylactic use of desmopressin was associated with elevated blood pressure and decreased serum sodium levels compared to the control group. Nonetheless, no significant adverse effects were reported in the included studies. Subgroup analyses comparing the route of administration (intravenous vs. intranasal) and type of surgery (rhinoplasty vs. endoscopic sinus surgery) showed that desmopressin had a beneficial effect on intraoperative bleeding and the surgical field, regardless of the route of administration or type of surgery.
Conclusion
The prophylactic use of desmopressin for nasal surgery effectively reduced intraoperative bleeding, improved the surgical field, and increased surgeon satisfaction, with no significant adverse effects. However, caution should be exercised when administering desmopressin as it may cause an elevation in postoperative blood pressure in patients with cardiopulmonary problems.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kelly EA, Gollapudy S, Riess ML, Woehlck HJ, Loehrl TA, Poetker DM. Quality of surgical field during endoscopic sinus surgery: a systematic literature review of the effect of total intravenous compared to inhalational anesthesia. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3(6):474–81.
Article2. Nowak S, Ołdak A, Kluzik A, Drobnik L. Impact of controlled induced hypotension on cognitive functions of patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22:898–907.
Article3. Choudhary P, Dutta A, Sethi N, Sood J, Rai D, Gupta M. Pre-induction fentanyl dose-finding study for controlled hypotension during functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Indian J Anaesth. 2019; 63(8):653–9.
Article4. Desborough MJ, Oakland K, Brierley C, Bennett S, Doree C, Trivella M, et al. Desmopressin use for minimising perioperative blood transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 7(7):CD001884.
Article5. Loomans JI, Kruip MJHA, Carcao M, Jackson S, van Velzen AS, Peters M, et al. Desmopressin in moderate hemophilia A patients: a treatment worth considering. Haematologica. 2018; 103(3):550–7.
Article6. Kim DH, Kim SW, Basurrah MA, Hwang SH. Clinical and laboratory features of various criteria of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022; 15(3):230–46.
Article7. Shao H, Kuang LT, Hou WJ, Zhang T. Effect of desmopressin administration on intraoperative blood loss and quality of the surgical field during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized, clinical trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015; 15:53.
Article8. Jahanshahi J, Tayebi E, Hashemian F, Bakhshaei MH, Ahmadi MS, Seif Rabiei MA. Effect of local desmopressin administration on intraoperative blood loss and quality of the surgical field during functional endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a triple-blinded clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 276(7):1995–9.
Article9. Haddady-Abianeh S, Rajabpour AA, Sanatkarfar M, Farahvash MR, Khorasani G, Molaei H. The hemostatic effect of desmopressin on bleeding as a nasal spray in open septorhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019; 43(6):1603–6.
Article10. Youssefy A, Ghabasiah A, Heidari F, Alvandi S, Bastaninezhad S, Hosseini J, et al. The effect of desmopressin intraoperatively on hemorrhage during the rhinoplasty surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022; 74(Suppl 3):4761–5.
Article11. Haddady-Abianeh S, Rahmati J, Delavari C, Molaei H. Comparison of the effect of injectable tranexamic acid and inhaled desmopressin in controlling bleeding and ecchymosis in open rhinoplasty. World J Plast Surg. 2022; 11(3):24–7.
Article12. Alrajhi AA, Alghamdi AS, Baali MH, Altowairqi AF, Khan MF, Alharthi AS, et al. Efficacy of prophylactic pre-operative desmopressin administration during functional endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Clin Otolaryngol. 2023; 48(2):139–50.
Article13. Hajimohamadi F, Hosseini J, Heidari F, Alvandi S, Bastaninezhad S, Ghabasiah A, et al. Desmopressin effects on bleeding during functional endoscopic sinus surgery on patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021; 42(5):103024.
Article14. Safaeian R, Hassani V, Ghandi A, Mohseni M. Desmopressin nasal spray reduces blood loss and improves the quality of the surgical field during functional endoscopic sinus surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2021; 37(2):261–5.
Article15. Akbarpour M, Jalali MM, Akbari M, Haddadi S, Fani G. Effect of desmopressin on bleeding during endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022; 7(4):920–7.
Article16. Li J, Li G, Chen L, Li P, Zhang Y. The effect of desmopressin acetate on FESS. Modern Prev Med. 2011; 38(15):3114–7.17. Ghadimi K, Levy JH, Welsby IJ. Perioperative management of the bleeding patient. Br J Anaesth. 2016; 117(suppl 3):iii18–30.
Article18. Kalot MA, Husainat N, El Alayli A, Abughanimeh O, Diab O, Tayiem S, et al. von Willebrand factor levels in the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2022; 6(1):62–71.
Article19. Franchini M. The use of desmopressin as a hemostatic agent: a concise review. Am J Hematol. 2007; 82(8):731–5.
Article20. Barinsky GL, Buziashvili D, Svider PF, Carron MA, Folbe AJ, Hsueh WD, et al. Perioperative desmopressin for patients undergoing otolaryngologic procedures: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019; 161(1):36–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy of Hypotensive Agents on Intraoperative Bleeding and Recovery Following General Anesthesia for Nasal Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Critical Appraisal of Systematic Review/Meta-analysis
- Introduction to systematic review and meta-analysis
- Meta-epidemiology