Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2021 May;14(2):200-209. 10.21053/ceo.2020.00584.
The Efficacy of Hypotensive Agents on Intraoperative Bleeding and Recovery Following General Anesthesia for Nasal Surgery: A Network Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2515433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2020.00584
Abstract
Objectives
. A systematic review of the literature was conducted to evaluate hypotensive agents in terms of their adverse effects and associations with perioperative morbidity in patients undergoing nasal surgery.
Methods
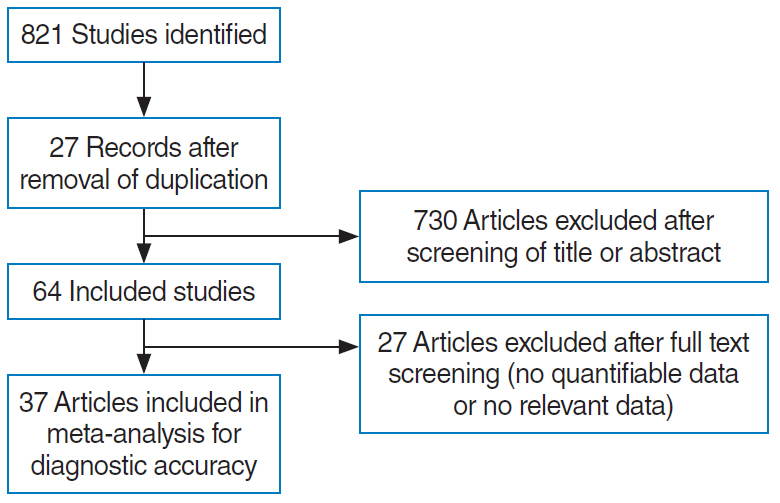
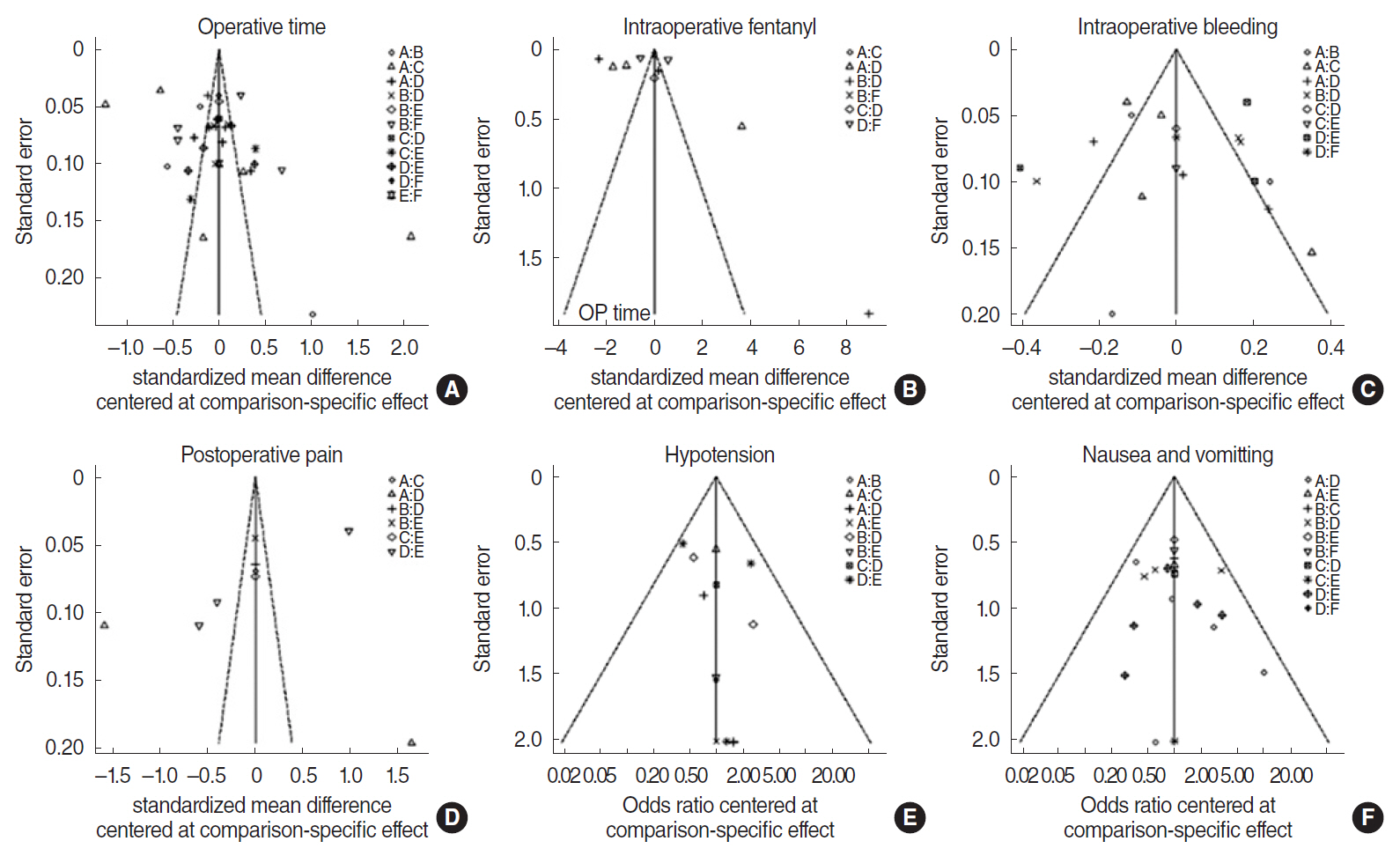
. Two authors independently searched databases (Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane databases) up to February 2020 for randomized controlled trials comparing the perioperative administration of a hypotensive agent with a placebo or other agent. The outcomes of interest for this analysis were intraoperative morbidity, operative time, intraoperative bleeding, hypotension, postoperative nausea/vomiting, and postoperative pain. Both a standard pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis were conducted.
Results
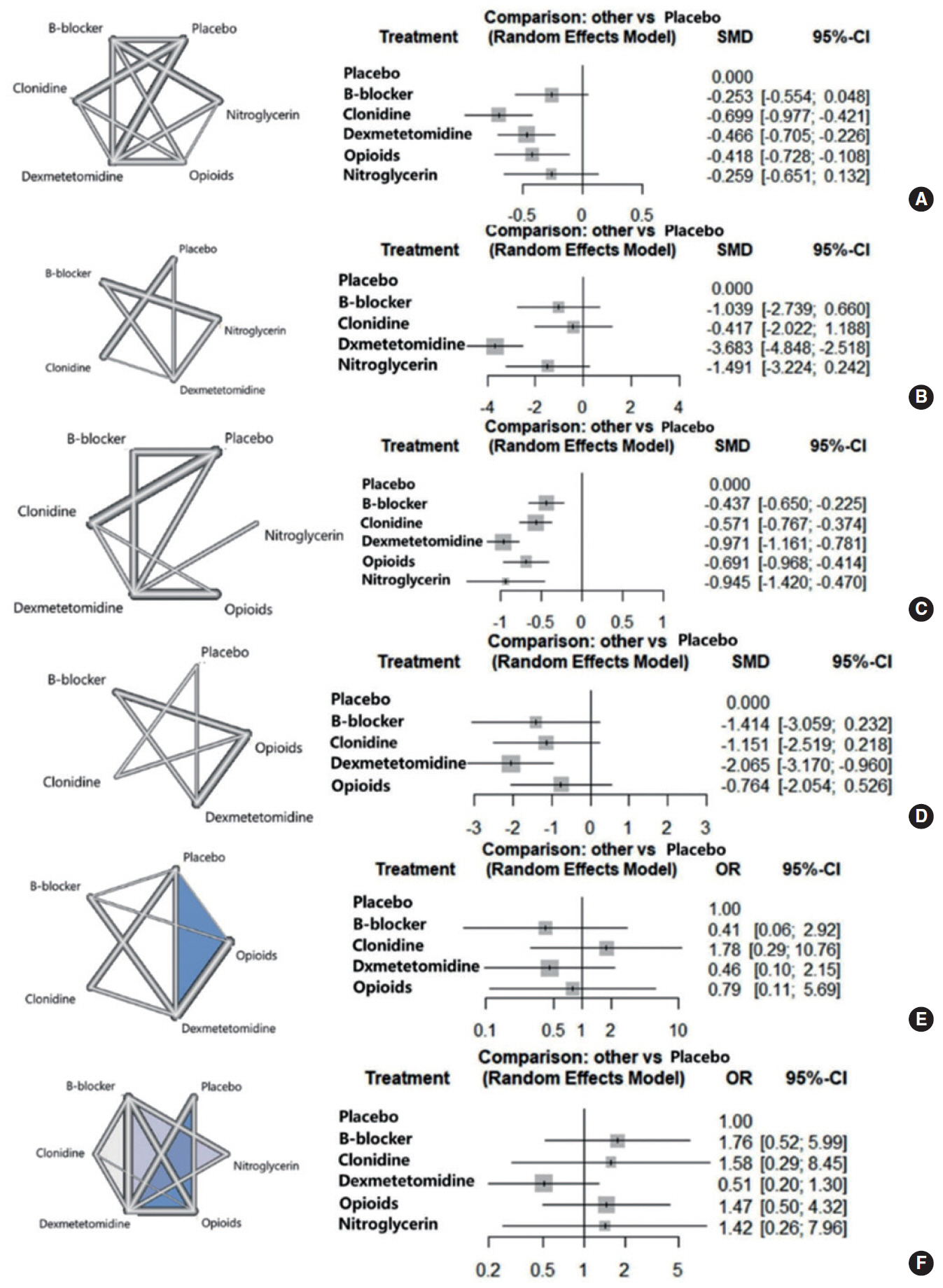
. Our analysis was based on 37 trials. Treatment networks consisting of six interventions (placebo, clonidine, dexmedetomidine, beta-blockers, opioids, and nitroglycerine) were defined for the network meta-analysis. Dexmedetomidine resulted in the greatest differences in intraoperative bleeding (−0.971; 95% confidence interval [CI], −1.161 to −0.781), intraoperative fentanyl administration (−3.683; 95% CI, −4.848 to −2.518), and postoperative pain (−2.065; 95% CI, −3.170 to −0.960) compared with placebo. The greatest difference in operative time compared with placebo was achieved with clonidine (−0.699; 95% CI, −0.977 to −0.421). All other agents also had beneficial effects on the measured outcomes. Dexmedetomidine was less likely than other agents to cause adverse effects.
Conclusion
. This study demonstrated the superiority of the systemic use of dexmedetomidine as a perioperative hypotensive agent compared with the other five tested agents. However, the other agents were also superior to placebo in improving operative time, intraoperative bleeding, and postoperative pain.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Choice of Anesthetic Agents for Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Can Sinus Surgeons Be Involved?
Yong Gi Jung
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(2):147-148. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2021.00395.
Reference
-
1. Shams T, El Bahnasawe NS, Abu-Samra M, El-Masry R. Induced hypotension for functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a comparative study of dexmedetomidine versus esmolol. Saudi J Anaesth. 2013; Apr. 7(2):175–80.
Article2. Lee K, Yoo BH, Yon JH, Kim KM, Kim MC, Lee WY, et al. General anesthesia versus monitored anesthetic care with dexmedetomidine for closed reduction of nasal bone fracture. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013; Sep. 65(3):209–14.
Article3. Kim H, Ha SH, Kim CH, Lee SH, Choi SH. Efficacy of intraoperative dexmedetomidine infusion on visualization of the surgical field in endoscopic sinus surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015; Oct. 68(5):449–54.
Article4. Bunker JP. Anesthetic effects on surgical blood loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964; Jul. 115:418–21.
Article5. Akata T. General anesthetics and vascular smooth muscle: direct actions of general anesthetics on cellular mechanisms regulating vascular tone. Anesthesiology. 2007; Feb. 106(2):365–91.6. Ayoglu H, Yapakci O, Ugur MB, Uzun L, Altunkaya H, Ozer Y, et al. Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine in reducing bleeding during septoplasty and tympanoplasty operations. J Clin Anesth. 2008; Sep. 20(6):437–41.
Article7. Gupta P, Choudhary R, Ojha D, Jethava D. Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant for hypotensive anaesthesia during functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS). IOSR Dental Med Sci. 2016; Aug. 15(8):143–6.
Article8. Rouse B, Chaimani A, Li T. Network meta-analysis: an introduction for clinicians. Intern Emerg Med. 2017; Feb. 12(1):103–11.
Article9. Cardesin A, Pontes C, Rosell R, Escamilla Y, Marco J, Escobar MJ, et al. A randomised double blind clinical trial to compare surgical field bleeding during endoscopic sinus surgery with clonidine-based or remifentanil-based hypotensive anaesthesia. Rhinology. 2015; Jun. 53(2):107–15.
Article10. Bairy L, Vanderstichelen M, Jamart J, Collard E. Clonidine or remifentanil for adequate surgical conditions in patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized study. PeerJ. 2017; May. 5:e3370.
Article11. Erdivanli B, Erdivanli OC, Sen A, Ozdemir A, Tugcugil E, Dursun E. Comparison of metoprolol and tramadol with remifentanil in endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018; Dec. 46(6):424–33.
Article12. Jangra K, Malhotra SK, Gupta A, Arora S. Comparison of quality of the surgical field after controlled hypotension using esmolol and magnesium sulfate during endoscopic sinus surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016; Jul-Sep. 32(3):325–8.
Article13. Das A, Chhaule S, Bhattacharya S, Basunia SR, Mitra T, Halder PS, et al. Controlled hypotension in day care functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a comparison between esmolol and dexmedetomidine: a prospective, double-blind, and randomized study. Saudi J Anaesth. 2016; Jul-Sep. 10(3):276–82.
Article14. Tugrul S, Dogan R, Senturk E, Kocak I, Sezen S, Bakan M, et al. Effect of the premedication with oral clonidine on surgical comfort in patients undergoing fess due to advanced nasal polyposis: a randomized double blind clinical trial. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016; Nov-Dec. 37(6):538–43.
Article15. Jabalameli M, Hashemi M, Soltani H, Hashemi J. Oral clonidine premedication decreases intraoperative bleeding in patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery. J Res Med Sci. 2005; Jan. 1:25–30.16. Wawrzyniak K, Kusza K, Cywinski JB, Burduk PK, Kazmierczak W. Premedication with clonidine before TIVA optimizes surgical field visualization and shortens duration of endoscopic sinus surgery: results of a clinical trial. Rhinology. 2013; Sep. 51(3):259–64.17. Mohseni M, Ebneshahidi A. The effect of oral clonidine premedication on blood loss and the quality of the surgical field during endoscopic sinus surgery: a placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Anesth. 2011; Aug. 25(4):614–7.
Article18. Alkan A, Honca M, Alkan A, Gulec H, Horasanli E. The efficacy of esmolol, remifentanil and nitroglycerin in controlled hypotension for functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; Oct. S1808-8694(18):30493–2.
Article19. Bajwa SJ, Kaur J, Kulshrestha A, Haldar R, Sethi R, Singh A. Nitroglycerine, esmolol and dexmedetomidine for induced hypotension during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a comparative evaluation. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016; Apr-Jun. 32(2):192–7.
Article20. El-Shmaa NS, Ezz HA, Younes A. The efficacy of Labetalol versus nitroglycerin for induction of controlled hypotension during sinus endoscopic surgery: a prospective, double-blind and randomized study. J Clin Anesth. 2017; Jun. 39:154–8.
Article21. Srivastava U, Dupargude AB, Kumar D, Joshi K, Gupta A. Controlled hypotension for functional endoscopic sinus surgery: comparison of esmolol and nitroglycerine. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; Aug. 65(Suppl 2):440–4.
Article22. Sajedi P, Rahimian A, Khalili G. Comparative evaluation between two methods of induced hypotension with infusion of remifentanil and labetalol during sinus endoscopy. J Res Pharm Pract. 2016; Oct-Dec. 5(4):264–71.
Article23. Cardesin A, Pontes C, Rosell R, Escamilla Y, Marco J, Escobar MJ, et al. Hypotensive anaesthesia and bleeding during endoscopic sinus surgery: an observational study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; Jun. 271(6):1505–11.
Article24. Wawrzyniak K, Burduk PK, Cywinski JB, Kusza K, Kazmierczak W. Improved quality of surgical field during endoscopic sinus surgery after clonidine premedication--a pilot study. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014; Jul. 4(7):542–7.
Article25. Nair S, Collins M, Hung P, Rees G, Close D, Wormald PJ. The effect of beta-blocker premedication on the surgical field during endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 2004; Jun. 114(6):1042–6.26. Shen PH, Weitzel EK, Lai JT, Wormald PJ, Ho CS. Intravenous esmolol infusion improves surgical fields during sevoflurane-anesthetized endoscopic sinus surgery: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; Nov-Dec. 25(6):e208–11.
Article27. Bayram A, Ulgey A, Gunes I, Ketenci I, Capar A, Esmaoglu A, et al. Comparison between magnesium sulfate and dexmedetomidine in controlled hypotension during functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2015; Jan-Feb. 65(1):61–7.
Article28. Kavalci G, Ethemoglu FB, Durukan P, Batuman A, Emre C. Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine and remiphentanyl on emergence agitation after sevoflurane anesthesia in adults undergoing septoplasty operation: a randomized double-blind trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013; Nov. 17(22):3019–23.29. Ozcan AA, Ozyurt Y, Saracoglu A, Erkal H, Suslu H, Arslan G, et al. Dexmedetomidine versus remifentanil for controlled hypotensive anesthesia in functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Turk J Anesth Reanim. 2012; Jul. 40(5):257–61.30. Kaur H, Tiwari RL, Bhargava J, Kasliwal N. Effect of dexmedetomidine on consumption of anesthetic agents, duration of surgery, time to extubation and post-operative emergence during endoscopic nasal surgeries: a pilot study. Scholars J Appl Med Sci. 2016; Apr. 4(6E):2180–6.
Article31. Xu K, Pan Y, Zhu M. Effects of dexmedetomidine on the recovery profiles from general anesthesia in patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016; Sep. 9(5):8405–10.32. Gupta K, Gupta PK, Bhatia KS, Rastogi B, Pandey MN, Agarwal S. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine as an anesthetic adjuvant for functional endoscopic sinus surgery under general anesthesia: a randomizedcontrolled study. Ain-Shams J Anaesthesiol. 2016; Sep. 9(2):207–11.
Article33. Kim SY, Kim JM, Lee JH, Song BM, Koo BN. Efficacy of intraoperative dexmedetomidine infusion on emergence agitation and quality of recovery after nasal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2013; Aug. 111(2):222–8.
Article34. Karabayirli S, Ugur KS, Demircioglu RI, Muslu B, Usta B, Sert H, et al. Surgical conditions during FESS; comparison of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; Jan. 274(1):239–45.
Article35. Lee J, Kim Y, Park C, Jeon Y, Kim D, Joo J, et al. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and remifentanil for controlled hypotension and recovery in endoscopic sinus surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013; Jul. 122(7):421–6.
Article36. Jiwanmall M, Joselyn AS, Kandasamy S. Intravenous clonidine as a part of balanced anaesthesia for controlled hypotension in functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomised controled trial. Indian J Anaesth. 2017; May. 61(5):418–23.
Article37. Kumari I, Sharma S, Surendran K, Naithani U, Saxena SS, Yadav R. Effect of dexmedetomidine on bleeding during endoscopic nasal surgery: a double blind, randomized, clinical study. Eur J Pharm Med Res. 2016; Mar. 3(12):290–4.38. Praveen DV, Pushparani A, Anand K, Sundaraperumal B. Comparison of dexmedetomidine with nitroglycerinefor hypotensive anaesthesia in. Indian J Clin Anesth. 2016; May. 3(3):376–88.39. Polat R, Peker K, Baran I, Bumin Aydın G, Topcu Guloksuz C, Donmez A. Comparison between dexmedetomidine and remifentanil infusion in emergence agitation during recovery after nasal surgery: A randomized double-blind trial. Anaesthesist. 2015; Oct. 64(10):740–6.40. Aksu R, Akin A, Bicer C, Esmaoglu A, Tosun Z, Boyaci A. Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine versus fentanyl on airway reflexes and hemodynamic responses to tracheal extubation during rhinoplasty: A double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2009; Jun. 70(3):209–20.
Article41. Rahimzadeh P, Faiz SH, Alebouyeh MR. Effects of premedication with metoprolol on bleeding and induced hypotension in nasal surgery. Anesth Pain Med. 2012; Winter. 1(3):157–61.
Article42. Shim S, Yoon BH, Shin IS, Bae JM. Network meta-analysis: application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol Health. 2017; Oct. 39:e2017047.
Article43. Khurshid DH, Muneer DK, Sadiq Malla M. Effect of dexmedetomidine on emergence agitation after nasal surgeries. Med Sci Clin Res. 2015; 3(9):7527–31.
Article44. Salanti G, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011; Feb. 64(2):163–71.
Article45. Higgins JP, Jackson D, Barrett JK, Lu G, Ades AE, White IR. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res Synth Methods. 2012; Jun. 3(2):98–110.
Article46. van Valkenhoef G, Dias S, Ades AE, Welton NJ. Automated generation of node-splitting models for assessment of inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. 2016; Mar. 7(1):80–93.47. Flather MD, Farkouh ME, Pogue JM, Yusuf S. Strengths and limitations of meta-analysis: larger studies may be more reliable. Control Clin Trials. 1997; Dec. 18(6):568–79.
Article48. Lee HS, Yoon HY, Jin HJ, Hwang SH. Can dexmedetomidine influence recovery profiles from general anesthesia in nasal surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018; Jan. 158(1):43–53.
Article49. Quijada-Manuitt MA, Escamilla Y, Vallano A, Cardesin A, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Pontes C. Use of α2-adrenergic agonists to improve surgical field visibility in endoscopy sinus surgery: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Ther. 2018; Jan. 40(1):136–49. e19.50. Snidvongs K, Tingthanathikul W, Aeumjaturapat S, Chusakul S. Dexmedetomidine improves the quality of the operative field for functional endoscopic sinus surgery: systematic review. J Laryngol Otol. 2015; Jul. 129 Suppl 3:S8–13.
Article51. Amorocho MC, Fat I. Anesthetic techniques in endoscopic sinus and skull base surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2016; Jun. 49(3):531–47.
Article52. Baker AR, Baker AB. Anaesthesia for endoscopic sinus surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010; Aug. 54(7):795–803.
Article53. Kanters S, Ford N, Druyts E, Thorlund K, Mills EJ, Bansback N. Use of network meta-analysis in clinical guidelines. Bull World Health Organ. 2016; Oct. 94(10):782–4.
Article54. Bhagat N, Yunus M, Karim HM, Hajong R, Bhattacharyya P, Singh M. Dexmedetomidine in attenuation of haemodynamic response and dose sparing effect on opioid and anaesthetic agents in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016; Nov. 10(11):UC01–5.55. Manne GR, Upadhyay MR, Swadia V. Effects of low dose dexmedetomidine infusion on haemodynamic stress response, sedation and postoperative analgesia requirement in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Indian J Anaesth. 2014; Nov-Dec. 58(6):726–31.
Article56. Khan ZP, Munday IT, Jones RM, Thornton C, Mant TG, Amin D. Effects of dexmedetomidine on isoflurane requirements in healthy volunteers. 1: Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions. Br J Anaesth. 1999; Sep. 83(3):372–80.
Article57. Tang C, Huang X, Kang F, Chai X, Wang S, Yin G, et al. Intranasal dexmedetomidine on stress hormones, inflammatory markers, and postoperative analgesia after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:939431.
Article58. Lee SK. Clinical use of dexmedetomidine in monitored anesthesia care. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2011; Dec. 61(6):451–2.
Article59. Bailar JC 3rd. The promise and problems of meta-analysis. N Engl J Med. 1997; Aug. 337(8):559–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Experiences of Induced Hypotension with Halothane and Trimetaphan combined with Halothane for Cerebral Aneurysm Surgery
- Does Desmopressin Reduce Intraoperative Bleeding in Patients Who Undergo Nasal Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Overview of Network Meta-analysis for a Rheumatologist
- Comparative evaluation of propofol versus dexmedetomidine infusion for hypotensive anesthesia during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a prospective randomized trial
- The hemostasis in intractable posterior nasal bleeding with angiographic embolization: A case report