Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Mar;48(2):312-320. 10.4093/dmj.2022.0421.
Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1International Healthcare Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Esther Formula Medical Food R&D Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Family Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2553601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0421
Abstract
- Background
There is still a lack of research on which diabetic drugs are more effective in preventing stroke. Our network metaanalysis aimed to compare cerebrovascular benefits among glucose-lowering treatments.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and the ClinicalTrials.gov registry for clinical trials from inception through May 25, 2021. We included both prespecified cerebrovascular outcomes and cerebrovascular events reported as severe adverse events. Subgroup analyses were conducted by stroke subtype, publication type, age of patients, baseline glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular risks.
Results
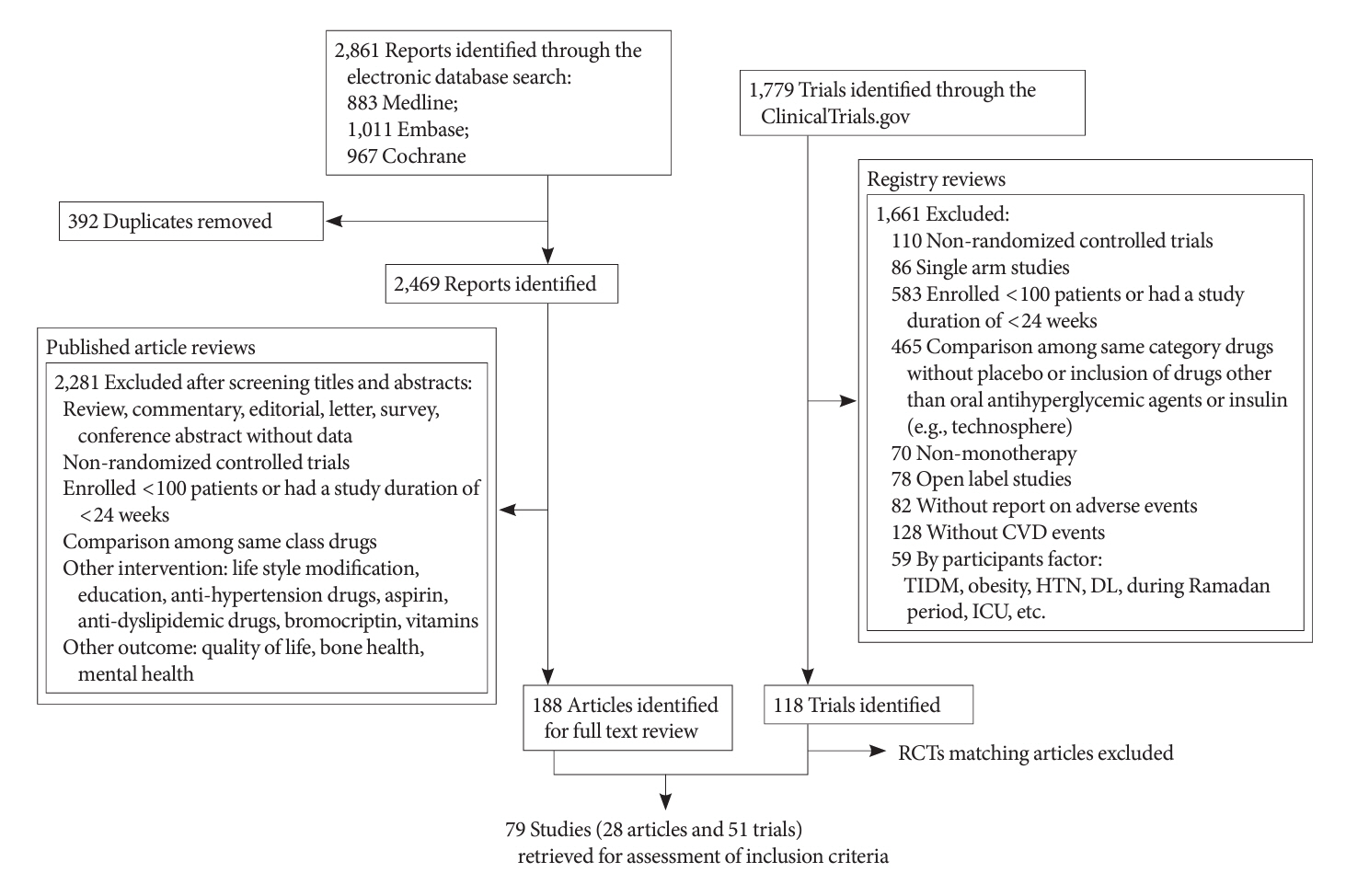
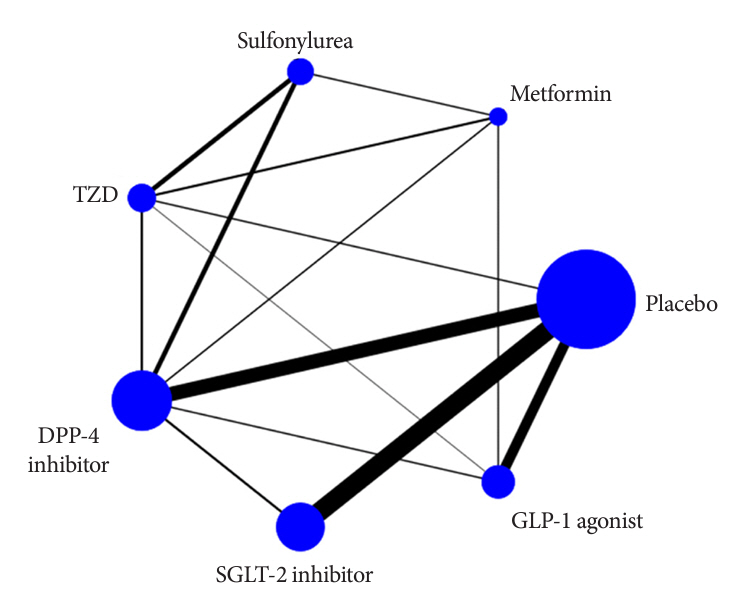
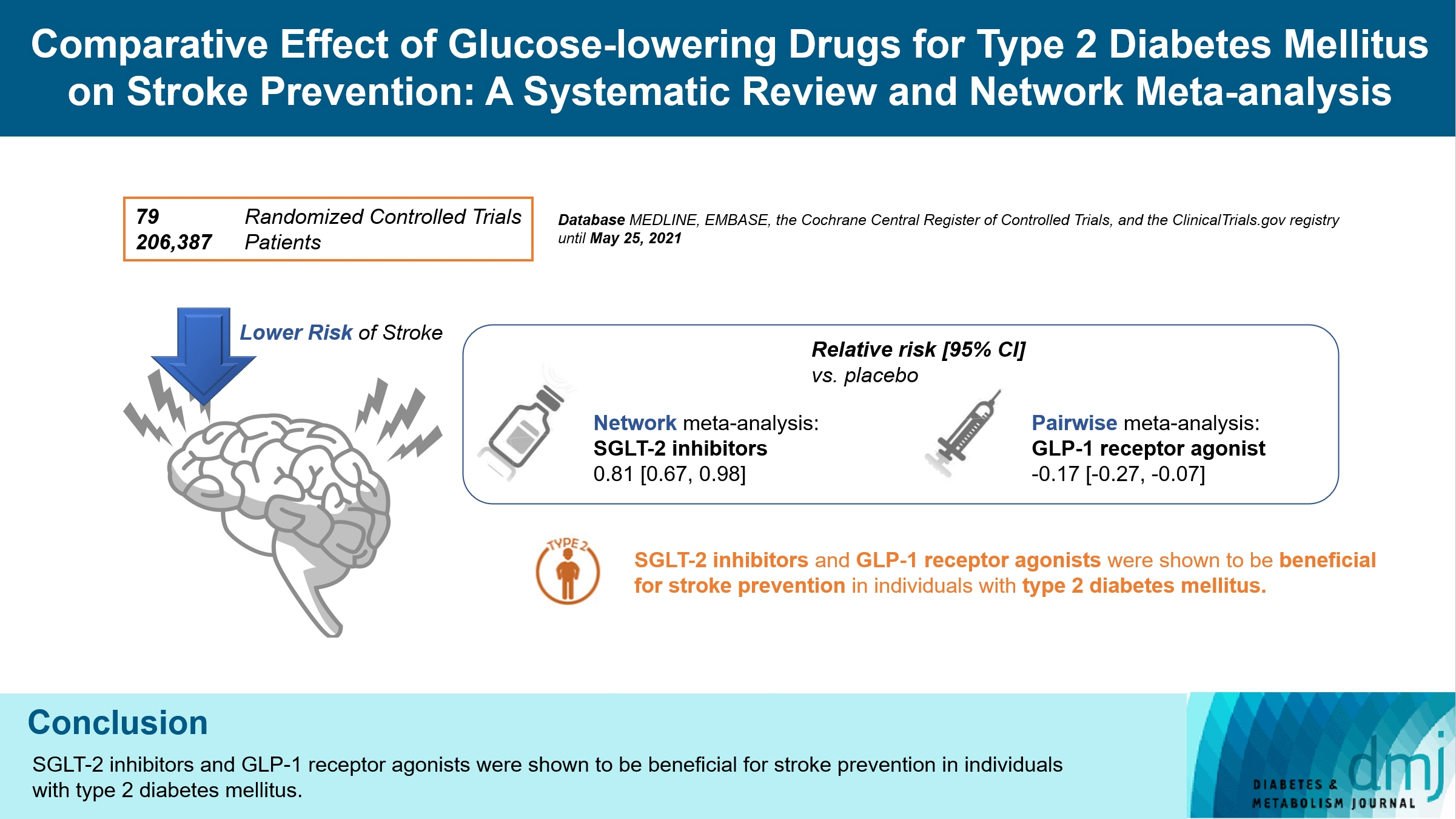
Of 2,861 reports and 1,779 trials screened, 79 randomized controlled trials comprising 206,387 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria. In the pairwise meta-analysis, the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist was associated with a lower risk of total stroke compared with placebo (relative risk [RR], –0.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.27 to –0.07). In the network meta- analysis, only the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor was associated with a reduction of total stroke, compared with placebo (RR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67 to 0.98). In the subgroup analyses, the use of SGLT-2 inhibitor and GLP-1 agonist was associated with a lower risk of stroke in those with high HbA1c (≥8.0) and low-risk of cardiovascular disease, respectively.
Conclusion
SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists were shown to be beneficial for stroke prevention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Agonists: A Beacon of Hope for Stroke Prevention in Diabetes
Jae-Han Jeon
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):213-214. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0079.
Reference
-
1. Shi H, Ge Y, Wang H, Zhang Y, Teng W, Tian L. Fasting blood glucose and risk of stroke: a dose-response meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2021; 40:3296–304.
Article2. Forstermann U, Xia N, Li H. Roles of vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2017; 120:713–35.
Article3. Park SK, Jung JY, Kim MH, Oh CM, Ha E, Shin SS, et al. The association between changes in proteinuria and the risk of cerebral infarction in the Korean population. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022; 192:110090.
Article4. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S125–43.5. Fei Y, Tsoi MF, Cheung BM. Cardiovascular outcomes in trials of new antidiabetic drug classes: a network meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:112.
Article6. Lee G, Oh SW, Hwang SS, Yoon JW, Kang S, Joh HK, et al. Comparative effectiveness of oral antidiabetic drugs in preventing cardiovascular mortality and morbidity: a network meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0177646.
Article7. Bloomgarden Z, Chilton R. Diabetes and stroke: an important complication. J Diabetes. 2021; 13:184–90.
Article8. Ahn CH, Lim S. Effects of thiazolidinedione and new antidiabetic agents on stroke. J Stroke. 2019; 21:139–50.
Article9. Wilcox R, Bousser MG, Betteridge DJ, Schernthaner G, Pirags V, Kupfer S, et al. Effects of pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without previous stroke: results from PROactive (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events 04). Stroke. 2007; 38:865–73.
Article10. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–28.
Article11. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:644–57.
Article12. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–57.
Article13. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1834–44.
Article14. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:311–22.
Article15. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, Dickstein K, Gerstein HC, Kober LV, et al. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2247–57.
Article16. Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1228–39.
Article17. Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D’Agostino RB Sr, Granger CB, Jones NP, et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018; 392:1519–29.18. Cornell JE. The PRISMA extension for network meta-analysis: bringing clarity and guidance to the reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses. Ann Intern Med. 2015; 162:797–8.
Article19. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5928.
Article20. Palmer TM, Sterne JAC. Meta-analysis in Stata: an updated collection from the Stata Journal. College Station: Stata Press;1998. Chapter 1, Metan: a command for meta-analysis in Stata. p. 3–28.21. Sinning C, Makarova N, Volzke H, Schnabel RB, Ojeda F, Dorr M, et al. Association of glycated hemoglobin A1c levels with cardiovascular outcomes in the general population: results from the BiomarCaRE (Biomarker for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe) consortium. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021; 20:223.
Article22. Tsai WH, Chuang SM, Liu SC, Lee CC, Chien MN, Leung CH, et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on stroke and its subtypes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:15364.
Article23. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:129–39.
Article24. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:117–28.
Article25. Cefalo CM, Cinti F, Moffa S, Impronta F, Sorice GP, Mezza T, et al. Sotagliflozin, the first dual SGLT inhibitor: current outlook and perspectives. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:20.
Article26. Bellastella G, Maiorino MI, Longo M, Scappaticcio L, Chiodini P, Esposito K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and prevention of stroke systematic review of cardiovascular outcome trials with meta-analysis. Stroke. 2020; 51:666–9.
Article27. Malhotra K, Katsanos AH, Lambadiari V, Goyal N, Palaiodimou L, Kosmidou M, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetes for stroke prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol. 2020; 267:2117–22.
Article28. Gerstein HC, Hart R, Colhoun HM, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Botros FT, et al. The effect of dulaglutide on stroke: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:106–14.
Article29. Kalra S, Mukherjee JJ, Venkataraman S, Bantwal G, Shaikh S, Saboo B, et al. Hypoglycemia: the neglected complication. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 17:819–34.
Article30. Mijajlovic MD, Aleksic VM, Sternic NM, Mirkovic MM, Bornstein NM. Role of prediabetes in stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017; 13:259–67.
Article31. Ren X, Wang Z, Guo C. Long-term glycemic variability and risk of stroke in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022; 14:6.
Article32. Sun B, Luo Z, Zhou J. Comprehensive elaboration of glycemic variability in diabetic macrovascular and microvascular complications. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021; 20:9.
Article33. Lee H, Park SE, Kim EY. Glycemic variability impacted by SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP 1 agonists in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2021; 10:4078.
Article34. Lee S, Lee H, Kim Y, Kim E. Effect of DPP-IV inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with T2DM: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:13296.
Article35. Kim K, Choi SH, Jang HC, Park YS, Oh TJ. Glucose profiles assessed by intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring system during the perioperative period of metabolic surgery. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:713–21.
Article36. Seino H, Onishi Y, Naito Y, Komatsu M. Lixisenatide improves glycemic outcomes of Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2016; 8:36.
Article37. Ferdinand KC, Izzo JL, Lee J, Meng L, George J, Salsali A, et al. Antihyperglycemic and blood pressure effects of empagliflozin in black patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Circulation. 2019; 139:2098–109.
Article38. Ryder REJ, Abdul-Ghani MA, DeFronzo RA. Diabetes medications with cardiovascular protection: the likelihood of benefit from combination therapy increases further following new evidence during 2020. Br J Diabetes. 2020; 20:84–8.
Article39. Bae JH, Park EG, Kim S, Kim SG, Hahn S, Kim NH. Comparative renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on individual outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021; 36:388–400.
Article40. Barkas F, Elisaf M, Tsimihodimos V, Milionis H. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and protection against stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2017; 43:1–8.
Article41. Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, Altuntas Y, Lalic NM, Morales Villegas EC, et al. PIONEER 1: randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide monotherapy in comparison with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:1724–32.
Article42. Mosenzon O, Blicher TM, Rosenlund S, Eriksson JW, Heller S, Hels OH, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5): a placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:515–27.43. Barkas F, Elisaf M, Milionis H. Protection against stroke with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol. 2019; 26:559–65.
Article44. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J. 2020; 96:156–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Glucose Lowering Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of Clinical Studies
- DPP-4 Inhibitors as a New Option for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
- Extent of Role: Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Carbohydrate counting implementation on pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association