Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Sep;28(3):206-214. 10.6065/apem.2244242.121.
Carbohydrate counting implementation on pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
- KMID: 2546345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2244242.121
Abstract
- Purpose
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, which is the most common type of diabetes among children, is not curable but can be managed well without a negative effect on quality of life. One of the treatments of type 1 diabetes mellitus is carbohydrate counting. This systematic review and meta-analysis sought to evaluate the efficacy of carbohydrate counting with regard to hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) reduction in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
Nine studies were assessed, with the primary outcome being glycemic control (HbA1c changes). We searched the following electronic databases: ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, and ScienceDirect. The quality of studies included was assessed using the risk of bias for randomized control trials and the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for observational and cross-sectional studies. Quantitative analyses were made and extrapolated into a forest plot.
Results
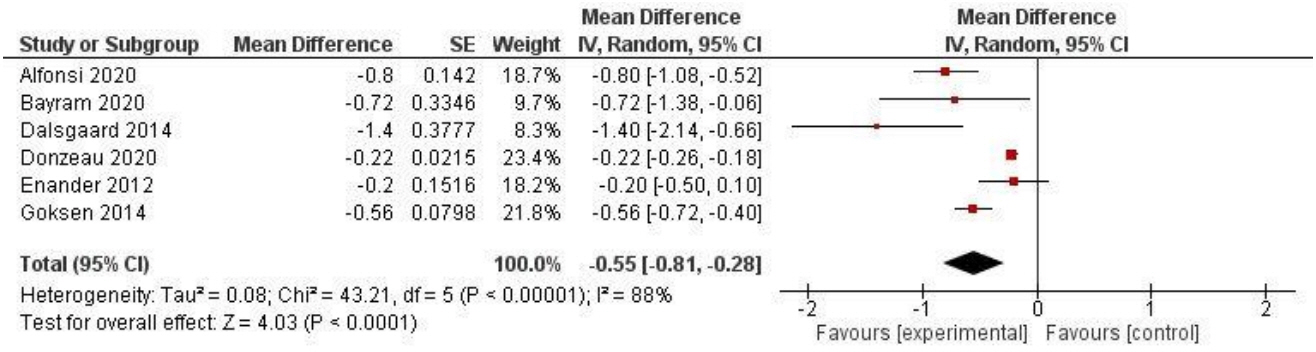
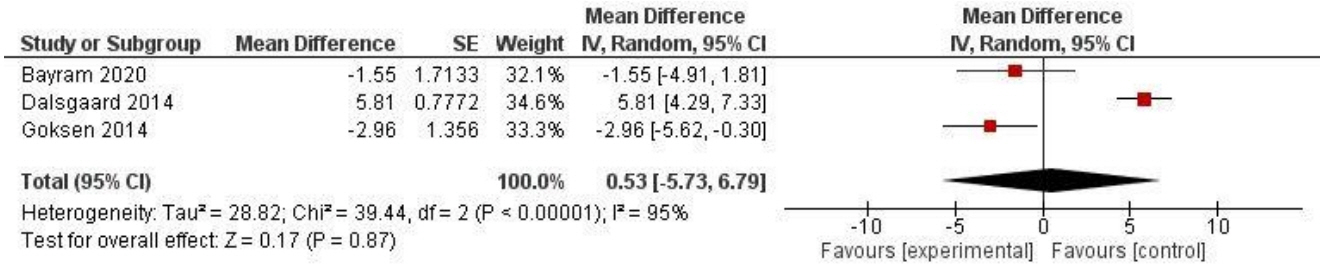
A total of 1,693 articles were identified. Four reviewers independently screened titles and abstracts. Of the 36 articles screened, 34 articles were found to be eligible. Of these, 25 studies were excluded because of unsuitable outcomes and study designs. Nine articles were included in the final analysis. Meta-analysis showed that there was a reduction in HbA1c in the carbohydrate counting group as compared to the control group. The cumulative effect of carbohydrate counting on HbA1c was a mean difference of -0.55 (95% confidence interval, -0.81 to -0.28, P<0.001). All of the studies exhibited similar results with the mean difference reduction favoring the interventional group. However, the heterogeneity analysis revealed an I2 value of 88%, implying high heterogeneity in the meta-analysis.
Conclusion
The meta-analysis showed evidence favoring the use of carbohydrate counting in the management of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM. Diabetes mellitus. In: Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 21st ed. Singapore: Elsevier Inc., 2021:572-9.2. Sperling M, Tamborlane M, Majzoub JA, Menon RK, Stratakis CA. Diabetes mellitus. In: Sperling M, Majzoub JA, Menon RK, Stratakis CA, editors. Sperling pediatric endocrinology. 5th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier-Saunders, 2020:846-9.3. Lupsa B, Inzucchi S. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. In: Loriaux L, editor. Endocrine emergencies: recognition and treatment [Internet]. Totowa: Humana Press; 2014 [cited 2022 Oct 19]. p. 15–30. Available from: https://books.google.com/books/about/Endocrine_Emergencies.html?id=A4a8BAAAQBAJ.4. Pulungan AB, Annisa D, Imada S. Type-1 diabetes mellitus in children: Indonesian situation and management. Sari Pediatri. 2019; 20:392–400.5. Besser REJ, Bell KJ, Couper JJ, Ziegler AG, Wherrett DK, Knip M, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: stages of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022; 23:1175–87.6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2022 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. 2022; 40:10–38.7. Tascini G, Berioli MG, Cerquiglini L, Santi E, Mancini G, Rogari F, et al. Carbohydrate counting in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Nutrients. 2018; 10:109.8. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n71.9. Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd ed. Hoboken: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2019:1-539.10. Critical Appraisal Tools | JBI [Internet]. JBI. 2022 [cited 2022 Oct 19]. Available from: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisaltools.11. Gökşen D, Atik Altınok Y, Ozen S, Demir G, Darcan S. Effects of carbohydrate counting method on metabolic control in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014; 6:74–8.12. Alfonsi JE, Choi EEY, Arshad T, Sammott SS, Pais V, Nguyen C, et al. Carbohydrate counting app using image recognition for youth with type 1 diabetes: pilot randomized control trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020; 8:e22074.13. Dalsgaard H, Saunders C, Padilha Pde C, Luescher JL, Szundy Berardo R, Accioly E. Glycemic control and lipid profile of children and adolescents undergoing two different dietetic treatments for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Hosp. 2014; 29:547–52.14. Bayram S, Kızıltan G, Akın O. Effect of adherence to carbohydrate counting on metabolic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 25:156–62.15. Fortins RF, Lacerda EMA, Silverio RNC, do Carmo CN, Ferreira AA, Felizardo C, et al. Predictor factors of glycemic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus treated at a referral service in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 154:138–45.16. Donzeau A, Bonnemaison E, Vautier V, Menut V, Houdon L, Bendelac N, et al. Effects of advanced carbohydrate counting on glucose control and quality of life in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020; 21:1240–8.17. Enander R, Gundevall C, Strömgren A, Chaplin J, Hanas R. Carbohydrate counting with a bolus calculator improves post-prandial blood glucose levels in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes using insulin pumps. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012; 13:545–51.18. Marigliano M, Morandi A, Maschio M, Sabbion A, Contreas G, Tomasselli F, et al. Nutritional education and carbohydrate counting in children with type 1 diabetes treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: the effects on dietary habits, body composition and glycometabolic control. Acta Diabetol. 2013; 50:959–64.19. Kostopoulou E, Livada I, Partsalaki I, Lamari F, Skiadopoulos S, Rojas Gil AP, et al. The role of carbohydrate counting in glycemic control and oxidative stress in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Hormones (Athens). 2020; 19:433–8.20. Schmidt S, Schelde B, Nørgaard K. Effects of advanced carbohydrate counting in patients with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med. 2014; 31:886–96.21. Fu S, Li L, Deng S, Zan L, Liu Z. Effectiveness of advanced carbohydrate counting in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:37067.22. Kalergis M, Pacaud D, Strychar I, Meltzer S, Jones PJ, Yale JF. Optimizing insulin delivery: assessment of three strategies in intensive diabetes management. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2000; 2:299–305.23. Gilbertson HR, Brand-Miller JC, Thorburn AW, Evans S, Chondros P, Werther GA. The effect of flexible low glycemic index dietary advice versus measured carbohydrate exchange diets on glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:1137–43.24. Meade LT, Rushton WE. Accuracy of carbohydrate counting in adults. Clin Diabetes. 2016; 34:142–7.25. Abacı A, Ataş A, Ünüvar T, Böber E, Büyükgebiz A. The effect of carbohydrate counting on metabolic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gülhane Tıp Dergisi. 2009; 51:1–5.26. Trento M, Trinetta A, Kucich C, Grassi G, Passera P, Gennari S, et al. Carbohydrate counting improves coping ability and metabolic control in patients with type 1 diabetes managed by Group Care. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011; 34:101–5.27. Robart E, Giovannini-Chami L, Savoldelli C, Baechler-Sadoul E, Gastaud F, Tran A, et al. Variation of carbohydrate intake in diabetic children on carbohydrate counting. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 150:227–35.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nutritional Management and Carbohydrate Counting for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hypertension
- Efficacy and Safety of Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2025;49:235-51)
- Medical Nutrition Therapy Using Carbohydrate Counting
- Erratum: Type of Manuscript Correction. Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on Adipocytokines in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials