Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Mar;48(2):279-289. 10.4093/dmj.2023.0225.
Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- 6Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University Hospital, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- 8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- 9Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
- 10Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Sejong General Hospital, Bucheon, Korea
- 11Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 12Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 13Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 14Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2553598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0225
Abstract
- Background
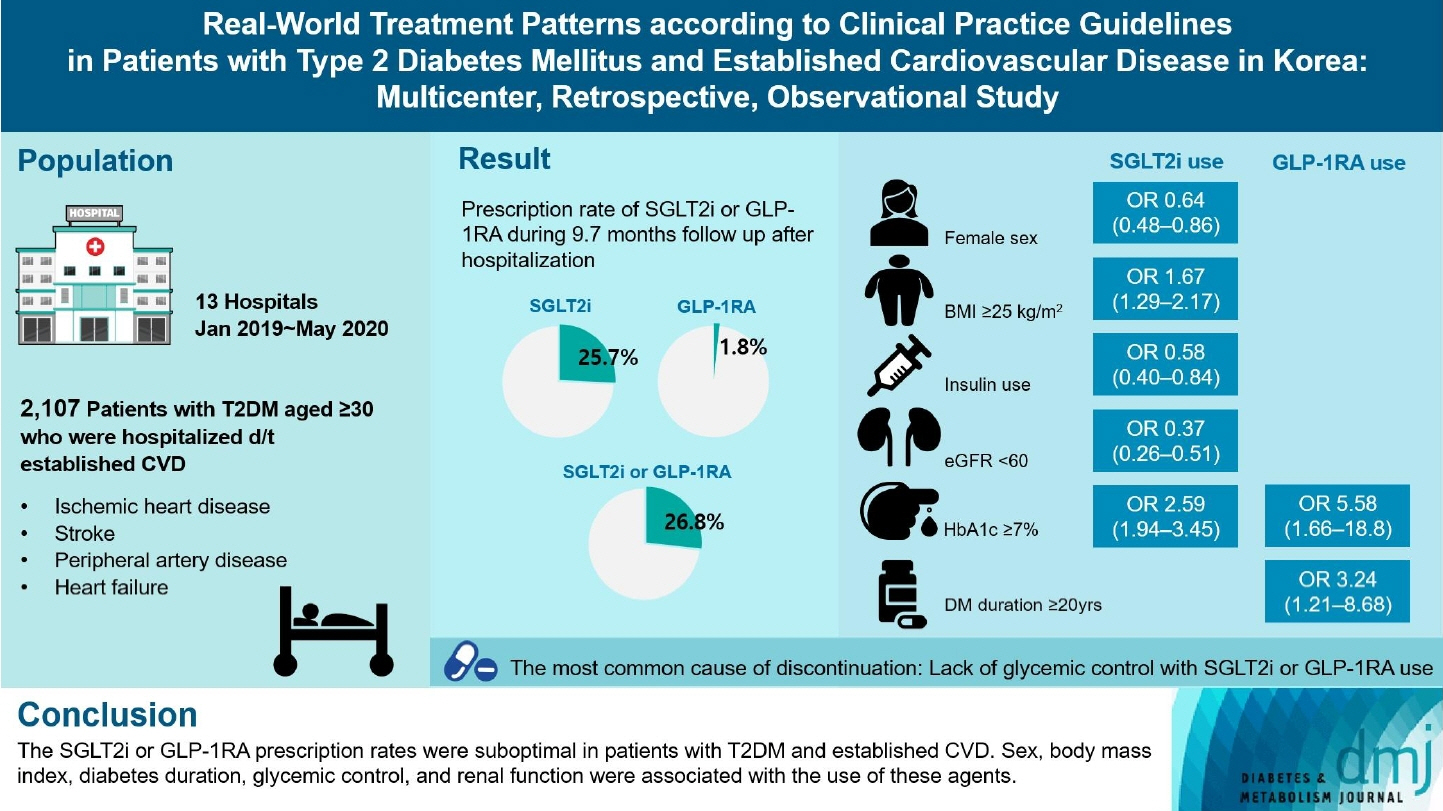
Recent diabetes management guidelines recommend that sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) with proven cardiovascular benefits should be prioritized for combination therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and established cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study was aimed at evaluating SGLT2i or GLP-1RA usage rates and various related factors in patients with T2DM and established CVD.
Methods
We enrolled adults with T2DM aged ≥30 years who were hospitalized due to established CVD from January 2019 to May 2020 at 13 secondary and tertiary hospitals in Korea in this retrospective observational study.
Results
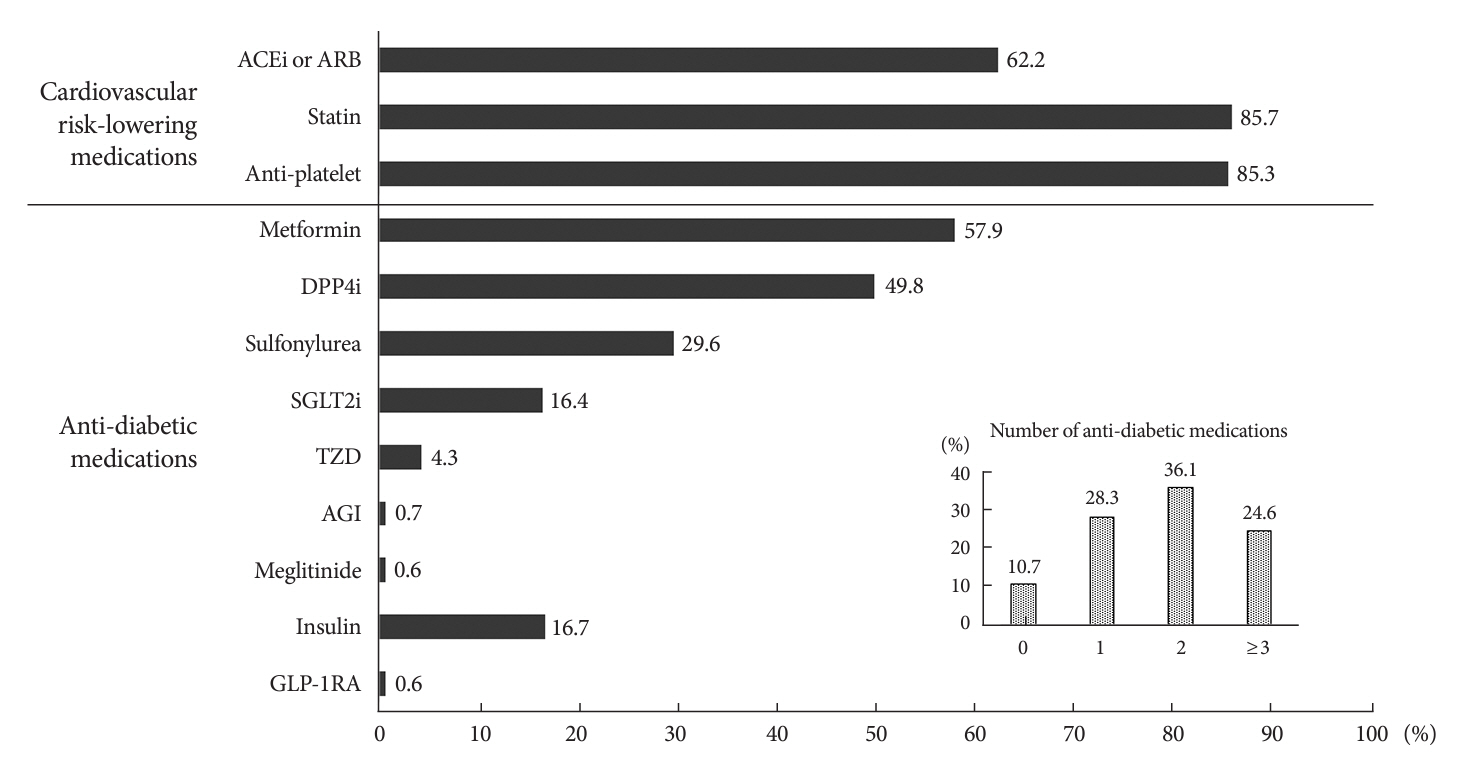
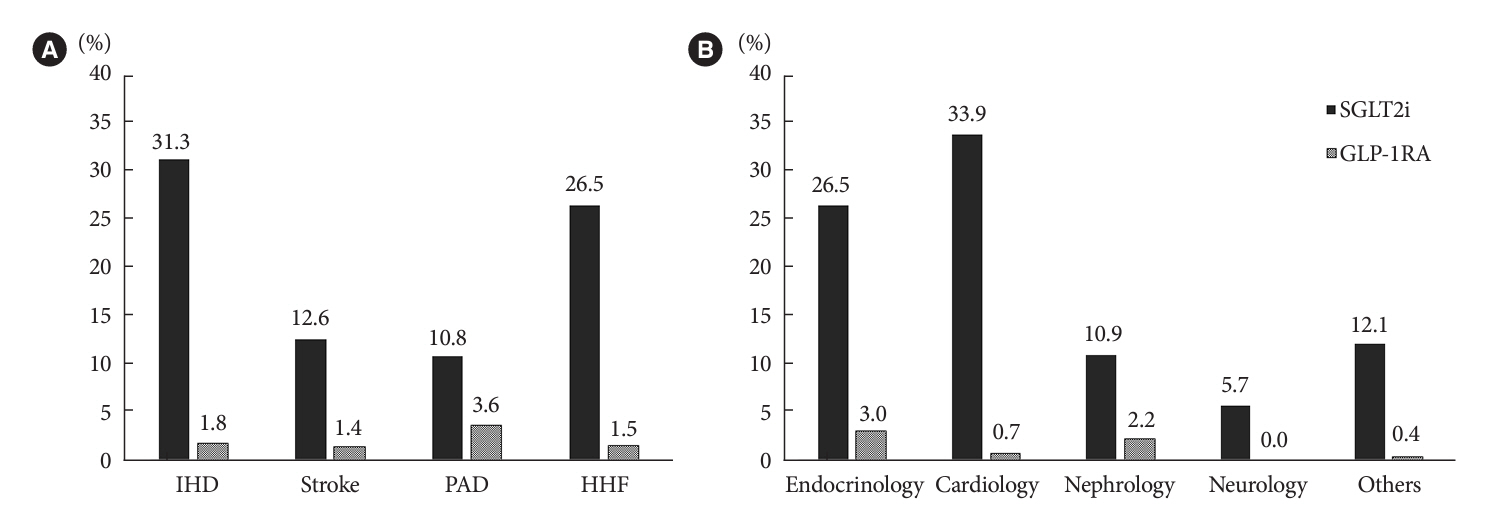
Overall, 2,050 patients were eligible for analysis among 2,107 enrolled patients. The mean patient age, diabetes duration, and glycosylated hemoglobin level were 70.0 years, 12.0 years, and 7.5%, respectively. During the mean follow-up duration of 9.7 months, 25.7% of the patients were prescribed SGLT2is after CVD events. However, only 1.8% were prescribed GLP-1RAs. Compared with SGLT2i non-users, SGLT2i users were more frequently male and obese. Furthermore, they had a shorter diabetes duration but showed worse glycemic control and better renal function at the time of the event. GLP-1RA users had a longer duration of diabetes and worse glycemic control at the time of the event than GLP-1RA non-users.
Conclusion
The SGLT2i or GLP-1RA prescription rates were suboptimal in patients with T2DM and established CVD. Sex, body mass index, diabetes duration, glycemic control, and renal function were associated with the use of these agents.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Enhancing Patient Outcomes: Prioritizing SGLT2is and GLP-1RAs in Diabetes with CVD
Gwanpyo Koh
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):208-212. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0096.
Reference
-
1. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–57.
Article2. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–28.
Article3. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:311–22.
Article4. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019; 394:121–30.5. Heerspink HJ, Stefansson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1436–46.
Article6. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S125–43.7. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:461–81.
Article8. Bae JH, Han KD, Ko SH, Yang YS, Choi JH, Choi KM, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:417–26.
Article9. Wilkinson S, Douglas I, Stirnadel-Farrant H, Fogarty D, Pokrajac A, Smeeth L, et al. Changing use of antidiabetic drugs in the UK: trends in prescribing 2000-2017. BMJ Open. 2018; 8:e022768.
Article10. Engler C, Leo M, Pfeifer B, Juchum M, Chen-Koenig D, Poelzl K, et al. Long-term trends in the prescription of antidiabetic drugs: real-world evidence from the Diabetes Registry Tyrol 2012-2018. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020; 8:e001279.
Article11. Yang A, Wu H, Lau ES, Zhang X, Shi M, Fan B, et al. Glucose-lowering drug use, glycemic outcomes, and severe hypoglycemia: 18-year trends in 0.9 million adults with Diabetes in Hong Kong (2002-2019). Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2022; 26:100509.
Article12. Shin H, Schneeweiss S, Glynn RJ, Patorno E. Trends in first-line glucose-lowering drug use in adults with type 2 diabetes in light of emerging evidence for SGLT-2i and GLP-1RA. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44:1774–82.
Article13. Pottegard A, Andersen JH, Sondergaard J, Thomsen RW, Vilsboll T. Changes in the use of glucose-lowering drugs: a Danish nationwide study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023; 25:1002–10.
Article14. Arnold SV, Inzucchi SE, Tang F, McGuire DK, Mehta SN, Maddox TM, et al. Real-world use and modeled impact of glucose-lowering therapies evaluated in recent cardiovascular outcomes trials: an NCDR® Research to Practice project. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017; 24:1637–45.
Article15. Funck KL, Knudsen JS, Hansen TK, Thomsen RW, Grove EL. Real-world use of cardioprotective glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a Danish nationwide cohort study, 2012 to 2019. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:520–9.
Article16. McCoy RG, Van Houten HK, Karaca-Mandic P, Ross JS, Montori VM, Shah ND. Second-line therapy for type 2 diabetes management: the treatment/benefit paradox of cardiovascular and kidney comorbidities. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44:2302–11.
Article17. Baek JH, Yang YS, Ko SH, Han KD, Kim JH, Moon MK, et al. Real-world prescription patterns and barriers related to the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors among Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:701–12.
Article18. Igarashi A, Bekker Hansen B, Langer J, Tavella F, Collings H, Davies N, et al. Preference for oral and injectable GLP-1 RA therapy profiles in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a discrete choice experiment. Adv Ther. 2021; 38:721–38.
Article19. Oh TJ, Moon JY, Hur KY, Ko SH, Kim HJ, Kim T, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor for renal function preservation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:489–97.
Article20. McGovern AP, Hogg M, Shields BM, Sattar NA, Holman RR, Pearson ER, et al. Risk factors for genital infections in people initiating SGLT2 inhibitors and their impact on discontinuation. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020; 8:e001238.
Article21. Cheong AJ, Teo YN, Teo YH, Syn NL, Ong HT, Ting AZ, et al. SGLT inhibitors on weight and body mass: a meta-analysis of 116 randomized-controlled trials. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022; 30:117–28.
Article22. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJ, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2295–306.
Article23. Jeong SJ, Lee SE, Shin DH, Park IB, Lee HS, Kim KA. Barriers to initiating SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease: a real-world study. BMC Nephrol. 2021; 22:177.
Article24. The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group, Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2023; 388:117–27.
Article25. Cai X, Gao X, Yang W, Chen Y, Zhang S, Zhou L, et al. No disparity of the efficacy and all-cause mortality between Asian and non-Asian type 2 diabetes patients with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors treatment: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig. 2018; 9:850–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Recommendations for Pharmacological Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors