J Korean Diabetes.
2023 Sep;24(3):127-134. 10.4093/jkd.2023.24.3.127.
2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Recommendations for Pharmacological Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2546629
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2023.24.3.127
Abstract
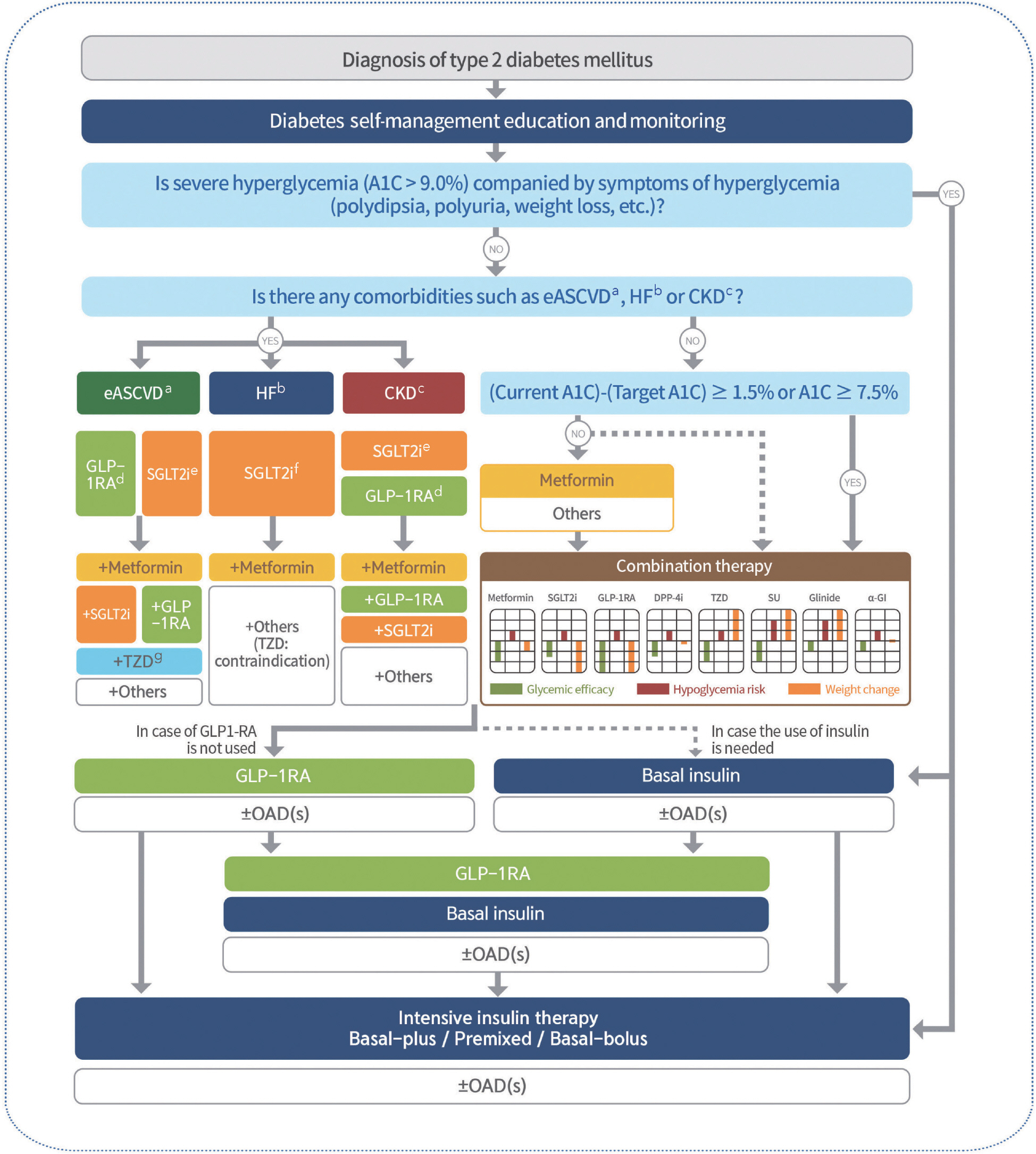
- The 2023 clinical practice guidelines for diabetes in Korea are reviewed and updated biennially by the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association based on the latest scientific research and clinical trials. The 2023 guidelines include several updates to recommendations for pharmacological treatment of type 2 diabetes. The new guidelines make it clear that the treatment plan should include antidiabetic agents proven to reduce cardiorenal risk in adults with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease. When considering injection-based combination therapy, GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are recommended prior to basal insulin. If the target blood glucose level cannot be reached with GLP-1 RAs or basal insulin treatment alone, combination treatment with GLP-1 RAs and basal insulin is recommended. This review summarizes the recommendations for pharmacological treatment for type 2 diabetes in the 2023 Korean Diabetes Association treatment guidelines, focusing on major revisions.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Zinman B., Wanner C., Lachin JM., Fitchett D., Bluhmki E., Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015. 373:2117–28.2.Wiviott SD., Raz I., Bonaca MP., Mosenzon O., Kato ET., Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019. 380:347–57.3.Marso SP., Daniels GH., Brown-Frandsen K., Kristensen P., Mann JF., Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016. 375:311–22.4.Gerstein HC., Colhoun HM., Dagenais GR., Diaz R., Lakshman-an M., Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019. 394:121–30.5.Choi JH., Lee KA., Moon JH., Chon S., Kim DJ., Kim HJ, et al. 2023 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. 47:575–94.6.Maloney A., Rosenstock J., Fonseca V. A model-based meta-analysis of 24 antihyperglycemic drugs for type 2 diabetes: comparison of treatment effects at therapeutic doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019. 105:1213–23.7.Cannon CP., Pratley R., Dagogo-Jack S., Mancuso J., Huyck S., Masiukiewicz U, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertug-liflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020. 383:1425–35.8.McMurray JJV., Solomon SD., Inzucchi SE., Køber L., Kosi-borod MN., Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019. 381:1995–2008.9.Packer M., Anker SD., Butler J., Filippatos G., Pocock SJ., Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020. 383:1413–24.10.Anker SD., Butler J., Filippatos G., Ferreira JP., Bocchi E., Böhm M, et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2021. 385:1451–61.11.Solomon SD., McMurray JJV., Claggett B., de Boer RA., De-Mets D., Hernandez AF, et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2022. 387:1089–98.12.Wanner Ch., Inzucchi SE., Zinman B. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016. 375:1801–2.13.Heerspink HJL., Stefánsson BV., Correa-Rotter R., Chertow GM., Greene T., Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020. 383:1436–46.14.Herrington WG., Staplin N., Wanner C., Green JB., Hauske SJ., Emberson JR., The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2023. 388:117–27.15.Marso SP., Bain SC., Consoli A., Eliaschewitz FG., Jódar E., Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016. 375:1834–44.16.Kaku K., Lee J., Mattheus M., Kaspers S., George J., Woerle HJ; EMPA-REG OUTCOME® Investigators. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease - results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME®. Circ J. 2017. 81:227–34.17.Zhang XL., Zhu QQ., Chen YH., Li XL., Chen F., Huang JA, et al. Cardiovascular safety, long-term noncardiovascular safety, and efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a sys-temic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analy-sis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. 7:e007165.18.Nauck MA., Mirna AEA., Quast DR. Meta-analysis of head-to-head clinical trials comparing incretin-based glu-cose-lowering medications and basal insulin: an update including recently developed glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist tirzepatide. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023. 25:1361–71.19.DeVries JH., Bain SC., Rodbard HW., Seufert J., D'Alessio D., Thomsen AB, et al. Sequential intensification of metformin treatment in type 2 diabetes with liraglutide fol-lowed by randomized addition of basal insulin prompted by A1C targets. Diabetes Care. 2012. 35:1446–54.20.Aroda VR., Bailey TS., Cariou B., Kumar S., Leiter LA., Raskin P, et al. Effect of adding insulin degludec to treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin and liraglutide: a double-blind randomized controlled trial (Begin: add to GLP-1 study). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016. 18:663–70.21.Rosenstock J., Aronson R., Grunberger G., Hanefeld M., Piatti P., Serusclat P, et al. Benefits of LixiLan, a titratable fixed-ratio combination of insulin glargine plus lixisenatide, versus insulin glargine and lixisenatide monocompo-nents in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral agents: the LixiLan-O randomized trial. Diabetes Care. 2016. 39:2026–35.22.Blonde L., Rosenstock J., Del Prato S., Henry R., Shehadeh N., Frias J, et al. Switching to iGlarLixi versus continuing daily or weekly GLP-1 RA in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by GLP-1 RA and oral antihyperglycemic therapy: the LixiLan-G randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2019. 42:2108–16.23.Gough SC., Bode B., Woo V., Rodbard HW., Linjawi S., Poulsen P, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-ratio com-bination of insulin degludec and liraglutide (IDegLira) compared with its components given alone: results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised, 26-week, treat-to-target trial in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014. 2:885–93.24.Linjawi S., Bode BW., Chaykin LB., Courrèges JP., Han-delsman Y., Lehmann LM, et al. The efficacy of IDegLira (insulin degludec/liraglutide combination) in adults with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with a GLP-1 receptor agonist and oral therapy: DUAL III randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017. 8:101–14.25.Buse JB., Bergenstal RM., Glass LC., Heilmann CR., Lewis MS., Kwan AY, et al. Use of twice-daily exenatide in Basal insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011. 154:103–12.26.Seino Y., Min KW., Niemoeller E., Takami A; EFC10887 GETGOAL-L Asia Study Investigators. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled on basal insulin with or without a sulfonylurea (GetGoal-L-Asia). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012. 14:910–7.27.Riddle MC., Aronson R., Home P., Marre M., Niemoeller E., Miossec P, et al. Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by established basal insulin: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled com-parison (GetGoal-L). Diabetes Care. 2013. 36:2489–96.28.Riddle MC., Forst T., Aronson R., Sauque-Reyna L., Sou-hami E., Silvestre L, et al. Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with newly initiated and continuously titrated basal insulin glargine: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled study (Get-Goal-Duo 1). Diabetes Care. 2013. 36:2497–503.29.Yang W., Min K., Zhou Z., Li L., Xu X., Zhu D, et al. Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide in a predominantly Asian popu-lation with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled with basal insulin: the GetGoal-L-C randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. 20:335–43.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Selection of Pharmacological Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Pumps
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors