J Korean Diabetes.
2021 Dec;22(4):259-267. 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.4.259.
2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2526209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2021.22.4.259
Abstract
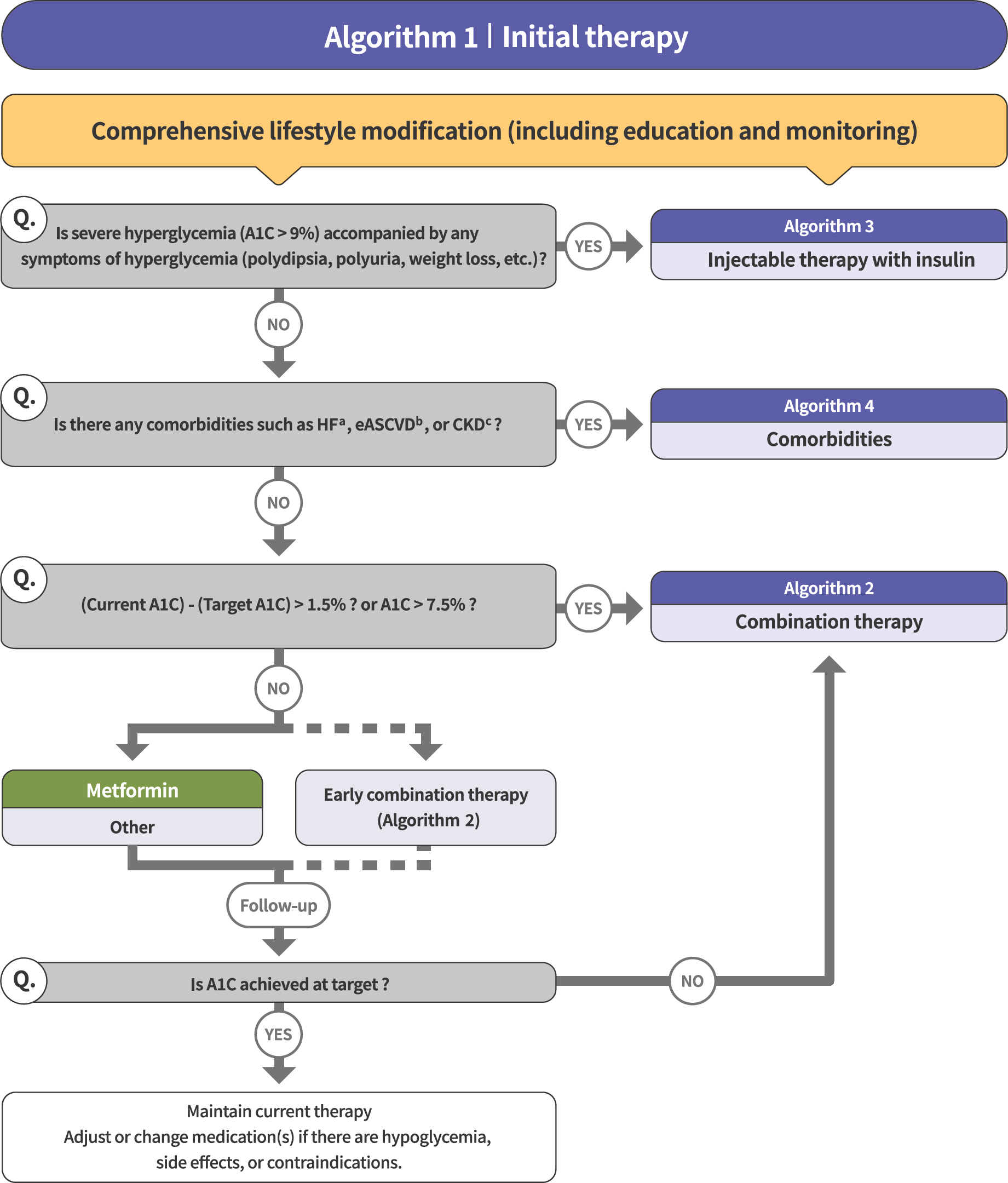
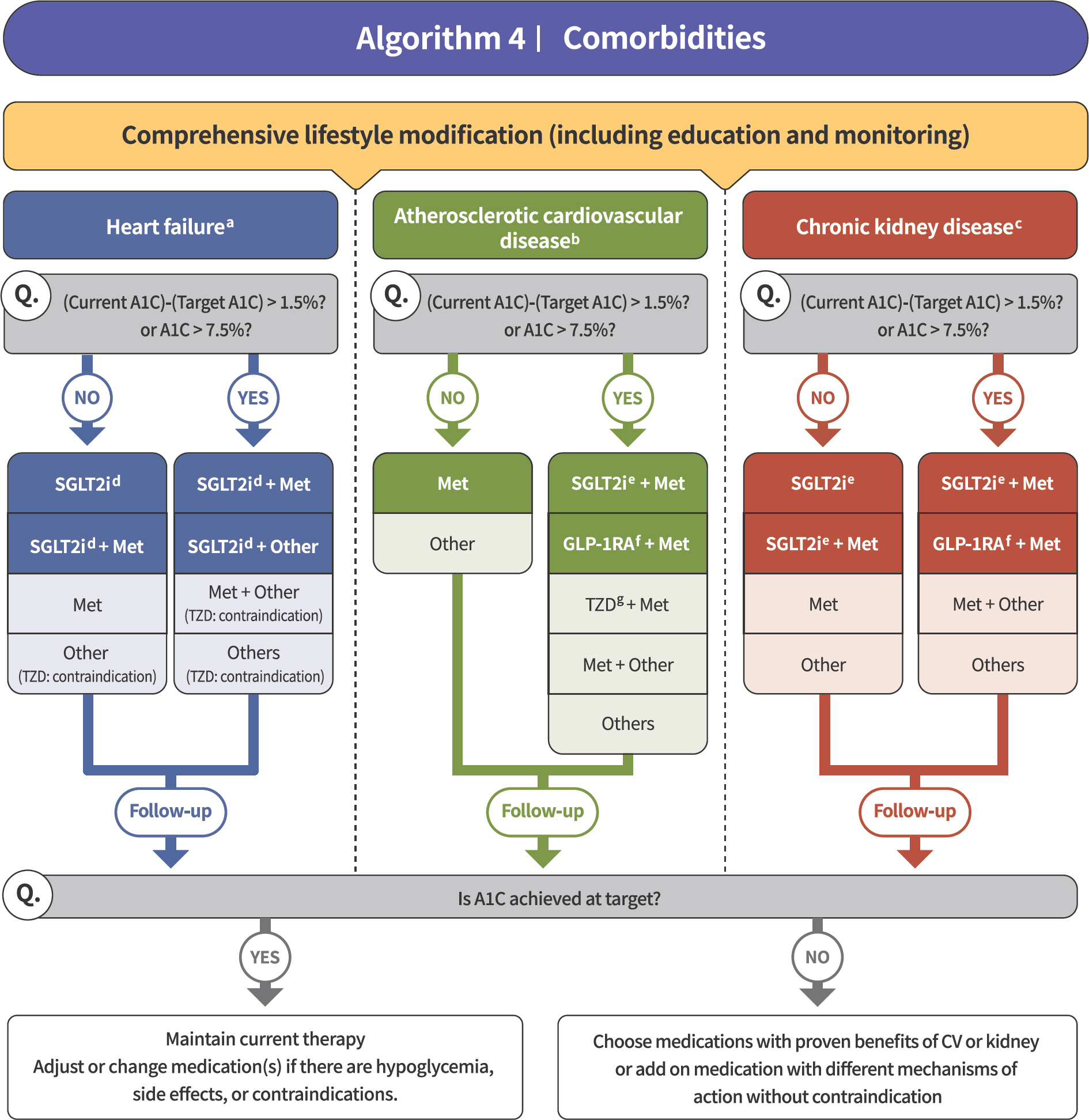
- The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association revised and updated the 7th Clinical Practice Guidelines in 2021. Intense multifactorial intervention including adequate control of glycemia, blood pressure, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol level and use of antiplatelet agents has been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In these recent guidelines, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2 inhibitors) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) with proven benefits were recommended in patients with heart failure and/or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) as mono- or combination therapy. SGLT2 inhibitors such as dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and ertugliflozin were recommended preferentially in patients with heart failure. In those with ASCVD, treatment including SGLT2 inhibitors such as empagliflozin and dapagliflozin or GLP-1 RAs such as dulaglutide, liraglutide, and semaglutide as a combination therapy was recommended.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Pharmacotherapy and the Korean Diabetes Association Support System
Kyu Yeon Hur
J Korean Diabetes. 2021;22(4):250-258. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.4.250.
Reference
-
1.Park JH., Ha KH., Kim BY., Lee JH., Kim DJ. Trends in cardiovascular complications and mortality among patients with diabetes in South Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. 45:283.
Article2.Gaede P., Lund-Andersen H., Parving HH., Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:580–91.
Article3.Korean Diabetes Association. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2021.4.Hur KY., Moon MK., Park JS., Kim SK., Lee SH., Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. 45:461–81.
Article5.American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic ap-proaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021. 44(Suppl 1):S111–24.6.Cosentino F., Grant PJ., Aboyans V., Bailey CJ., Ceriello A., Delgado V, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2020. 41:255–323.7.Zinman B., Wanner C., Lachin JM., Fitchett D., Bluhmki E., Hantel S, et al. EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015. 373:2117–28.
Article8.Cannon CP., Pratley R., Dagogo-Jack S., Mancuso J., Huyck S., Masiukiewicz U, et al. VERTIS CV Investigators. cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020. 383:1425–35.
Article9.Wiviott SD., Raz I., Bonaca MP., Mosenzon O., Kato ET., Cahn A, et al. DECLARE–TIMI 58 Investigators. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019. 380:347–57.
Article10.Zelniker TA., Wiviott SD., Raz I., Im K., Goodrich EL., Furtado RHM, et al. Comparison of the effects of gluca-gon-like peptide receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019. 139:2022–31.
Article11.Zelniker TA., Wiviott SD., Raz I., Im K., Goodrich EL., Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and second-ary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019. 393:31–9.
Article12.McGuire DK., Shih WJ., Cosentino F., Charbonnel B., Cherney DZI., Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Car-diol. 2021. 6:148–58.13.Arnott C., Li Q., Kang A., Neuen BL., Bompoint S., Lam CSP, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition for the prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and me-ta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. 9:e014908.
Article14.Marso SP., Daniels GH., Brown-Frandsen K., Kristensen P., Mann JF., Nauck MA, et al. LEADER Trial Investigators. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016. 375:311–22.
Article15.Gerstein HC., Colhoun HM., Dagenais GR., Diaz R., Lakshmanan M., Pais P, et al. REWIND Investigators. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2019. 394:121–30.16.Marso SP., Bain SC., Consoli A., Eliaschewitz FG., Jódar E., Leiter LA, et al. SUSTAIN-6 Investigators. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016. 375:1834–44.
Article17.McMurray JJV., Solomon SD., Inzucchi SE., K⊘ber L., Kosi-borod MN., Martinez FA, et al. DAPA-HF Trial Committees and Investigators. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019. 381:1995–2008.18.Packer M., Anker SD., Butler J., Filippatos G., Pocock SJ., Carson P, et al. EMPEROR-Reduced Trial Investigators. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020. 383:1413–24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Pharmacotherapy and the Korean Diabetes Association Support System
- 2021 Korean Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Risk Factors Management in Diabetic Patients