Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Mar;48(2):253-264. 10.4093/dmj.2023.0128.
Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2553596
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0128
Abstract
- Background
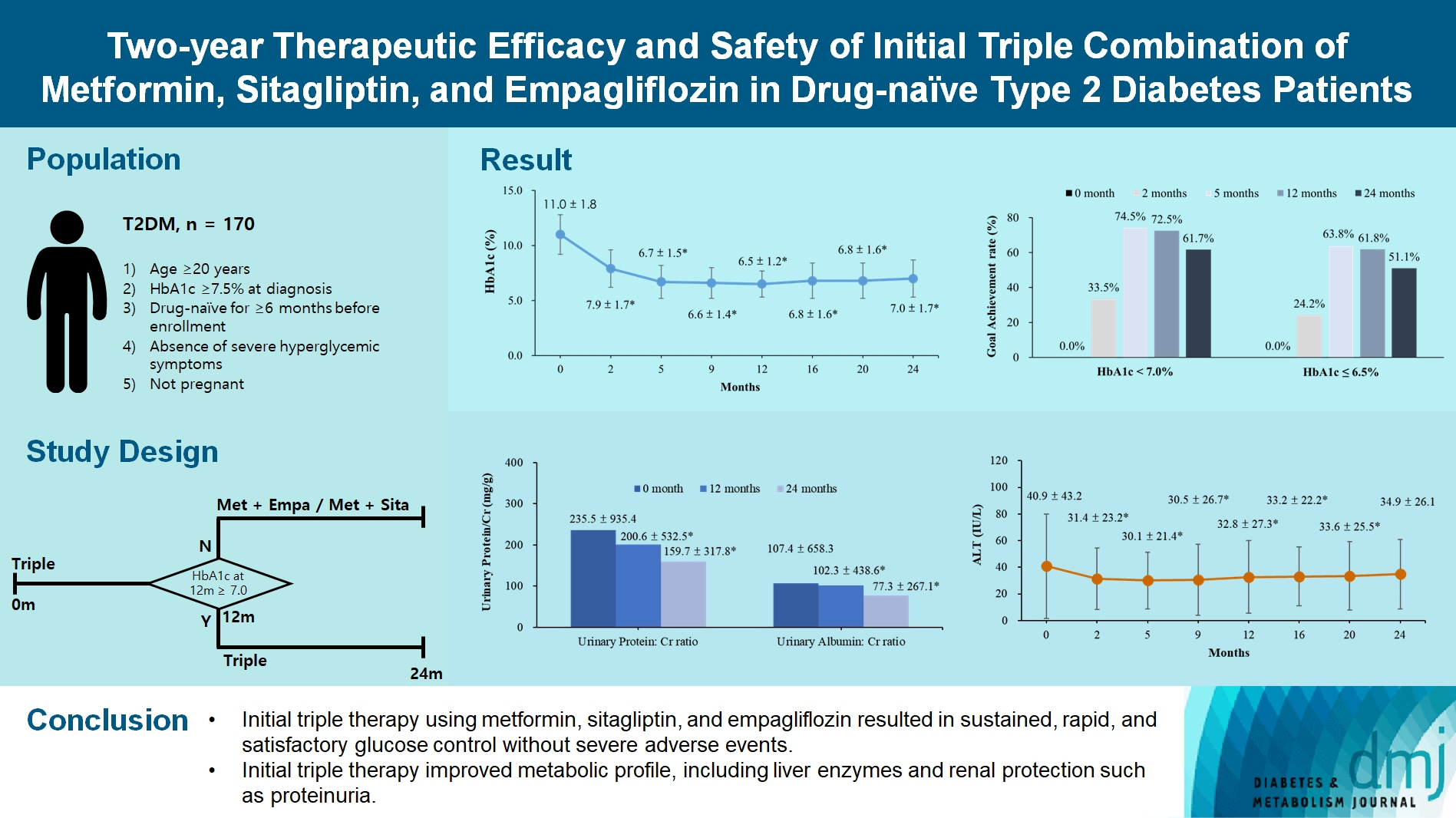
We investigated the long-term efficacy and safety of initial triple therapy using metformin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
We enrolled 170 drug-naïve patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level >7.5% who had started triple therapy (metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin). Glycemic, metabolic, and urinary parameters were measured for 24 months.
Results
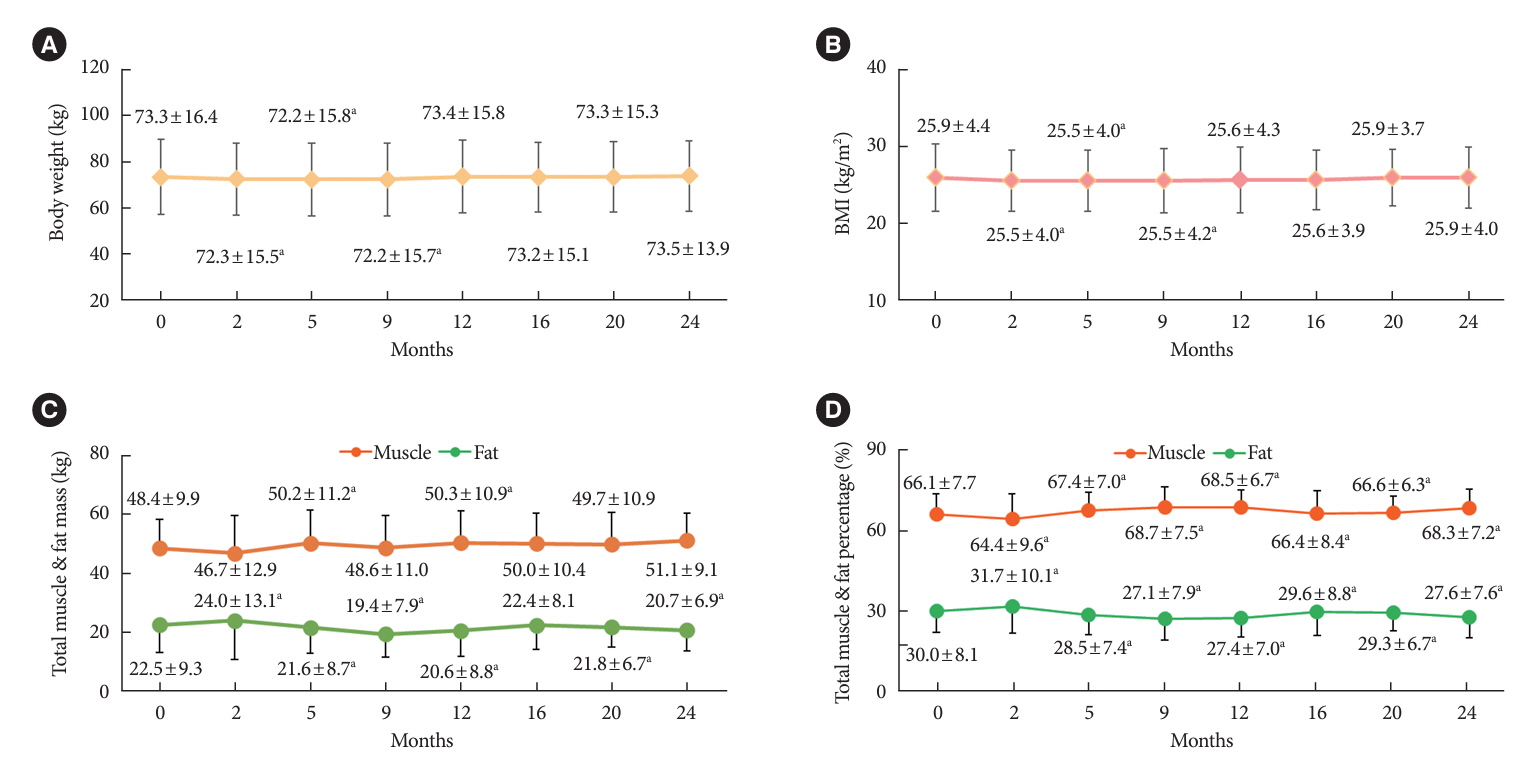
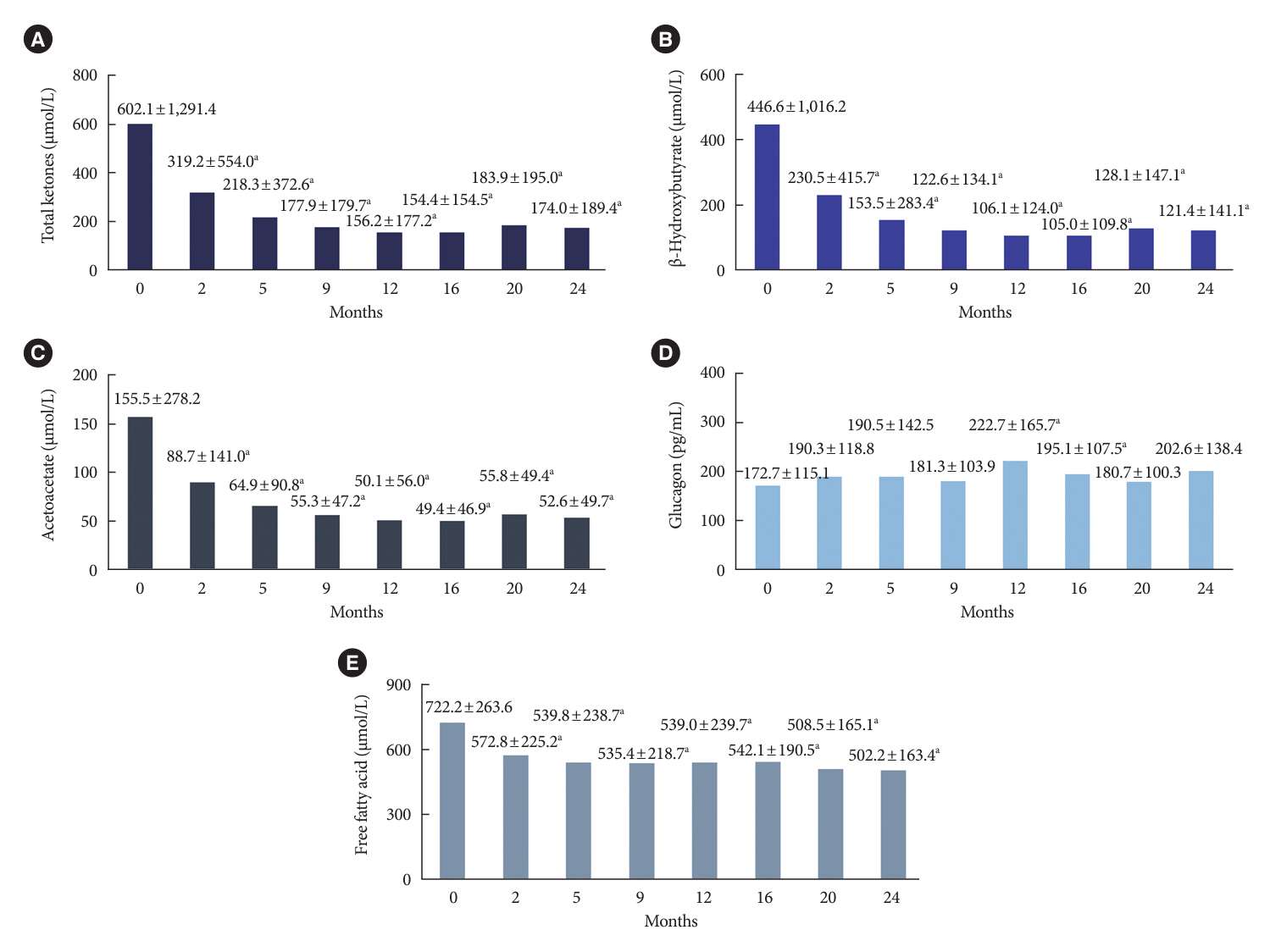
After 24 months, HbA1c level decreased significantly from 11.0%±1.8% to 7.0%±1.7%. At 12 and 24 months, the rates of achievement of the glycemic target goal (HbA1c <7.0%) were 72.5% and 61.7%, respectively, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance indices improved. Whole-body fat percentage decreased by 1.08%, and whole-body muscle percentage increased by 0.97% after 24 months. Fatty liver indices and albuminuria improved significantly. The concentration of ketone bodies was elevated at the baseline but decreased after 24 months. There were no serious adverse events, including ketoacidosis.
Conclusion
Initial triple combination therapy with metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin led to achievement of the glycemic target goal, which was maintained for 24 months without severe hypoglycemia but with improved metabolic function and albuminuria. This combination therapy may be a good strategy for drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (
Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64)
Young-Hwan Park, Minji Sohn, Soo Lim
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):1012-1013. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0485.Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (
Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64)
Eun Young Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):1005-1007. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0417.
Reference
-
1. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2545–59.
Article2. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–89.
Article3. Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:580–91.
Article4. Juarez DT, Ma C, Kumasaka A, Shimada R, Davis J. Failure to reach target glycated a1c levels among patients with diabetes who are adherent to their antidiabetic medication. Popul Health Manag. 2014; 17:218–23.
Article5. Cersosimo E, Johnson EL, Chovanes C, Skolnik N. Initiating therapy in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: combination therapy vs a stepwise approach. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:497–507.
Article6. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015; 58:429–42.
Article7. Zinman B. Initial combination therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: is it ready for prime time? Am J Med. 2011; 124(1 Suppl):S19–34.
Article8. Cahn A, Cefalu WT. Clinical considerations for use of initial combination therapy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39(Suppl 2):S137–45.
Article9. Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:410–7.
Article10. Wu D, Li L, Liu C. Efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and metformin as initial combination therapy and as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:30–7.
Article11. Matthews DR, Paldanius PM, Proot P, Chiang Y, Stumvoll M, Del Prato S, et al. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): a 5-year, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2019; 394:1519–29.
Article12. Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:2669–701.
Article13. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S125–43.14. Ko SH, Hur KY, Rhee SY, Kim NH, Moon MK, Park SO, et al. Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2017; 41:337–48.
Article15. Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C, Maggs D, Adams J, Cersosimo E, et al. Initial combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjects with new-onset diabetes: results from the Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (EDICT): a randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:268–75.16. Lim S, Ku EJ, Lee SY, Lee JH, Lee JE, Kim KM, et al. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of initial triple combination of metformin, sitagliptin, and lobeglitazone in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: initial triple study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020; 8:e000807.17. Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:1317–26.
Article18. Pratley RE, Eldor R, Raji A, Golm G, Huyck SB, Qiu Y, et al. Ertugliflozin plus sitagliptin versus either individual agent over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin: the VERTIS FACTORIAL randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:1111–20.19. Lim S, Sohn M, Shin Y, Ferrannini E. Initial combination of metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: safety and metabolic effects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022; 24:757–62.20. Ji L, Chan JC, Yu M, Yoon KH, Kim SG, Choi SH, et al. Early combination versus initial metformin monotherapy in the management of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: an East Asian perspective. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:3–17.21. Wu Q, Liu M, Fang Z, Li C, Zou F, Hu L, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin at different doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022; 47:270–86.
Article22. Ozcelik S, Celik M, Vural A, Aydin B. The effect of low and high dose empagliflozin on HbA1c and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a real-world data. North Clin Istanb. 2019; 7:167–73.23. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–9.
Article24. Jeong S, Kim K, Chang J, Choi S, Kim SM, Son JS, et al. Development of a simple nonalcoholic fatty liver disease scoring system indicative of metabolic risks and insulin resistance. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8:1414.
Article25. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001; 285:2486–97.26. Kim BY, Kang SM, Kang JH, Kang SY, Kim KK, Kim KB, et al. 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021; 30:81–92.
Article27. Hou X, Liu J, Song J, Wang C, Liang K, Sun Y, et al. Relationship of hemoglobin A1c with β cell function and insulin resistance in newly diagnosed and drug naive type 2 diabetes patients. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:8797316.28. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999; 281:2005–12.
Article29. Polidori D, Iijima H, Goda M, Maruyama N, Inagaki N, Crawford PA. Intra- and inter-subject variability for increases in serum ketone bodies in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:1321–6.
Article30. Shin Y, Choi H, Lim S. Comparison betweeen dapagliflozin add-on therapy and insulin dose escalation in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: DVI study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 175:108843.
Article31. Omar B, Ahren B. Pleiotropic mechanisms for the glucose-lowering action of DPP-4 inhibitors. Diabetes. 2014; 63:2196–202.
Article32. Szekeres Z, Toth K, Szabados E. The effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on lipid metabolism. Metabolites. 2021; 11:87.
Article33. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–28.
Article34. Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJ, Neal B, Perkovic V, Billot L, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:845–54.
Article35. Warren B, Rebholz CM, Sang Y, Lee AK, Coresh J, Selvin E, et al. Diabetes and trajectories of estimated glomerular filtration rate: a prospective cohort analysis of the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1646–53.
Article36. Hickman IJ, Macdonald GA. Impact of diabetes on the severity of liver disease. Am J Med. 2007; 120:829–34.
Article37. Rhee EJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes: an epidemiological perspective. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2019; 34:226–33.
Article38. Seino Y, Inagaki N, Haneda M, Kaku K, Sasaki T, Fukatsu A, et al. Efficacy and safety of luseogliflozin added to various oral antidiabetic drugs in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2015; 6:443–53.
Article39. Johansson L, Hockings PD, Johnsson E, Dronamraju N, Maaske J, Garcia-Sanchez R, et al. Dapagliflozin plus saxagliptin add-on to metformin reduces liver fat and adipose tissue volume in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22:1094–101.
Article40. Dharmalingam M, Yamasandhi PG. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 22:421–8.
Article41. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–86.
Article42. Rea F, Ciardullo S, Savare L, Perseghin G, Corrao G. Comparing medication persistence among patients with type 2 diabetes using sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in real-world setting. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 180:109035.
Article43. McInnes N, Hall S, Sultan F, Aronson R, Hramiak I, Harris S, et al. Remission of type 2 diabetes following a short-term intervention with insulin glargine, metformin, and dapagliflozin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 105:dgaa248.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64)
- Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:253-64)
- Efficacy of Sitagliptin When Added to Ongoing Therapy in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Glycemic Effectiveness of Metformin-Based Dual-Combination Therapies with Sulphonylurea, Pioglitazone, or DPP4-Inhibitor in Drug-Naive Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects