J Pathol Transl Med.
2024 Mar;58(2):87-90. 10.4132/jptm.2023.12.28.
Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma arising in an endovascular graft: first case report in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2553476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.28
Abstract
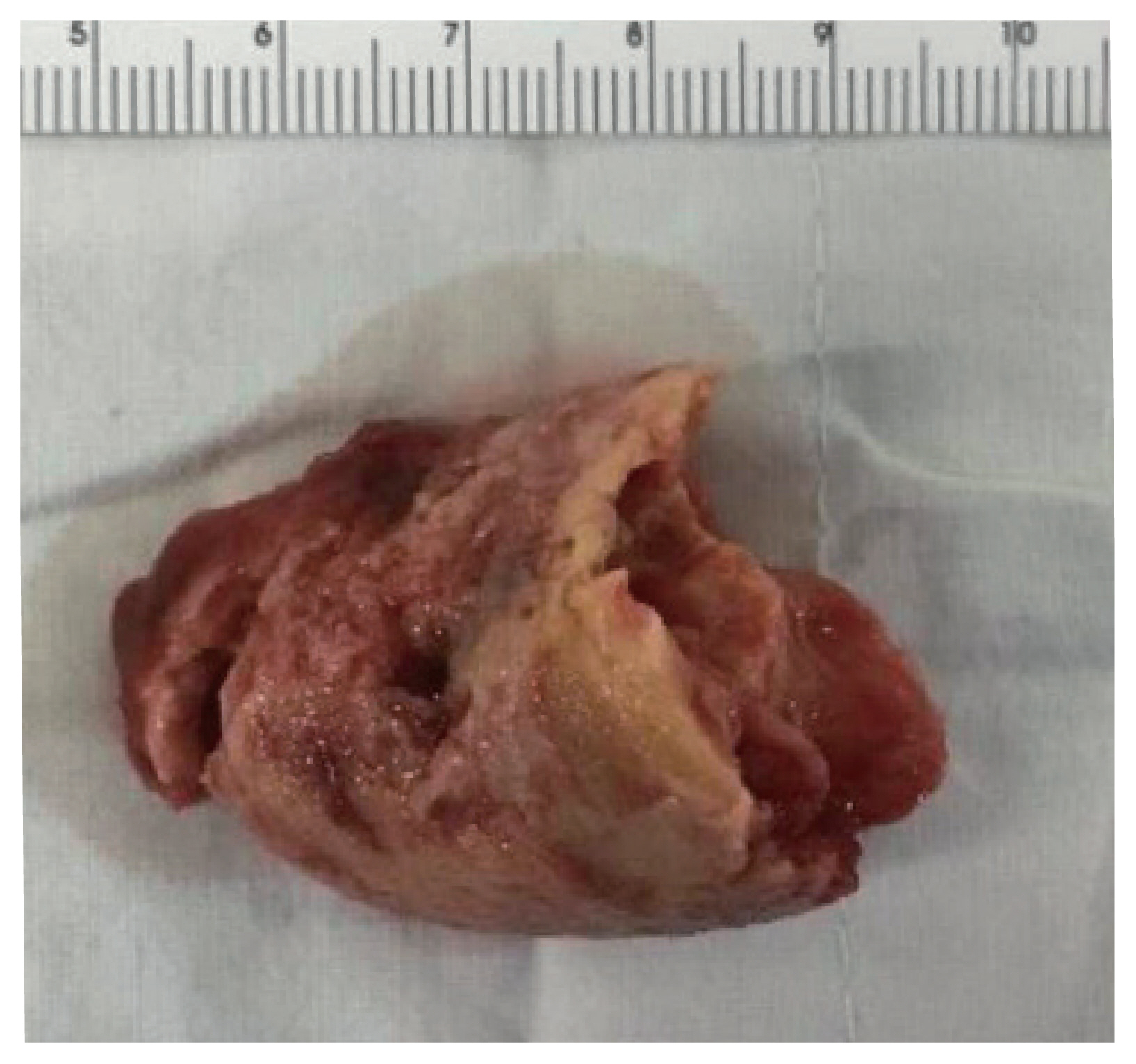
- Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma (FA-LBCL) is an extremely rare subtype of LBCL that consists of microscopic aggregates of atypical large B cells in the background of fibrin. Here, we report the first case of FA-LBCL in Korea. A 57-year-old male presented with a large amount of thrombus in the thoracic aorta during follow-up for graft replacement of the thoracoabdominal aorta 8 years prior. The removed thrombus, measuring 4.3 × 3.1 cm, histologically exhibited eosinophilic fibrinous material with several small clusters of atypical lymphoid cells at the periphery. The atypical cells were positive for CD20 by immunohistochemistry and for Epstein-Barr virus by in situ hybridization. The Ki-67 proliferation rate was 85%. The patient was still alive with no recurrence at the 7-year follow-up after thrombectomy. Although the diagnosis can be very difficult and challenging due to its paucicellular features, pathologists should be aware of FALBCL, which has likely been underestimated in routine evaluations of thrombi.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2017.2. Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: lymphoid neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022; 36:1720–48.3. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO classification of tumors: thoracic tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2021.4. Miller DV, Firchau DJ, McClure RF, Kurtin PJ, Feldman AL. Epstein-Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising on cardiac prostheses. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010; 34:377–84.5. Gruver AM, Huba MA, Dogan A, Hsi ED. Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma: part of the spectrum of cardiac lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012; 36:1527–37.6. Boyer DF, McKelvie PA, de Leval L, et al. Fibrin-associated EBV-positive large B-cell lymphoma: an indolent neoplasm with features distinct from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation. Am J Surg Pathol. 2017; 41:299–312.7. Di Napoli A, Soma L, Quintanilla-Martinez L, et al. Cavity-based lymphomas: challenges and novel concepts. A report of the 2022 EA4HP/SH lymphoma workshop. Virchows Arch. 2023; 483:299–316.8. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004; 103:275–82.9. Loong F, Chan AC, Ho BC, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation as an incidental finding and new clinical scenarios. Mod Pathol. 2010; 23:493–501.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Developing at the Ileocolonic Anastomosis Site after Right Hemicolectomy for Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report
- A case of Ki-1 positive large-cell lymphoma
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Secondary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma