Child Kidney Dis.
2024 Feb;28(1):27-34. 10.3339/ckd.24.001.
First-morning urine osmolality changes in children with nocturnal enuresis at the end of treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Urology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- 3Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2553177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.24.001
Abstract
- Purpose
The ability to concentrate urine becomes an important index in determining nocturnal enuresis (NE) treatment. The aim of our study was to investigate first-morning urine osmolality (Uosm) changes at the end of treatment compared to before treatment in children with NE.
Methods
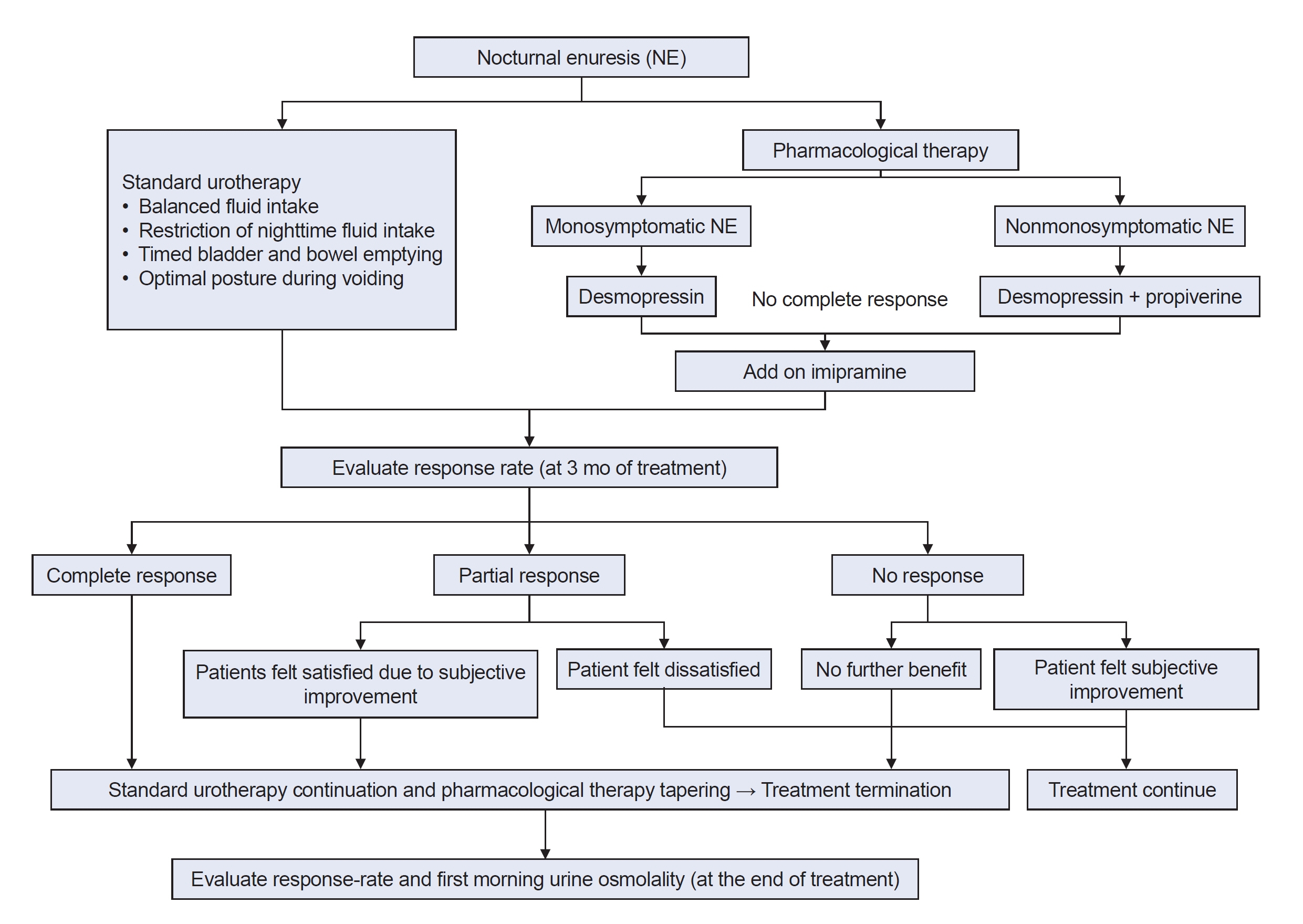
A total of 71 children with NE were divided into two groups according to the level of first-morning Uosm before treatment: high group (≥800 mOsm/kg) and low group (<800 mOsm/kg). Baseline parameters were obtained from uroflowmetry, frequency volume charts for at least 2 days, and a questionnaire for lower urinary tract symptoms. All patients were basically treated with standard urotherapy and medication. The first-morning Uosm was measured twice, before treatment and at the end of treatment.
Results
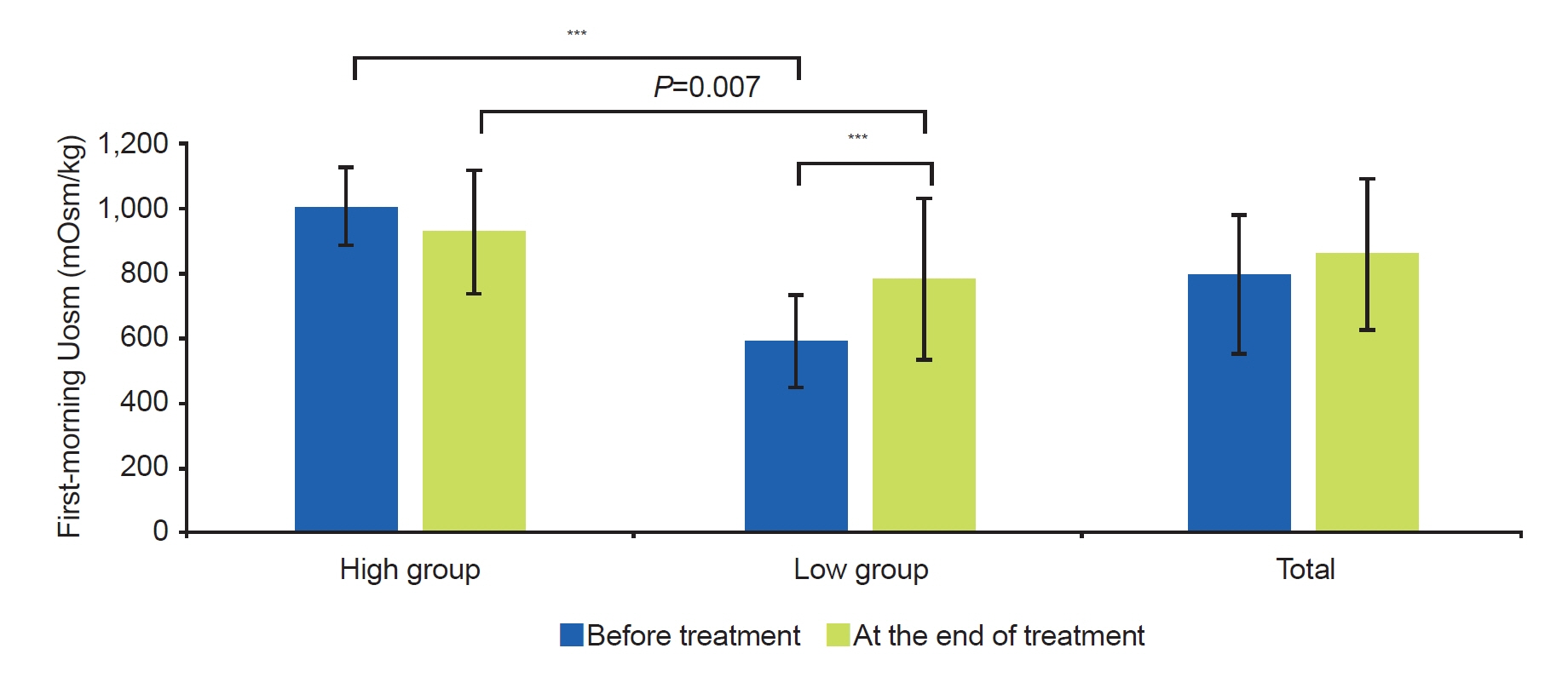
The response rate was higher in the low group after 3 months of treatment than in the high group (P=0.041). However, there was no difference between the two groups at the end of the treatment. In the high group, the first-morning Uosm at the end of treatment did not show a significant change compared to before treatment. In contrast, the first-morning Uosm increased in the low group at the end of treatment (P<0.001). However, it was still lower than that of the high group (P=0.007).
Conclusions
The ability to concentrate nocturnal urine was improved at the end of treatment compared to before treatment in the low Uosm NE children. NE improved faster in the low Uosm group before treatment than in the high group.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Austin PF, Bauer SB, Bower W, Chase J, Franco I, Hoebeke P, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: update report from the standardization committee of the International Children’s Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016; 35:471–81.
Article2. Chung JM, Lee SD, Kang DI, Kwon DD, Kim KS, Kim SY, et al. An epidemiologic study of voiding and bowel habits in Korean children: a nationwide multicenter study. Urology. 2010; 76:215–9.
Article3. Van Herzeele C, Walle JV, Dhondt K, Juul KV. Recent advances in managing and understanding enuresis. F1000Res. 2017; 6:1881.
Article4. Arda E, Cakiroglu B, Thomas DT. Primary nocturnal enuresis: a review. Nephrourol Mon. 2016; 8:e35809.
Article5. Neveus T, Lackgren G, Tuvemo T, Stenberg A. Osmoregulation and desmopressin pharmacokinetics in enuretic children. Pediatrics. 1999; 103:65–70.
Article6. Lee GK, Chung JM, Lee SD. First-morning urine osmolality and nocturnal enuresis in children: a single-center prospective cohort study. Investig Clin Urol. 2023; 64:501–9.
Article7. Pagana KD, Pagana TJ. Mosby's manual of diagnostic and laboratory tests. 7th ed. Elsevier Health Sciences;2017.8. Eller DA, Homsy YL, Austin PF, Tanguay S, Cantor A. Spot urine osmolality, age and bladder capacity as predictors of response to desmopressin in nocturnal enuresis. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1997; 183:41–5.9. Kawauchi A, Watanabe H, Miyoshi K. Early morning urine osmolality in nonenuretic and enuretic children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1996; 10:696–8.
Article10. Steffens J, Netzer M, Isenberg E, Alloussi S, Ziegler M. Vasopressin deficiency in primary nocturnal enuresis: results of a controlled prospective study. Eur Urol. 1993; 24:366–70.
Article11. Eggert P, Kuhn B. Antidiuretic hormone regulation in patients with primary nocturnal enuresis. Arch Dis Child. 1995; 73:508–11.
Article12. Abdovic S, Cuk M, Hizar I, Milosevic M, Jerkovic A, Saraga M. Pretreatment morning urine osmolality and oral desmopressin lyophilisate treatment outcome in patients with primary monosymptomatic enuresis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021; 53:1529–34.
Article13. Dehoorne JL, Raes AM, van Laecke E, Hoebeke P, Vande Walle JG. Desmopressin resistant nocturnal polyuria secondary to increased nocturnal osmotic excretion. J Urol. 2006; 176:749–53.
Article14. Sozubir S, Ergun G, Celik A, Ulman I, Avanoglu A. The influence of urine osmolality and other easily detected parameters on the response to desmopressin in the management of monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis in children. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2006; 58:207–12.15. Leech SC, McHugh K, Sullivan PB. Evaluation of a method of assessing faecal loading on plain abdominal radiographs in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1999; 29:255–8.
Article16. Unuvar T, Sonmez F. The role of urine osmolality and ions in the pathogenesis of primary enuresis nocturna and in the prediction of responses to desmopressin and conditioning therapies. Int Urol Nephrol. 2005; 37:751–7.
Article17. Folwell AJ, Macdiarmid SA, Crowder HJ, Lord AD, Arnold EP. Desmopressin for nocturnal enuresis: urinary osmolality and response. Br J Urol. 1997; 80:480–4.
Article18. Medel R, Dieguez S, Brindo M, Ayuso S, Canepa C, Ruarte A, et al. Monosymptomatic primary enuresis: differences between patients responding or not responding to oral desmopressin. Br J Urol. 1998; 81 Suppl 3:46–9.
Article19. Neveus T, Eggert P, Evans J, Macedo A, Rittig S, Tekgul S, et al. Evaluation of and treatment for monosymptomatic enuresis: a standardization document from the International Children’s Continence Society. J Urol. 2010; 183:441–7.
Article20. Vande Walle J, Rittig S, Bauer S, Eggert P, Marschall-Kehrel D, Tekgul S, et al. Practical consensus guidelines for the management of enuresis. Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171:971–83.
Article21. Akagawa S, Tsuji S, Akagawa Y, Yamanouchi S, Kimata T, Kaneko K. Desmopressin response in nocturnal enuresis showing concentrated urine. Pediatr Int. 2020; 62:701–4.
Article22. Kamperis K, Rittig S, Radvanska E, Jorgensen KA, Djurhuus JC. The effect of desmopressin on renal water and solute handling in desmopressin resistant monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. J Urol. 2008; 180:707–14.
Article23. Lee KS, Chang JB, Jang JY, Ko YH, Park YH, Song PH. Role of urine osmolality as a predictor of the effectiveness of combined imipramine and desmopressin in the treatment of monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2015; 32:85–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Value of Functional Bladder Capacity, Urine Osmolality, and Daytime Storage Symptoms for Severity of Nocturnal Enuresis
- Role of urine osmolality as a predictor of the effectiveness of combined imipramine and desmopressin in the treatment of monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis
- First-morning urine osmolality and nocturnal enuresis in children: A single-center prospective cohort study
- Therapeutic Effect of Nocturnal Water Restriction in Children with Primary Nocturnal Enuresis
- Enuresis and Urine Concentration in Healthy Preschool Children