Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2024 Feb;29(1):29-37. 10.6065/apem.2346044.022.
Comparison of anthropometric, metabolic, and body compositional abnormalities in Korean children and adolescents born small, appropriate, and large for gestational age: a population-based study from KNHANES V (2010–2011)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Sejong, Korea
- KMID: 2553015
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2346044.022
Abstract
- Purpose
The impacts of growth restriction and programming in the fetal stage on metabolic and bone health in children and adolescents are poorly understood. Moreover, there is insufficient evidence for the relationship between current growth status and metabolic components. Herein, we compared the growth status, metabolic and body compositions, and bone mineral density in Korean children and adolescents based on birth weight at gestational age.
Methods
We studied 1,748 subjects (272 small for gestational age [SGA], 1,286 appropriate for gestational age [AGA], and 190 large for gestational age [LGA]; 931 men and 817 women) aged 10–18 years from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) V (2010–2011). Anthropometric measurements, fasting blood biochemistry, and body composition data were analyzed according to birth weight and gestational age.
Results
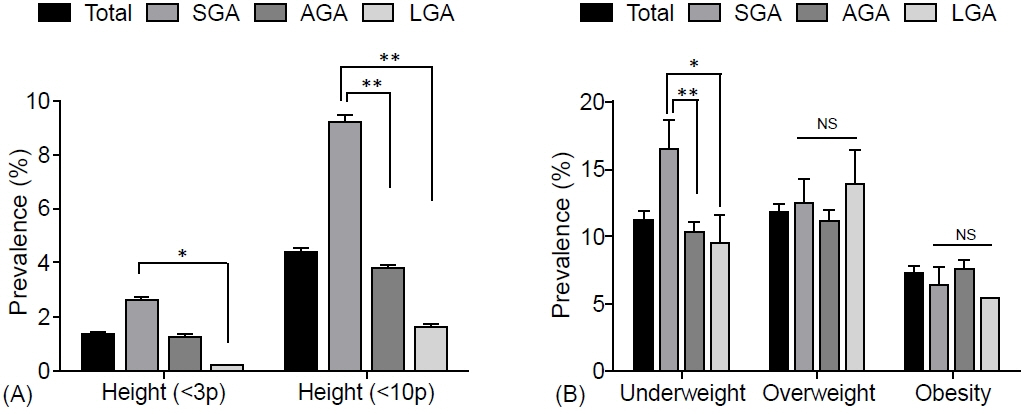
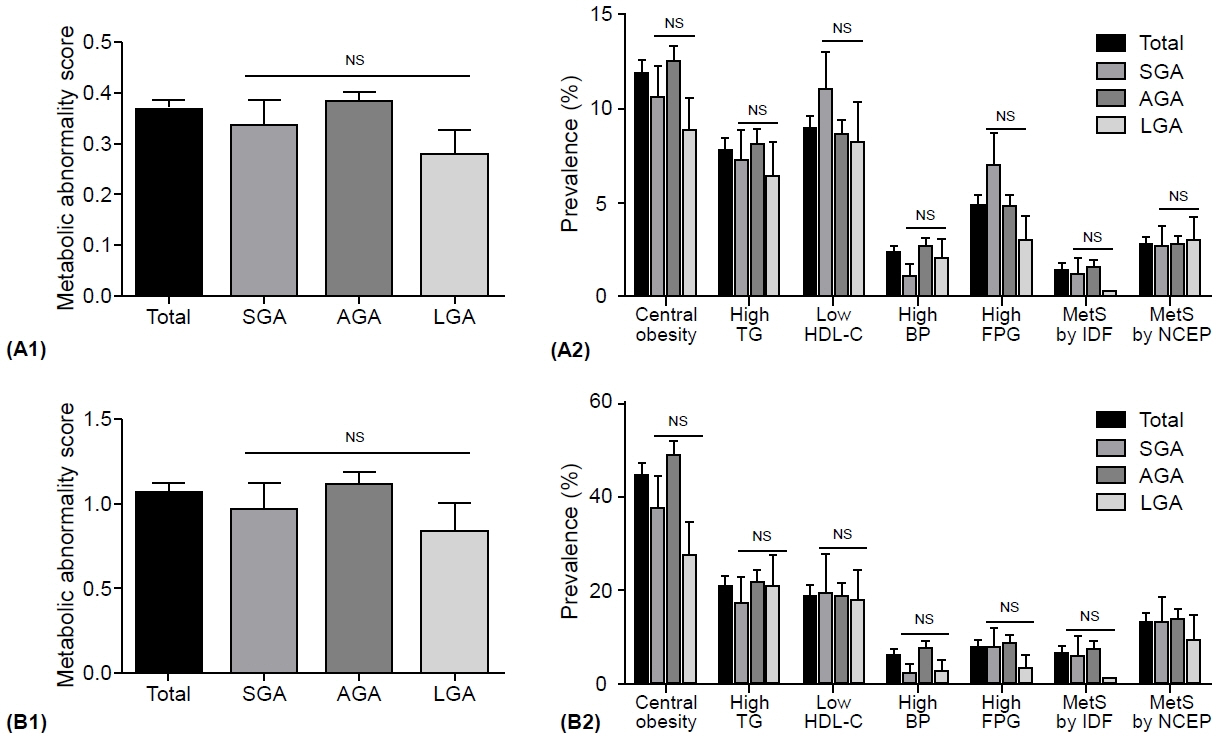
The prevalence of low birth weight (14.7% vs. 1.2% in AGA and 3.2% in LGA, p<0.001) and current short stature (2.237 [1.296–3.861] compared to AGA, p=0.004) in SGA subjects was greater than that in other groups; however, the prevalence of overweight and obesity risks, metabolic syndrome (MetS), and MetS component abnormalities was not. Moreover, no significant differences were found in age- and sex-adjusted lean mass ratio, fat mass ratio, truncal fat ratio, bone mineral content, or bone density among the SGA, AGA, and LGA groups in Korean children and adolescents.
Conclusion
Our data demonstrate that birth weight alone may not be a determining factor for body composition and bone mass in Korean children and adolescents. Further prospective and longitudinal studies in adults are necessary to confirm the impact of SGA on metabolic components and bone health.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009; 120:1640–5.2. Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005; 365:1415–28.
Article3. Al-Hamad D, Raman V. Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Transl Pediatr. 2017; 6:397–407.4. Vanlancker T, Schaubroeck E, Vyncke K, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Breidenassel C, González-Gross M, et al. Comparison of definitions for the metabolic syndrome in adolescents. Eur J Pediatr. 2017; 176:241–52.5. Park SI, Suh J, Lee HS, Song K, Choi Y, Oh JS, et al. Tenyear trends of metabolic syndrome prevalence and nutrient intake among Korean children and adolescents: a population-based study. Yonsei Med J. 2021; 62:344–51.6. Chiavaroli V, Derraik JG, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS. Born large for gestational age: bigger is not always better. J Pediatr. 2016; 170:307–11.7. Hong YH, Chung S. Small for gestational age and obesity related comorbidities. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 23:4–8.
Article8. Kuhle S, Maguire B, Ata N, MacInnis N, Dodds L. Birth weight for gestational age, anthropometric measures, and cardiovascular disease markers in children. J Pediatr. 2017; 182:99–106.
Article9. Crume TL, Scherzinger A, Stamm E, McDuffie R, Bischoff KJ, Hamman RF, et al. The long-term impact of intrauterine growth restriction in a diverse U.S. cohort of children: the EPOCH study. Obesity. 2014; 22:608–15.
Article10. Lim JS, Lim SW, Ahn JH, Song BS, Shim KS, Hwang IT. New Korean reference for birth weight by gestational age and sex: data from the Korean Statistical Information Service (2008-2012). Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 19:146–53.
Article11. Olsen IE, Groveman SA, Lawson ML, Clark RH, Zemel BS. New intrauterine growth curves based on United States data. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:e214. –24.
Article12. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Korean Pediatric Society Committee for the Development of Growth Standard for Korean Children and Adolescents. 2007 Korean children and adolescents growth standard: commentary for the development of 2007 growth chart [Internet]. Cheongju (Korea): KCDC, Division of Chronic Disease Surveillance; c2019 [cited 2022 Dec 11]. Available from: http://www.cdc.go.kr/.13. Kang MJ, Hong HS, Chung SJ, Lee YA, Shin CH, Yang SW. Body composition and bone density reference data for Korean children, adolescents, and young adults according to age and sex: results of the 2009-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). J Bone Miner Metab. 2016; 34:429–39.
Article14. Zimmet P, Alberti K Gerrge MM, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007; 8:299–306.15. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome. An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement: executive summary. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2005; 4:198–203.16. Kim JH, Kim DH, Lim JS. Growth status of children and adolescents born small for gestational age at full term in Korea: data from the KNHANES-V. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 33:743–50.
Article17. Finken MJJ, van der Steen M, Smeets CCJ, Walenkamp MJE, de Bruin C, Hokken-Koelega ACS, et al. Children born small for gestational age: differential diagnosis, molecular genetic evaluation, and implications. Endocr Rev. 2018; 39:851–94.18. Giabicani E, Pham A, Brioude F, Mitanchez D, Netchine I. Diagnosis and management of postnatal fetal growth restriction. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 32:523–34.
Article19. Byberg L, McKeigue PM, Zethelius B, Lithell HO. Birth weight and the insulin resistance syndrome: association of low birth weight with truncal obesity and raised plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 but not with abdominal obesity or plasma lipid disturbances. Diabetologia. 2000; 43:54–60.
Article20. Hirchler V, Bugna J, Roque M, Gilligan T, Gonzalez C. Does low birth weight predict obesity/overweight and metabolic syndrome in elementary school children? Arch Med Res. 2008; 39:796–802.
Article21. Ramadhani MI, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Castro Cabezas M, Vos LE, Oren A, et al. Lower birth weight predict metabolic syndrome in young adult: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Young Adults (ARYA) study. Atherosclerosis. 2006; 184:21–7.
Article22. Euser AM, Dekker FW, Hallan SI. Intrauterine growth restriction: no unifying risk factor for the metabolic syndrome in young adults. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010; 17:314–20.
Article23. Pilgaard K, Færch K, Poulsen P, Larsen C, Andersson EA, Pisinger C, et al. Impact of size at birth and prematurity on adult anthropometry in 4744 middle-aged Danes: the Inter99 study. J Dev Orig Health Dis. 2010; 1:319–28.24. Ibáñez L, Ong K, Dunger DB, de Zegher F. Early development of adiposity and insulin resistance after catchup weight gain in small for gestational age children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:2153–8.25. Ibáñez L, López-Bermejo A, Díaz M, Marcos MV, Casano P, de Zegher F. Abdominal fat partitioning and highmolecular-weight adiponectin in short children born small for gestational age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:1049–52.
Article26. Van der Steen M, Smeets CC, Kerkhof GF, Hokken-Koelega AC. Metabolic health of young adults who were born small for gestational age and treated with growth hormone, after cessation of growth hormone treatment: a 5-year longitudinal study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5:106–16.
Article27. Rasmussen EL, Malis C, Jensen CB, Jensen JE, Storgaard H, Poulsen P, et al. Altered fat tissue distribution in young adult men who had low birth weight. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:151–3.
Article28. Mericq V, Martinez-Aguayo A, Uauy R, Iñiguez G, Van der Steen M, Hokken-Koelega A. Long-term metabolic risk among children born premature or small for gestational age. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017; 13:50–62.
Article29. Miras M, Ochetti M, Martín S, Silvano L, Sobrero G, Castro L, et al. Serum levels of adiponectin and leptin in children born small for gestational age: relation to insulin sensitivity parameters. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 23:463–71.
Article30. Andersen LG, Holst C, Michaelsen KF, Baker JL, Sørensen TI. Weight and weight gain during early infancy predict childhood obesity: a case cohort study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2012; 36:1306–11.31. Hong YH, Lee JE. Large for gestational age and obesityrelated comorbidities. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021; 30:124–31.
Article32. Mullett MD, Cottrell L, Lilly C, Gadikota K, Dong L, Hobbs G, et al. Association between birth characteristics and coronary disease risk factors among fifth graders. J Pediatr. 2014; 164:78–82.
Article33. Biosca M, Rodríguez G, Ventura P, Samper MP, Labayen I, Collado MP, et al. Central adiposity in children born small and large for gestational age. Nutr Hosp. 2011; 26:971–6.34. Dolan MS, Sorkin JD, Hoffman DJ. Birth weight is inversely associated with central adipose tissue in healthy children and adolescents. Obesity(Silver Spring). 2007; 15:1600–8.
Article35. Wells JC, Dumith SC, Ekelund U, Reichert FF, Menezes AM, Victora CG, et al. Associations of intrauterine and postnatal weight and length gains with adolescent body composition: prospective birth cohort study from Brazil. J Adolesc Health. 2012; 51(6 Suppl):S58–64.
Article36. Leunissen RW, Stijnen T, Hokken-Koelega AC. Influence of birth size on body composition in early adulthood: the programming factors for growth and metabolism (PROGRAM)-study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009; 70:245–51.
Article37. Longhi S, Mercolini F, Carloni L, Nguyen L, Fanolla A, Radetti G. Prematurity and low birth weight lead to altered bone geometry, strength, and quality in children. J Endocrinol Investig. 2015; 38:563–8.
Article38. Baird J, Kurshid MA, Kim M, Harvey N, Dennison E, Cooper C. Does birth weight predict bone mass in adulthood? A systemic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporosis Int. 2011; 22:1323–34.39. Buttazzoni C, Rosengren B, Tveit M, Landin L, Nilsson JÅ, Karlsson M. Preterm children born small for gestational age are at risk for low adult bone mass. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016; 98:105–13.
Article40. Deodati A, Manco M, Mariani M, Bocchini S, Högler W, Cappa M, et al. Bone density and body composition in small for gestational age children with adequate catch up growth: a preliminary retrospective case control study. Bone. 2021; 153:116114.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Non-Obese Adolescents Born Small for Gestational Age
- Body Composition Changes in Korean Children and Adolescents
- Large for Gestational Age and Obesity-Related Comorbidities
- Age at menarche and adult height in girls born small for gestational age
- The Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents Born Small for Gestational Age