Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2024 Jan;12(1):80-86. 10.14791/btrt.2023.0047.
Central Nervous System Dissemination of Solitary Sporadic Supratentorial Hemangioblastoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of 1 Neurosurgery and 2 Pathology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2552331
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2023.0047
Abstract
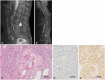
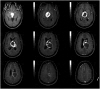
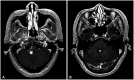
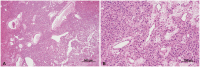
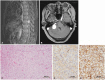
- We report a patient with whole neuroaxis dissemination of a sporadic supratentorial hemangioblastoma (HB) for more than 15 years. A 68-year-old female patient presented with severe radiating pain in the right leg. Gadolinium-enhanced lumbar spine MRI showed an intradural mass (2.5 cm in diameter) at the L4 level. The patient had been severely disabled for 22 years after a previous intraventricular brain tumor resection. At that time, the diagnosis was angioblastic meningioma, which was thought to be incorrect. At 14 years after the brain surgery, gamma knife radiosurgery was performed three times for newly developed or recurred supratentorial and infratentorial tumors in the cerebrospinal fluid pathway. The patient underwent lumbar spinal surgery, and a gross total removal of the mass was performed, which confirmed the histopathological diagnosis of HB. We reexamined the old histopathological specimen of the intraventricular tumor from 20 years ago and changed the diagnosis from angioblastic meningioma to supratentorial HB. Six months after spinal surgery, the patient underwent a second spinal surgery and brain surgery, and the histopathological diagnosis was HB following both surgeries, which was the same following the first spinal surgery. Here, we report a sporadic supratentorial HB patient who showed cranial and spinal disseminations for more than two decades along with a literature review
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bains SJ, Niehusmann PF, Meling TR, Saxhaug C, Zuchner M, Brandal P. Disseminated central nervous system hemangioblastoma in a patient with no clinical or genetic evidence of von Hippel-Lindau disease-a case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2019; 161:343–349. PMID: 30652202.
Article2. Chung SY, Jeun SS, Park JH. Disseminated hemangioblastoma of the central nervous system without von Hippel-Lindau disease. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2014; 2:96–101. PMID: 25408933.
Article3. Kim HR, Suh YL, Kim JW, Lee JI. Disseminated hemangioblastomatosis of the central nervous system without von Hippel-Lindau disease: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:755–759. PMID: 19654966.
Article4. Amelot A, Bouazza S, Polivka M, George B, Bresson D. Sporadically second localization of cerebellar hemangioblastoma in sella turcica mimicking a meningioma with no associated von Hippel-Lindau disease. Br J Neurosurg. 2015; 29:589–591. PMID: 25817084.
Article5. Choyke PL, Glenn GM, Walther MM, Patronas NJ, Linehan WM, Zbar B. von Hippel-Lindau disease: genetic, clinical, and imaging features. Radiology. 1995; 194:629–642. PMID: 7862955.
Article6. Girmens JF, Erginay A, Massin P, Scigalla P, Gaudric A, Richard S. Treatment of von Hippel-Lindau retinal hemangioblastoma by the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor SU5416 is more effective for associated macular edema than for hemangioblastomas. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:194–196. PMID: 12834696.
Article7. Hasselblatt M, Jeibmann A, Gerss J, Behrens C, Rama B, Wassmann H, et al. Cellular and reticular variants of haemangioblastoma revisited: a clinicopathologic study of 88 cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2005; 31:618–622. PMID: 16281910.
Article8. Kato M, Ohe N, Okumura A, Shinoda J, Nomura A, Shuin T, et al. Hemangioblastomatosis of the central nervous system without von Hippel-Lindau disease: a case report. J Neurooncol. 2005; 72:267–270. PMID: 15937651.
Article9. Lee JY, Dong SM, Park WS, Yoo NJ, Kim CS, Jang JJ, et al. Loss of heterozygosity and somatic mutations of the VHL tumor suppressor gene in sporadic cerebellar hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:504–508. PMID: 9458097.10. Omar AI. Bevacizumab for the treatment of surgically unresectable cervical cord hemangioblastoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012; 6:238. PMID: 22883663.
Article11. Raghavan R, Krumerman J, Rushing EJ, White CL 3rd, Chason DP, Watson ML, et al. Recurrent (nonfamilial) hemangioblastomas involving spinal nerve roots: case report. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:1443–1448. PMID: 11126917.
Article12. Ramachandran R, Lee HS, Matthews B, Shatzel A, Tihan T. Intradural extramedullary leptomeningeal hemangioblastomatosis and paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis diagnosed at autopsy: an unlikely pair. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:104–108. PMID: 18181660.
Article13. Takayanagi S, Mukasa A, Tanaka S, Nomura M, Omata M, Yanagisawa S, et al. Differences in genetic and epigenetic alterations between von Hippel-Lindau disease-related and sporadic hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system. Neuro Oncol. 2017; 19:1228–1236. PMID: 28379443.
Article14. Tohyama T, Kubo O, Kusano R, Miura N, Himuro H. [A case of hemangioblastoma with subarachnoid dissemination]. No Shinkei Geka. 1990; 18:83–88. Japanese. PMID: 2304611.15. Bakshi R, Mechtler LL, Patel MJ, Lindsay BD, Messinger S, Gibbons KJ. Spinal leptomeningeal hemangioblastomatosis in von Hippel-Lindau disease: magnetic resonance and pathological findings. J Neuroimaging. 1997; 7:242–244. PMID: 9344008.
Article16. Mohan J, Brownell B, Oppenheimer DR. Malignant spread of haemangioblastoma: report on two cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976; 39:515–525. PMID: 1084914.
Article17. Reyns N, Assaker R, Louis E, Lejeune JP. Leptomeningeal hemangioblastomatosis in a case of von Hippel-Lindau disease: case report. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:1212–1215. discussion 1215-6. PMID: 12699568.
Article18. Weil RJ, Vortmeyer AO, Zhuang Z, Pack SD, Theodore N, Erickson RK, et al. Clinical and molecular analysis of disseminated hemangioblastomatosis of the central nervous system in patients without von Hippel-Lindau disease. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:775–787. PMID: 11990821.
Article19. Hanse MC, Vincent A, van den Bent MJ. Hemangioblastomatosis in a patient with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurooncol. 2007; 82:163–164. PMID: 17256106.
Article20. Akimoto J, Fukuhara H, Suda T, Nagai K, Hashimoto R, Michihiro K. Disseminated cerebellar hemangioblastoma in two patients without von Hippel-Lindau disease. Surg Neurol Int. 2014; 5:145. PMID: 25324974.
Article21. Seystahl K, Weller M, Bozinov O, Reimann R, Rushing E. Neuropathological characteristics of progression after prolonged response to bevacizumab in multifocal hemangioblastoma. Oncol Res Treat. 2014; 37:209–212. PMID: 24732646.
Article22. Kim H, Park IS, Jo KW. Meningeal supratentorial hemangioblastoma in a patient with von Hippel-Lindau disease mimicking angioblastic menigioma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013; 54:415–419. PMID: 24379949.
Article23. Crivelli G, Dario A, Cerati M, Dorizzi A. Solid supratentorial haemangioblastoma. Case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 1992; 36:161–166. PMID: 1484303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multifocal Spinal Hemangioblastoma in von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case Report of Recurrent and Disseminated Cerebellar Hemangioblastoma
- Congenital Cystic Supratentorial Hemangioblastoma Associated with Intracystic Hemorrhage: Case Report
- Supratentorial Meningeal Hemangioblastoma: Case Report
- Disseminated Hemangioblastoma of the Central Nervous System without Von Hippel-Lindau Disease