Ann Lab Med.
2023 Sep;43(5):493-502. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.493.
Status of Pre-analytical Quality Management of Laboratory Tests at Primary Clinics in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 4Seegene Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Gwangju & Honam Reference Laboratory, Seegene Medical Foundation, Gwangju, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551998
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.493
Abstract
- Background
The quality of laboratory test results is crucial for accurate clinical diagnosis and treatment. Pre-analytical errors account for approximately 60%–70% of all laboratory test errors. Laboratory test results may be largely impacted by pre-analytical phase management. However, primary care clinics currently do not have pre-analytical quality management audit systems. We aimed to understand the current status of pre-analytical quality management in laboratory medicine in Korean primary care clinics.
Methods
Questionnaires were designed to focus on essential components of the pre-analytical process of primary care clinics. An online survey platform was used to administer the survey to internal medicine or family medicine physicians in primary care clinics.
Results
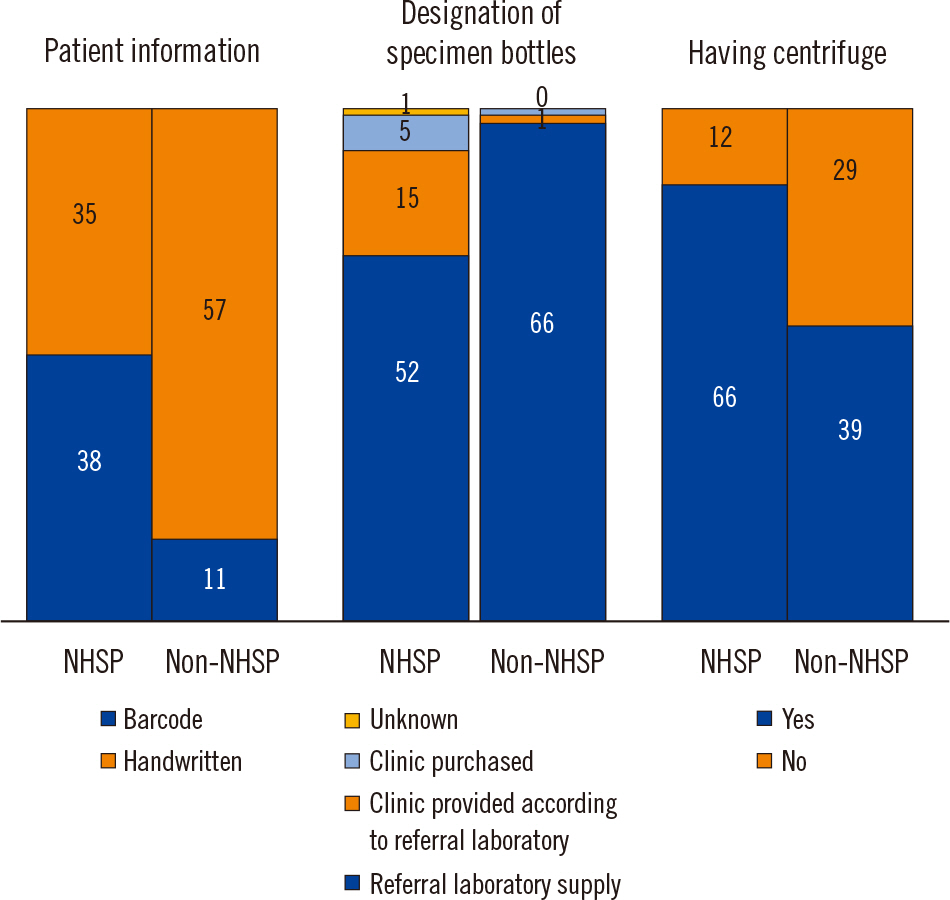
A total of 141 physicians provided a complete response to the questionnaire. In 65.2% of the clinics, patient information was hand-labeled rather than barcoded on the specimen bottles; 14.2% of clinics displayed only one piece of patient information (name or identification number), and 19.9% of clinics displayed two pieces of information. Centrifuges were not available in 29.1% of the clinics. Institutions carrying out the National Health Screening Program (NHSP) used more barcode system and had more centrifuges than institutions that did not carrying out the NHSP.
Conclusions
Pre-analytical quality management is inadequate in many primary clinics. We suggest implementation of a mandatory management system, allowing for a pre-analytical quality management to be carried out in primary care clinics.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Plebani M. 2010; The detection and prevention of errors in laboratory medicine. Ann Clin Biochem. 47:101–10. DOI: 10.1258/acb.2009.009222. PMID: 19952034.
Article2. Bonini P, Plebani M, Ceriotti F, Rubboli F. 2002; Errors in laboratory medicine. Clin Chem. 48:691–8. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/48.5.691. PMID: 11978595.
Article3. Carraro P, Plebani M. 2007; Errors in a stat laboratory: types and frequencies 10 years later. Clin Chem. 53:1338–42. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.088344. PMID: 17525103.
Article4. Chang J, Kim S, Yoo SJ, Park EJ, Um TH, Cho CR. 2020; Preanalytical errors in the central laboratory of a university hospital based on the analysis of year-round data. Clin Lab. 66:200110. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200110. PMID: 32902239.
Article5. Heireman L, Van Geel P, Musger L, Heylen E, Uyttenbroeck W, Mahieu B. 2017; Causes, consequences and management of sample hemolysis in the clinical laboratory. Clin Biochem. 50:1317–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.09.013. PMID: 28947321.
Article6. Daves M, Roccaforte V, Giacomi M, Riva M, Leitner M, Platzgummer S, et al. 2017; Effect of delayed centrifugation of whole blood on serum samples stability. Riv Ital Med Lab. 13:41–4. DOI: 10.1007/s13631-017-0146-x.
Article7. Laboratory Medicine Foundation. https://lmf.or.kr/. Updated on Dec 2022.8. Kim H, Kim S, Yun YM, Um TH, Chang J, Lee KS, et al. 2020; Status of quality control for laboratory tests of medical institutions in Korea: analysis of 10 years of data on external quality assessment participation. Healthcare (Basel). 8:75. DOI: 10.3390/healthcare8020075. PMID: 32230819. PMCID: PMC7349217.
Article9. Lippi G, Chance JJ, Church S, Dazzi P, Fontana R, Giavarina D, et al. 2011; Preanalytical quality improvement: from dream to reality. Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:1113–26. DOI: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.600. PMID: 21517699.
Article10. CLSI. 2019. Accuracy in patient and specimen identification. 2nd ed. CLSI GP33. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:11. CLSI. 2010. Tubes and additives for venous and capillary blood specimen collection. CLSI GP39-A6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:12. CLSI. 2017. Collection of diagnostic venous blood specimens. 7th ed. CLSI GP41. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:13. CLSI. 2010. Procedures for the handling and processing of blood specimens for common laboratory tests. 4th ed. CLSI GP44. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:14. CLSI. 2017. Essential elements of a phlebotomy training program. 1st ed. CLSI GP48. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:15. Chong M-S, Lee K. 2021; Survey of the referral laboratory sample managements of medical clinics in Jeju Island. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 43:94–106. DOI: 10.15263/jlmqa.2021.43.2.94.
Article16. Wan Azman WN, Omar J, Koon TS, Tuan Ismail TS. 2019; Hemolyzed specimens: major challenge for identifying and rejecting specimens in clinical laboratories. Oman Med J. 34:94–8. DOI: 10.5001/omj.2019.19. PMID: 30918601. PMCID: PMC6425048.
Article17. Alammari D, Banta JE, Shah H, Reibling E, Ramadan M. 2021; Meaningful use of electronic health records and ambulatory healthcare quality measures. Cureus. 13:e13036. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.13036.
Article18. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. Hospital progress to meaningful use. https://www.healthit.gov/data/quickstats/hospital-progress-meaningful-use. Updated on Aug 2017.19. Lee J, Koh J, Kim JY. 2021; Popularization of medical information. Healthc Inform Res. 27:110–5. DOI: 10.4258/hir.2021.27.2.110. PMID: 34015876. PMCID: PMC8137873.
Article20. Kim YG, Jung K, Park YT, Shin D, Cho SY, Yoon D, et al. 2017; Rate of electronic health record adoption in South Korea: a nation-wide survey. Int J Med Inform. 101:100–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.02.009. PMID: 28347440.
Article21. Logical observation identifiers names and codes. About LOINC. https://loinc.org/about/. Updated on Dec 2022.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Risk Management in the Clinical Laboratory
- Diagnostic Stewardship on the Extra-Analytical Phase to Secure Quality Assurance of Diagnostic Tests for Clostridioides difficile Infection
- Analysis of Factors Influencing the Generation of Unqualified Clinical Samples and Measures to Prevent this Generation
- HbA1c: A Review of Analytical and Clinical Aspects
- Managing the Pre- and Post-analytical Phases of the Total Testing Process