J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Feb;39(5):e53. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e53.
Early Prediction of Mortality for Septic Patients Visiting Emergency Room Based on Explainable Machine Learning: A Real-World Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Informatics, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Institute of Medical Science, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3Department of Medical Bigdata Convergence, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 4Department of Convergence Security, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 5Department of Biomedical Research Institute, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea
- 6University-Industry Cooperation Foundation, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 7Department of Research and Development, ZIOVISION Co. Ltd., Chuncheon, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 10Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 11Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Seoul National University of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea
- 12Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e53
Abstract
- Background
Worldwide, sepsis is the leading cause of death in hospitals. If mortality rates in patients with sepsis can be predicted early, medical resources can be allocated efficiently. We constructed machine learning (ML) models to predict the mortality of patients with sepsis in a hospital emergency department.
Methods
This study prospectively collected nationwide data from an ongoing multicenter cohort of patients with sepsis identified in the emergency department. Patients were enrolled from 19 hospitals between September 2019 and December 2020. For acquired data from 3,657 survivors and 1,455 deaths, six ML models (logistic regression, support vector machine, random forest, extreme gradient boosting [XGBoost], light gradient boosting machine, and categorical boosting [CatBoost]) were constructed using fivefold cross-validation to predict mortality. Through these models, 44 clinical variables measured on the day of admission were compared with six sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) components (PaO 2 /FIO 2 [PF], platelets (PLT), bilirubin, cardiovascular, Glasgow Coma Scale score, and creatinine). The confidence interval (CI) was obtained by performing 10,000 repeated measurements via random sampling of the test dataset. All results were explained and interpreted using Shapley’s additive explanations (SHAP).
Results
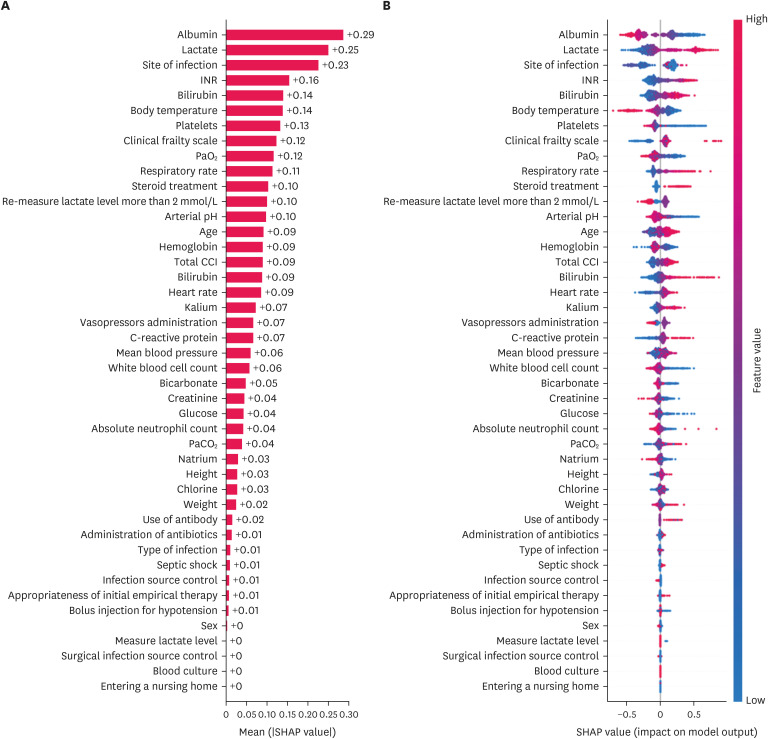
Of the 5,112 participants, CatBoost exhibited the highest area under the curve (AUC) of 0.800 (95% CI, 0.756–0.840) using clinical variables. Using the SOFA components for the same patient, XGBoost exhibited the highest AUC of 0.678 (95% CI, 0.626–0.730). As interpreted by SHAP, albumin, lactate, blood urea nitrogen, and international normalization ratio were determined to significantly affect the results. Additionally, PF and PLTs in the SOFA component significantly influenced the prediction results.
Conclusion
Newly established ML-based models achieved good prediction of mortality in patients with sepsis. Using several clinical variables acquired at the baseline can provide more accurate results for early predictions than using SOFA components. Additionally, the impact of each variable was identified.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rudd KE, Kissoon N, Limmathurotsakul D, Bory S, Mutahunga B, Seymour CW, et al. The global burden of sepsis: barriers and potential solutions. Crit Care. 2018; 22(1):232. PMID: 30243300.2. Park DW, Chun BC, Kim JM, Sohn JW, Peck KR, Kim YS, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of community-acquired severe sepsis and septic shock: a prospective observational study in 12 university hospitals in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27(11):1308–1314. PMID: 23166410.3. Reaven MS, Rozario NL, McCarter MS, Heffner AC. Incidence and risk factors associated with early death in patients with emergency department septic shock. Acute Crit Care. 2022; 37(2):193–201. PMID: 35172528.4. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8):801–810. PMID: 26903338.5. Kim HI, Park S. Sepsis: early recognition and optimized treatment. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2019; 82(1):6–14. PMID: 30302954.6. Seymour CW, Kennedy JN, Wang S, Chang CH, Elliott CF, Xu Z, et al. Derivation, validation, and potential treatment implications of novel clinical phenotypes for sepsis. JAMA. 2019; 321(20):2003–2017. PMID: 31104070.7. Liu H, Zhang L, Xu F, Li S, Wang Z, Han D, et al. Establishment of a prognostic model for patients with sepsis based on SOFA: a retrospective cohort study. J Int Med Res. 2021; 49(9):3000605211044892. PMID: 34586931.8. Thakur R, Naga Rohith V, Arora JK. Mean SOFA score in comparison with APACHE II score in predicting mortality in surgical patients with sepsis. Cureus. 2023; 15(3):e36653. PMID: 37113362.9. Koozi H, Lidestam A, Lengquist M, Johnsson P, Frigyesi A. A simple mortality prediction model for sepsis patients in intensive care. J Intensive Care Soc. 2023; 24(4):372–378. PMID: 37841294.10. Li W, Wang M, Zhu B, Zhu Y, Xi X. Prediction of median survival time in sepsis patients by the SOFA score combined with different predictors. Burns Trauma. 2020; 8:tkz006. PMID: 32346543.11. Pan X, Xie J, Zhang L, Wang X, Zhang S, Zhuang Y, et al. Evaluate prognostic accuracy of SOFA component score for mortality among adults with sepsis by machine learning method. BMC Infect Dis. 2023; 23(1):76. PMID: 36747139.12. Yang J, Liao Y, Dai Y, Hu L, Cai Y. Prediction of prognosis in sepsis patients by the SOFA score combined with miR-150. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2022; 31(1):9–15. PMID: 34738345.13. Liu Z, Meng Z, Li Y, Zhao J, Wu S, Gou S, et al. Prognostic accuracy of the serum lactate level, the SOFA score and the qSOFA score for mortality among adults with Sepsis. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2019; 27(1):51. PMID: 31039813.14. Li Y, Yan C, Gan Z, Xi X, Tan Z, Li J, et al. Prognostic values of SOFA score, qSOFA score, and LODS score for patients with sepsis. Ann Palliat Med. 2020; 9(3):1037–1044. PMID: 32498525.15. Yue S, Li S, Huang X, Liu J, Hou X, Zhao Y, et al. Machine learning for the prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis. J Transl Med. 2022; 20(1):215. PMID: 35562803.16. Kijpaisalratana N, Sanglertsinlapachai D, Techaratsami S, Musikatavorn K, Saoraya J. Machine learning algorithms for early sepsis detection in the emergency department: a retrospective study. Int J Med Inform. 2022; 160:104689. PMID: 35078027.17. Yao RQ, Jin X, Wang GW, Yu Y, Wu GS, Zhu YB, et al. A machine learning-based prediction of hospital mortality in patients with postoperative sepsis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020; 7:445. PMID: 32903618.18. Moor M, Rieck B, Horn M, Jutzeler CR, Borgwardt K. Early prediction of sepsis in the ICU using machine learning: a systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:607952. PMID: 34124082.19. Du M, Haag DG, Lynch JW, Mittinty MN. Comparison of the tree-based machine learning algorithms to cox regression in predicting the survival of oral and pharyngeal cancers: ANALYSES based on SEER database. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12(10):2802. PMID: 33003533.20. Hou N, Li M, He L, Xie B, Wang L, Zhang R, et al. Predicting 30-days mortality for MIMIC-III patients with sepsis-3: a machine learning approach using XGboost. J Transl Med. 2020; 18(1):462. PMID: 33287854.21. Hu CA, Chen CM, Fang YC, Liang SJ, Wang HC, Fang WF, et al. Using a machine learning approach to predict mortality in critically ill influenza patients: a cross-sectional retrospective multicentre study in Taiwan. BMJ Open. 2020; 10(2):e033898.22. Rodríguez A, Mendoza D, Ascuntar J, Jaimes F. Supervised classification techniques for prediction of mortality in adult patients with sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. 2021; 45:392–397. PMID: 33036848.23. Greco M, Caruso PF, Spano S, Citterio G, Desai A, Molteni A, et al. Machine learning for early outcome prediction in septic patients in the emergency department. Algorithms. 2023; 16(2):76.24. van Doorn WP, Stassen PM, Borggreve HF, Schalkwijk MJ, Stoffers J, Bekers O, et al. A comparison of machine learning models versus clinical evaluation for mortality prediction in patients with sepsis. PLoS One. 2021; 16(1):e0245157. PMID: 33465096.25. Kong G, Lin K, Hu Y. Using machine learning methods to predict in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the ICU. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020; 20(1):251. PMID: 33008381.26. Park S, Jeon K, Oh DK, Choi EY, Seong GM, Heo J, et al. Normothermia in patients with sepsis who present to emergency departments is associated with low compliance with sepsis bundles and increased in-hospital mortality rate. Crit Care Med. 2020; 48(10):1462–1470. PMID: 32931189.27. Valera Durán M. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Rev Electron AnestesiaR. 2017; 9:2.28. Na SJ, Oh DK, Park S, Lee YJ, Hong SB, Park MH, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of neutropenic sepsis: a multicenter cohort study. Shock. 2022; 57(5):659–665. PMID: 35066514.29. Yeo HJ, Lee YS, Kim TH, Jang JH, Lee HB, Oh DK, et al. Vasopressor initiation within 1 hour of fluid loading is associated with increased mortality in septic shock patients: analysis of national registry data. Crit Care Med. 2022; 50(4):e351–e360. PMID: 34612848.30. Jeon K, Na SJ, Oh DK, Park S, Choi EY, Kim SC, et al. Characteristics, management and clinical outcomes of patients with sepsis: a multicenter cohort study in Korea. Acute Crit Care. 2019; 34(3):179–191. PMID: 31723927.31. Singh D, Singh B. Investigating the impact of data normalization on classification performance. Appl Soft Comput. 2020; 97:105524.32. Feng J, Xu H, Mannor S, Yan S. Robust logistic regression and classification. In : NIPS'14: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; December 8-13, 2014; Montreal, Canada. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press;2014. p. 253–261.33. Cortes C, Vapnik V. Support-vector networks. Mach Learn. 1995; 20(3):273–297.34. Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001; 45(1):5–32.35. Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In : Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. KDD’16; August 13-17, 2016; San Francisco, CA, USA. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery;2016. p. 785–794.36. Ke G, Meng Q, Finley T, Wang T, Chen W, Ma W, et al. LightGBM: a highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2017; 30:3149–3157.37. Prokhorenkova L, Gusev G, Vorobev A, Dorogush AV, Gulin A. CatBoost: unbiased boosting with categorical features. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2018; 31:6638–6648.38. Lundberg SM, Lee SI. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2017; 30:4765–4774.39. Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2011; 12(85):2825–2830.40. Akiba T, Sano S, Yanase T, Ohta T, Koyama M. Optuna: a next-generation hyperparameter optimization framework. In : Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining; August 4-8, 2019; Anchorage, AK, USA. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery;2019. p. 2623–2631.41. Amland RC, Hahn-Cover KE. Clinical decision support for early recognition of sepsis. Am J Med Qual. 2019; 34(5):494–501. PMID: 31479290.42. Do SN, Dao CX, Nguyen TA, Nguyen MH, Pham DT, Nguyen NT, et al. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score for predicting mortality in patients with sepsis in Vietnamese intensive care units: a multicentre, cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2023; 13(3):e064870.43. Moreno R, Rhodes A, Piquilloud L, Hernandez G, Takala J, Gershengorn HB, et al. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score: has the time come for an update? Crit Care. 2023; 27(1):15. PMID: 36639780.44. Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, Brunkhorst FM, Rea TD, Scherag A, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315(8):762–774. PMID: 26903335.45. Schinkel M, Nanayakkara PW, Wiersinga WJ. Sepsis performance improvement programs: from evidence toward clinical implementation. Crit Care. 2022; 26(1):77. PMID: 35337358.46. Burney M, Underwood J, McEvoy S, Nelson G, Dzierba A, Kauari V, et al. Early detection and treatment of severe sepsis in the emergency department: identifying barriers to implementation of a protocol-based approach. J Emerg Nurs. 2012; 38(6):512–517. PMID: 22079648.47. Rajula HS, Verlato G, Manchia M, Antonucci N, Fanos V. Comparison of conventional statistical methods with machine learning in medicine: diagnosis, drug development, and treatment. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020; 56(9):455. PMID: 32911665.48. Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Winslow C, Meltzer DO, Kattan MW, Edelson DP. Multicenter comparison of machine learning methods and conventional regression for predicting clinical deterioration on the wards. Crit Care Med. 2016; 44(2):368–374. PMID: 26771782.49. Nohara Y, Matsumoto K, Soejima H, Nakashima N. Explanation of machine learning models using shapley additive explanation and application for real data in hospital. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022; 214:106584. PMID: 34942412.50. Janiesch C, Zschech P, Heinrich K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electron Mark. 2021; 31(3):685–695.51. Ribas Ripoll VJ, Vellido A, Romero E, Ruiz-Rodríguez JC. Sepsis mortality prediction with the Quotient Basis Kernel. Artif Intell Med. 2014; 61(1):45–52. PMID: 24726036.52. Zhang Z, Hong Y. Development of a novel score for the prediction of hospital mortality in patients with severe sepsis: the use of electronic healthcare records with LASSO regression. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(30):49637–49645. PMID: 28548951.53. Li X, Zhou Y, Dvornek NC, Gu Y, Ventola P, Duncan JS. Efficient Shapley explanation for features importance estimation under uncertainty. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2020; 12261:792–801. PMID: 34308439.54. Bakker J, Nijsten MW, Jansen TC. Clinical use of lactate monitoring in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2013; 3(1):12. PMID: 23663301.55. Quinlan GJ, Martin GS, Evans TW. Albumin: biochemical properties and therapeutic potential. Hepatology. 2005; 41(6):1211–1219. PMID: 15915465.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predicting the mortality of pneumonia patients visiting the emergency department through machine learning
- Explainable machine learning using perioperative serial laboratory results to predict postoperative mortality in patients with peritonitis-induced sepsis
- Machine Learning vs. Statistical Model for Prediction Modelling: Application in Medical Imaging Research
- Explainable artificial intelligence in emergency medicine: an overview
- Clinical Study of Hospital Mortality in Patients Visiting the Emergency Room at Nighttime in a City of Korea