Ann Surg Treat Res.
2023 Oct;105(4):237-244. 10.4174/astr.2023.105.4.237.
Explainable machine learning using perioperative serial laboratory results to predict postoperative mortality in patients with peritonitis-induced sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Medical Informatics & Statistics, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2023.105.4.237
Abstract
- Purpose
Sepsis is one of the most common causes of death after surgery. Several conventional scoring systems have been developed to predict the outcome of sepsis; however, their predictive power is insufficient. The present study applies explainable machine-learning algorithms to improve the accuracy of predicting postoperative mortality in patients with sepsis caused by peritonitis.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of data from demographic, clinical, and laboratory analyses, including the delta neutrophil index (DNI), WBC and neutrophil counts, and CRP level. Laboratory data were measured before surgery, 12–36 hours after surgery, and 60–84 hours after surgery. The primary study output was the probability of mortality. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) of several machine-learning algorithms using the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS) 3 models were compared. ‘SHapley Additive exPlanations’ values were used to indicate the direction of the relationship between a variable and mortality.
Results
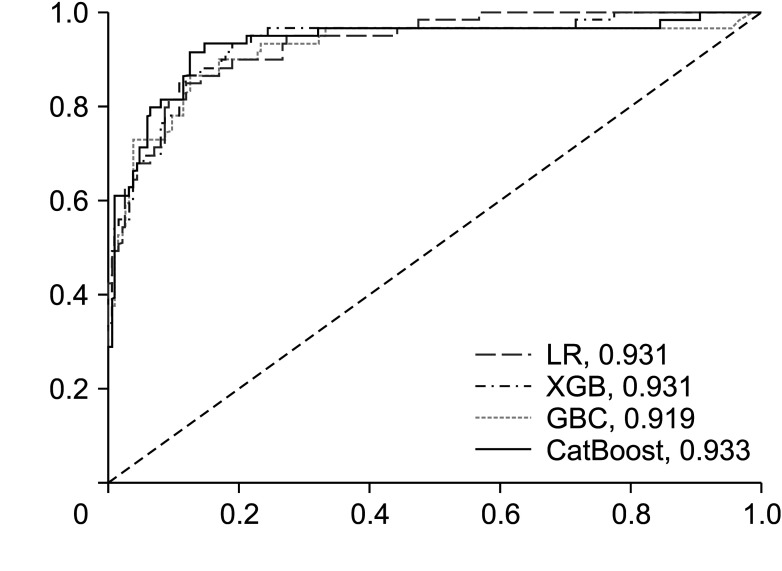
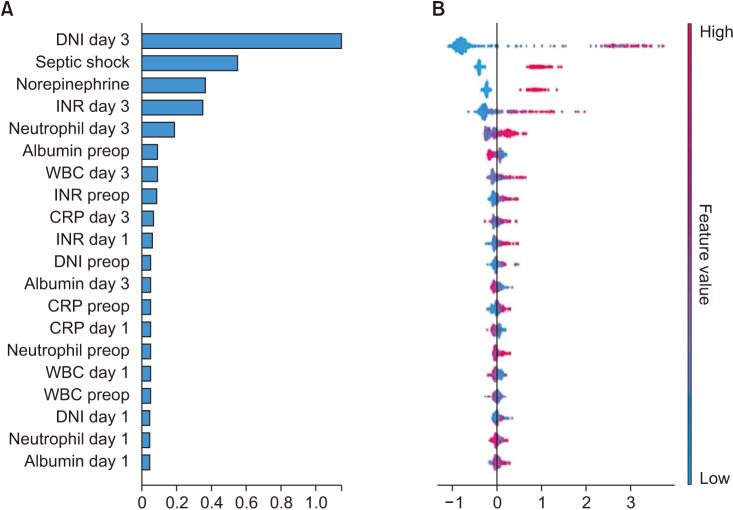
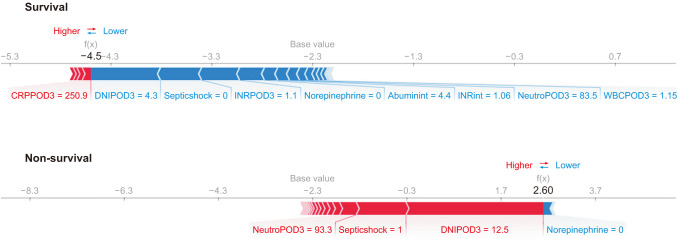
The CatBoost model yielded the highest AUC (0.933) for mortality compared to SAPS3 and SOFA (0.860 and 0.867, respectively). Increased DNI on day 3, septic shock, use of norepinephrine therapy, and increased international normalized ratio on day 3 had the greatest impact on the model’s prediction of mortality.
Conclusion
Machine-learning algorithms increase the accuracy of predicting postoperative mortality in patients with sepsis caused by peritonitis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1368–1377. PMID: 11794169.2. Coen D, Cortellaro F, Pasini S, Tombini V, Vaccaro A, Montalbetti L, et al. Towards a less invasive approach to the early goal-directed treatment of septic shock in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2014; 32:563–568. PMID: 24666743.3. Jo YH, Kim K, Lee JH, Kang C, Kim T, Park HM, et al. Red cell distribution width is a prognostic factor in severe sepsis and septic shock. Am J Emerg Med. 2013; 31:545–548. PMID: 23380094.
Article4. Dickinson JD, Kollef MH. Early and adequate antibiotic therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2011; 13:399–405. PMID: 21822574.
Article5. Huttunen R, Aittoniemi J. New concepts in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of bacteremia and sepsis. J Infect. 2011; 63:407–419. PMID: 21840338.
Article6. Pierrakos C, Vincent JL. Sepsis biomarkers: a review. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R15. PMID: 20144219.
Article7. Kofoed K, Andersen O, Kronborg G, Tvede M, Petersen J, Eugen-Olsen J, et al. Use of plasma C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, neutrophils, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in combination to diagnose infections: a prospective study. Crit Care. 2007; 11:R38. PMID: 17362525.
Article8. Shapiro NI, Trzeciak S, Hollander JE, Birkhahn R, Otero R, Osborn TM, et al. A prospective, multicenter derivation of a biomarker panel to assess risk of organ dysfunction, shock, and death in emergency department patients with suspected sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37:96–104. PMID: 19050610.
Article9. Kang MW, Kim J, Kim DK, Oh KH, Joo KW, Kim YS, et al. Machine learning algorithm to predict mortality in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Crit Care. 2020; 24:42. PMID: 32028984.
Article10. Yang F, Wang HZ, Mi H, Lin CD, Cai WW. Using random forest for reliable classification and cost-sensitive learning for medical diagnosis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009; 10 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S22.
Article11. Obermeyer Z, Emanuel EJ. Predicting the future: big data, machine learning, and clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1216–1219. PMID: 27682033.
Article12. Lauritsen SM, Kristensen M, Olsen MV, Larsen MS, Lauritsen KM, Jørgensen MJ, et al. Explainable artificial intelligence model to predict acute critical illness from electronic health records. Nat Commun. 2020; 11:3852. PMID: 32737308.
Article13. Kong G, Lin K, Hu Y. Using machine learning methods to predict in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the ICU. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020; 20:251. PMID: 33008381.
Article14. Lin MY, Li CC, Lin PH, Wang JL, Chan MC, Wu CL, et al. Explainable machine learning to predict successful weaning among patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: a retrospective cohort study in central Taiwan. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:663739. PMID: 33968967.
Article15. Zhang Z, Beck MW, Winkler DA, Huang B, Sibanda W, Goyal H, et al. Opening the black box of neural networks: methods for interpreting neural network models in clinical applications. Ann Transl Med. 2018; 6:216. PMID: 30023379.
Article16. Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:1250–1256. PMID: 12682500.
Article17. Moreno RP, Metnitz PG, Almeida E, Jordan B, Bauer P, Campos RA, et al. SAPS 3: from evaluation of the patient to evaluation of the intensive care unit. Part 2: development of a prognostic model for hospital mortality at ICU admission. Intensive Care Med. 2005; 31:1345–1355. PMID: 16132892.
Article18. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996; 22:707–710. PMID: 8844239.
Article19. Keats AS. The ASA classification of physical status: a recapitulation. Anesthesiology. 1978; 49:233–236. PMID: 697075.20. Ali Moez. PyCaret 3.0: an open-source, low-code machine learning library in Python [Internet]. 2020. Available from: https://pycaret.gitbook.io/docs/.21. Lundberg SM, Lee SI. In : von Luxburg U, Guyon I, Bengio S, Wallach H, Fergus R, editors. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. NIPS'17: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; 2017 Dec 4-9; Long Beach (CA). Curran Associates Inc.;2017. p. 4768–4777.22. Bi S, Chen S, Li J, Gu J. Machine learning-based prediction of in-hospital mortality for post cardiovascular surgery patients admitting to intensive care unit: a retrospective observational cohort study based on a large multi-center critical care database. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022; 226:107115. PMID: 36126435.23. Basile-Filho A, Lago AF, Menegueti MG, Nicolini EA, Rodrigues LA, Nunes RS, et al. The use of APACHE II, SOFA, SAPS 3, C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, and lactate to predict mortality of surgical critically ill patients: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e16204. PMID: 31261567.24. Pawar RD, Shih JA, Balaji L, Grossestreuer AV, Patel PV, Hansen CK, et al. Variation in SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) Score Performance in Different Infectious States. J Intensive Care Med. 2021; 36:1217–1222. PMID: 32799718.25. Kim JW, Park JH, Kim DJ, Choi WH, Cheong JC, Kim JY. The delta neutrophil index is a prognostic factor for postoperative mortality in patients with sepsis caused by peritonitis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0182325. PMID: 28763506.26. Arts DG, de Keizer NF, Vroom MB, de Jonge E. Reliability and accuracy of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scoring. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:1988–1993. PMID: 16148470.
Article27. Pirracchio R, Petersen ML, Carone M, Rigon MR, Chevret S, van der Laan MJ. Mortality prediction in intensive care units with the Super ICU Learner Algorithm (SICULA): a population-based study. Lancet Respir Med. 2015; 3:42–52. PMID: 25466337.
Article28. Fransvea P, Fransvea G, Liuzzi P, Sganga G, Mannini A, Costa G. Study and validation of an explainable machine learning-based mortality prediction following emergency surgery in the elderly: a prospective observational study. Int J Surg. 2022; 107:106954. PMID: 36229017.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Prediction of Mortality for Septic Patients Visiting Emergency Room Based on Explainable Machine Learning: A Real-World Multicenter Study
- Explainable artificial intelligence in emergency medicine: an overview
- Predicting the mortality of pneumonia patients visiting the emergency department through machine learning
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning’s role in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- Use of Machine Learning in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Narrative Review