Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jan;43(1):92-95. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.92.
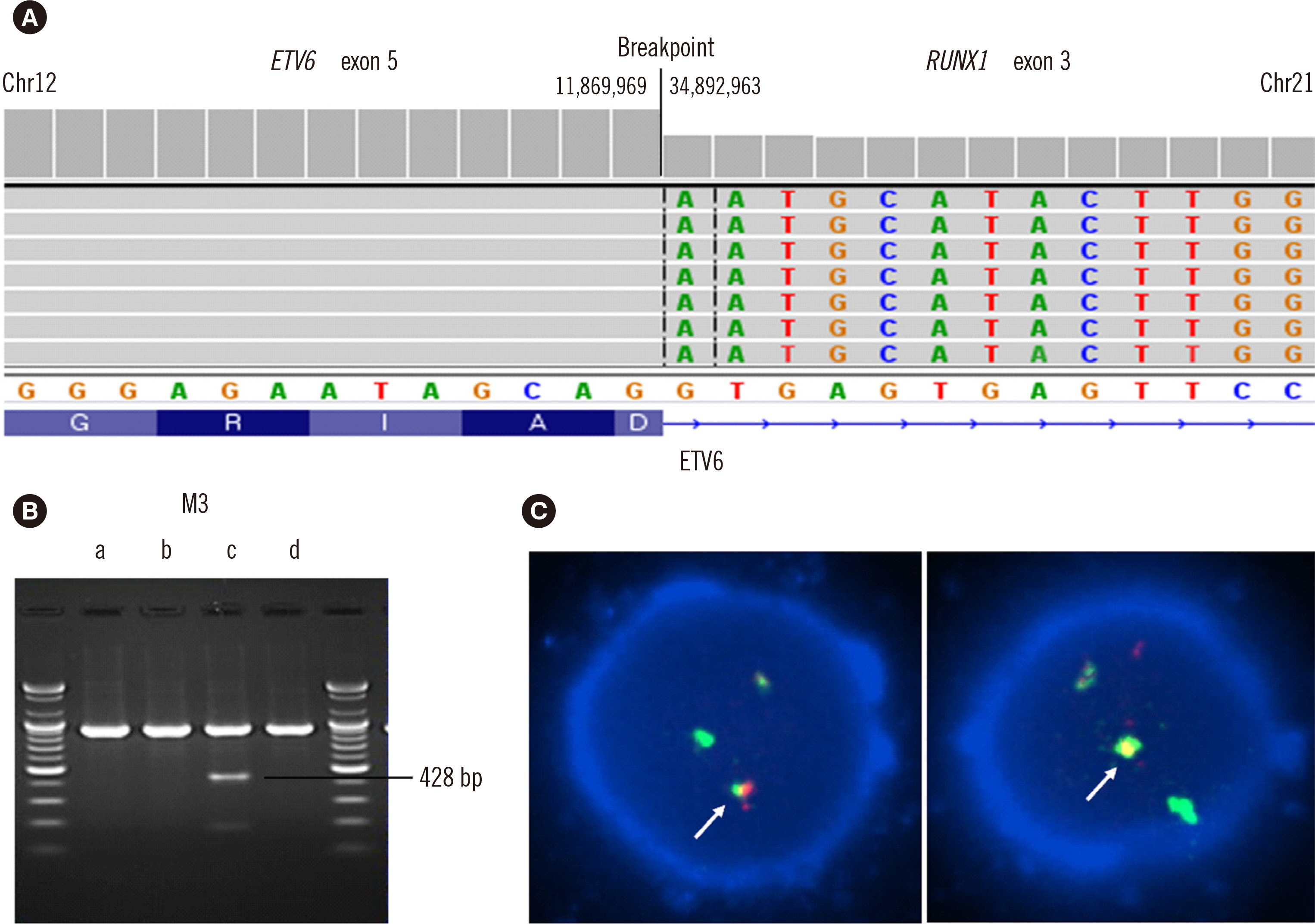
First Case of ETV6–RUNX1 Fusion in Adult De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia Detected Using Targeted RNA Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2551608
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.92
Figure
Reference
-
1. Linka Y, Ginzel S, Krüger M, Novosel A, Gombert M, Kremmer E, et al. 2013; The impact of TEL-AML1 (ETV6-RUNX1) expression in precursor B cells and implications for leukaemia using three different genome-wide screening methods. Blood Cancer J. 3:e151. DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2013.48. PMID: 24121163. PMCID: PMC3816209.
Article2. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. 2008. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 5th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer;Lyon: p. 250.3. Bohlander SK. 2005; ETV6: a versatile player in leukemogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 15:162–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.01.008. PMID: 15826831.
Article4. Fischer M, Schwieger M, Horn S, Niebuhr B, Ford A, Roscher S, et al. 2005; Defining the oncogenic function of the TEL/AML1 (ETV6/RUNX1) fusion protein in a mouse model. Oncogene. 24:7579–91. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208931. PMID: 16044150.
Article5. Lee JJ, Cho H, Park KS, Kim YJ, Cho SY, Han JJ, et al. 2021; First case report of acute myeloid leukemia with MN1-ETV6 rearrangement at relapse. Lab Med Online. 11:145–8. DOI: 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.2.145.
Article6. Kim KH, Kim MJ, Ahn JY, Park PW, Seo YH, Jeong JH. 2016; Acute myeloid leukemia with t(4;12)(q12;p13): report of 2 cases. Blood Res. 51:133–7. DOI: 10.5045/br.2016.51.2.133. PMID: 27382559. PMCID: PMC4931932.
Article7. Higgins A, Shah MV. 2020; Genetic and genomic landscape of secondary and therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Genes (Basel). 11:749. DOI: 10.3390/genes11070749. PMID: 32640569. PMCID: PMC7397259.
Article8. Deltcheva E, Nimmo R. 2017; RUNX transcription factors at the interface of stem cells and cancer. Biochem J. 474:1755–68. DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160632. PMID: 28490659.
Article9. Sood R, Kamikubo Y, Liu P. Role of RUNX1 in hematological malignancies. Blood. 2017; 129:2070–82. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-687830. PMID: 28179279. PMCID: PMC5391618.
Article10. Rodríguez-Hernández G, Casado-García A, Isidro-Hernández M, Picard D, Raboso-Gallego J, Alemán-Arteaga S, et al. 2021; The second oncogenic hit determines the cell fate of ETV6-RUNX1 positive leukemia. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:704591. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.704591. PMID: 34336858. PMCID: PMC8320889.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Concurrent Chromosomal Aberrations Involving Three-way t(3;21;8)(p21;q22;q22) and Two-way t(2;11)(q31;p15) Translocations in a Case of de novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Myeloid Sarcoma in Patients with RUNX1/RUNX1T1 Positive AML and a c-kit Mutation
- First Case Report of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with MN1-ETV6 Rearrangement at Relapse
- Outcome and Prognostic Factors for ETV6/RUNX1 Positive Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated at a Single Institution in Korea
- Rapid Detection of Prognostically Significant Fusion Transcripts in Acute Leukemia Using Simplified Multiplex Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction