Lab Med Online.
2016 Oct;6(4):246-249. 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.4.246.
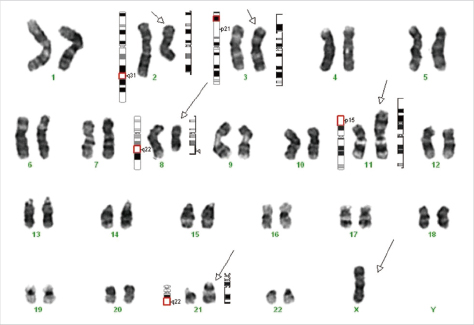
Two Concurrent Chromosomal Aberrations Involving Three-way t(3;21;8)(p21;q22;q22) and Two-way t(2;11)(q31;p15) Translocations in a Case of de novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. creatgeon@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Green Cross Genome, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 2353427
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2016.6.4.246
Abstract
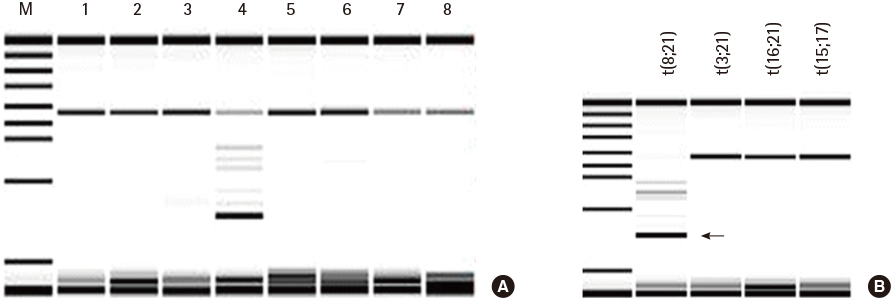
- One of the most frequent structural chromosomal anomaly is t(8;21)(q22;q22) that occurs in approximately 5-15% of all acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, t(3;21)(p21;q22) and t(2;11)(q31;p15) translocations are rarely reported in AML. Here, we report a unique case of AML with two translocations, t(3;21;8)(p21;q22;q22) and t(2;11)(q31;p15). Using multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, we identified a RUNX1-RUNX1T1 fusion gene. Following a second relapse, the patient did not respond to therapy and died 55 months following the first diagnosis. We believe that this is the first case describing concurrent chromosomal aberrations involving three-way t(3;21;8) and two-way t(2;11) translocations in de novo acute myeloid leukemia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Xiao Z, Greaves MF, Buffler P, Smith MT, Segal MR, Dicks BM, et al. Molecular characterization of genomic AML1-ETO fusions in childhood leukemia. Leukemia. 2001; 15:1906–1913.
Article2. Kim H, Kim M, Lim J, Kim Y, Han K, Kim SY, et al. A case of acute myeloid leukemia with masked t(8;21). Korean J Lab Med. 2006; 26:338–342.
Article3. Peterson LF, Boyapati A, Ahn EY, Biggs JR, Okumura AJ, Lo MC, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia with the 8q22;21q22 translocation: secondary mutational events and alternative t(8;21) transcripts. Blood. 2007; 110:799–805.
Article4. Vundinti BR, Kerketta L, Madkaikar M, Jijina F, Ghosh K. Three way translocation in a new variant of t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia involving Xp22. Indian J Cancer. 2008; 45:30–32.
Article5. Chen Z, Sandberg AA. Molecular cytogenetic aspects of hematological malignancies: clinical implications. Am J Med Genet. 2002; 115:130–141.
Article6. Taketani T, Taki T, Shibuya N, Ito E, Kitazawa J, Terui K, et al. The HO-XD11 gene is fused to the NUP98 gene in acute myeloid leukemia with t(2;11)(q31;p15). Cancer Res. 2002; 62:33–37.7. Huang L, Abruzzo LV, Valbuena JR, Medeiros LJ, Lin P. Acute myeloid leukemia associated with variant t(8;21) detected by conventional cytogenetic and molecular studies: a report of four cases and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006; 125:267–272.
Article8. Elia L, Mancini M, Moleti L, Meloni G, Buffolino S, Krampera M, et al. A multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction strategy for the diagnostic molecular screening of chimeric genes: a clinical evaluation on 170 patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2003; 88:275–279.9. Hsiao HH, Sashida G, Kodama A, Fukutake K, Ohyashiki K. Variant translocation t(2;21;8)(q36;q22;q22) with RUNX1/CBFA2T1 (AML1/ETO) transcript in a case of acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005; 159:96–97.
Article10. Ishida F, Ueno M, Tanaka H, Makishima H, Suzawa K, Hosaka S, et al. t(8;21;14)(q22;q22;q24) is a novel variant of t(8;21) with chimeric transcripts of AML1-ETO in acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002; 132:133–135.
Article11. Ishii Y, Sashida G, Takaku TI, Sumi M, Nakajima A, Ohyashiki K. Cryptic chromosomal anomaly in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia leading to AML1/ETO fusion with unfavorable prognostic factors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005; 160:94–95.
Article12. Nishii K, Usui E, Katayama N, Lorenzo F 5th, Nakase K, Kobayashi T, et al. Characteristics of t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with additional chromosomal abnormality: concomitant trisomy 4 may constitute a distinctive subtype of t(8;21) AML. Leukemia. 2003; 17:731–737.
Article13. Grigg AP, Gascoyne RD, Phillips GL, Horsman DE. Clinical, haematological and cytogenetic features in 24 patients with structural rearrangements of the Q arm of chromosome 3. Br J Haematol. 1993; 83:158–165.
Article14. Giles FJ, Kanemaki TJ, Schreck RR, Qasabian L, Fuerst MP, Lim SW. Translocation (3;21;8)(q21;q22;q22) in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. A case report and review of prognostic indicators. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1998; 104:66–69.15. Tien HF, Wang CH, Chuang SM, Chow JM, Lee FY, Liu MC, et al. Cytogenetic studies, ras mutation, and clinical characteristics in primary myelodysplastic syndrome. A study on 68 Chinese patients in Taiwan. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1994; 74:40–49.
Article16. Raza-Egilmez SZ, Jani-Sait SN, Grossi M, Higgins MJ, Shows TB, Aplan PD. NUP98-HOXD13 gene fusion in therapy-related acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:4269–4273.17. Shimada H, Arai Y, Sekiguchi S, Ishii T, Tanitsu S, Sasaki M. Generation of the NUP98-HOXD13 fusion transcript by a rare translocation, t(2;11)(q31;p15), in a case of infant leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000; 110:210–213.
Article18. Arai Y, Kyo T, Miwa H, Arai K, Kamada N, Kita K, et al. Heterogenous fusion transcripts involving the NUP98 gene and HOXD13 gene activation in a case of acute myeloid leukemia with the t(2;11)(q31;p15) translocation. Leukemia. 2000; 14:1621–1629.
Article19. Slape C, Lin YW, Hartung H, Zhang Z, Wolff L, Aplan PD. NUP98-HOX translocations lead to myelodysplastic syndrome in mice and men. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2008; 39:64–68.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Masked t(8;21) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Cytogenetic Abnormality of 45,X,-Y,t(8;17)(q22;p13)
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with a De novo t(11;19) Chromosomal Translocation
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22) (AML1/ETO) in a Patient with Marked Hypocellularity and Low Blasts Count
- A Novel Translocation Involving RUNX1 and HOXA Gene Clusters in a Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(7;21)(p15;q22)
- The Cytogenetic Study of Acute and Chronic Leukemic Patients in Korea