Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jan;43(1):82-85. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.82.
Establishment of Reference Intervals of Cytokeratin 19 Fragment Antigen 21-1 in Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551606
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.82
Abstract
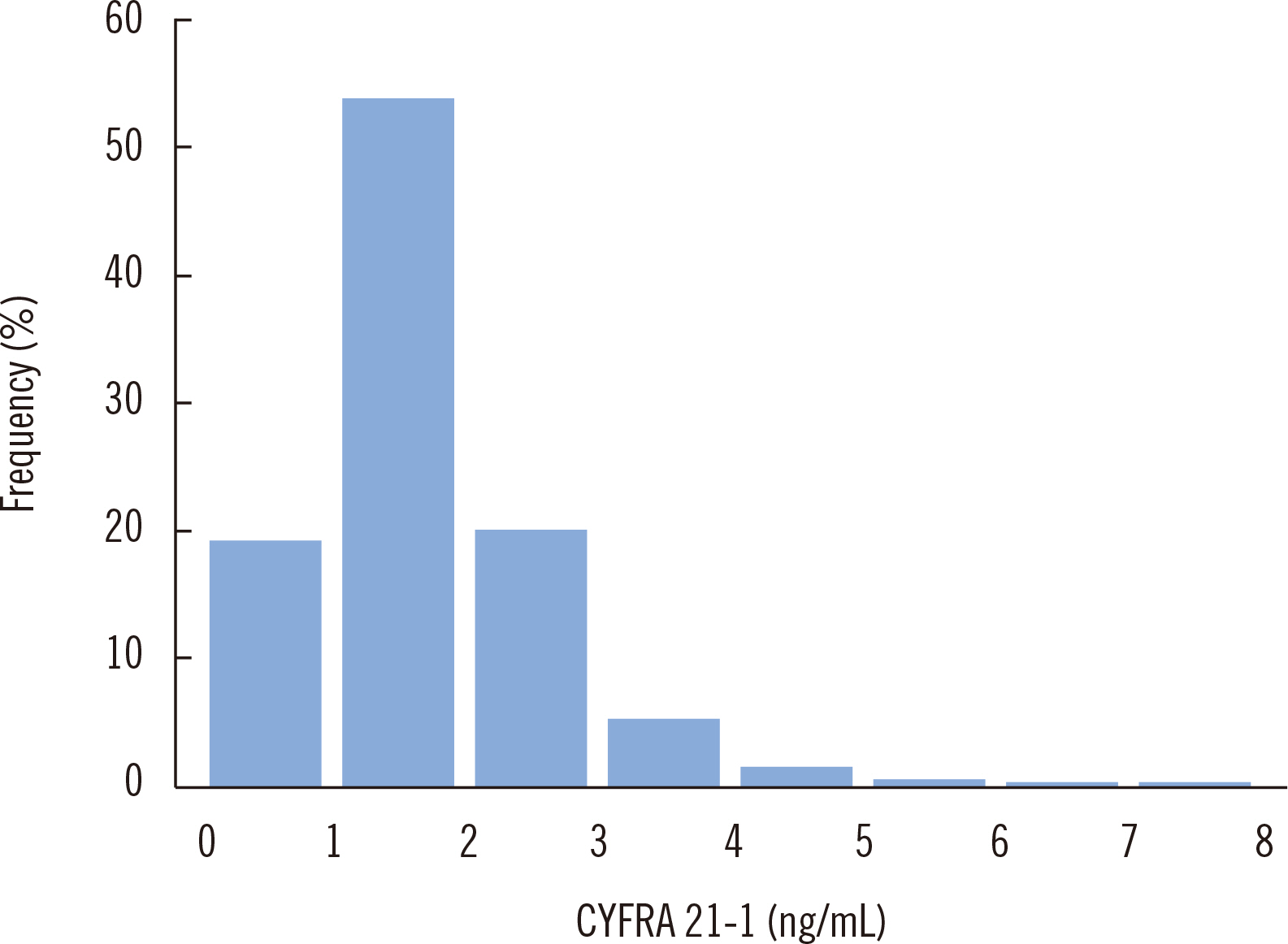
- Cytokeratin 19 fragment antigen 21-1 (CYFRA 21-1) is useful for predicting and monitoring non-small cell lung cancer prognosis. We established reference intervals (RIs) of CYFRA 21-1 in Korean adults, including those older than 60 years. Data of 4,098 apparently healthy subjects (age range, 20–87 years) were analyzed after excluding those with a history of malignancy, high tumor marker concentrations (except CYFRA 21-1), and/or abnormal findings on a chest computed tomography scan through medical chart review. After removing two outliers, RIs of CYFRA 21-1 were determined using data of 4,096 subjects based on the non-parametric method (2.5th and 97.5th percentiles) according to CLSI guidelines EP28-A3c. The subjects were divided into two and four groups according to sex and age (20–40, 41–50, 51–60, and >60 years), respectively, and the median CYFRA 21-1 concentration was compared between the groups. The RI of CYFRA 21-1 was 0.66–3.84 ng/mL, applicable to both men and women. Regardless of sex, the CYFRA 21-1 concentration increased with age, suggesting that age-dependent RIs of CYFRA 21-1 should be applied. Rather than using a single RI provided by the manufacturer, the RI of CYFRA 21-1 should be continually verified and established in each clinical laboratory.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71:209–49. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. PMID: 33538338.
Article2. Clark SB, Alsubait S. 2022. Non small cell lung cancer. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, (FL): StatPearls Publishing.3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2022. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2022/2022-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf. Updated on Jan 2022.4. Garcia-Valdecasas Gayo S, Ruiz-Alvarez MJ, Gonzalez-Gay D, Ramos-Corral R, Marquez-Lietor E, Del Amo N, et al. 2020; CYFRA 21-1 in patients with suspected cancer: evaluation of an optimal cutoff to assess the diagnostic efficacy and prognostic value. Adv Lab Med. 1:20200005. DOI: 10.1515/almed-2020-0005.5. Marrakchi R, Ouerhani S, Benammar S, Rouissi K, Bouhaha R, Bougatef K, et al. 2008; Detection of cytokeratin 19 mRNA and CYFRA 21-1 (cytokeratin 19 fragments) in blood of Tunisian women with breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 23:238–43. DOI: 10.1177/172460080802300407. PMID: 19199272.
Article6. Schalhorn A, Fürst H, Stieber P. 2001; Tumor markers in lung cancer. J Lab Med. 25:353–61. DOI: 10.1515/labm.2001.25.9-10.353. PMID: 22153832.7. Liu L, Teng J, Zhang L, Cong P, Yao Y, Sun G, et al. 2017; The combination of the tumor markers suggests the histological diagnosis of lung cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2017:2013989. DOI: 10.1155/2017/2013989. PMID: 28607926. PMCID: PMC5451759.
Article8. Yoshimura A, Uchino J, Hasegawa K, Tsuji T, Shiotsu S, Yuba T, et al. 2019; Carcinoembryonic antigen and CYFRA 21-1 responses as prognostic factors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 8:227–34. DOI: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.06.08. PMID: 31367536. PMCID: PMC6626854.
Article9. Kagawa Y, Sone K, Oguri T, Horiuchi M, Fukuda S, Uemura T, et al. 2022; Predictive role of CYFRA 21-1 for S-1 monotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Respir Investig. 60:393–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.resinv.2021.11.014. PMID: 35216954.
Article10. DeAntoni EP, Crawford ED, Oesterling JE, Ross CA, Berger ER, McLeod DG, et al. 1996; Age- and race-specific reference ranges for prostate-specific antigen from a large community-based study. Urology. 48:234–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0090-4295(96)00091-X. PMID: 8753735.
Article11. Lee MK, Park YK, Park AJ. 2001; Reevaluation of the reference range of prostate-specific antigen in Korean men. J Clin Pathol Qual Control. 23:221–5.12. Woo HY, Kim YJ, Park H. 2008; Establishment of reference intervals of tumor markers in Korean adults. Korean J Lab Med. 28:179–84. DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.3.179. PMID: 18594168.
Article13. Kweon SS. 2018; Updates on cancer epidemiology in Korea, 2018. Chonnam Med J. 54:90–100. DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.90. PMID: 29854674. PMCID: PMC5972130.
Article14. CLSI. 2010. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory; approved guideline-third edition. CLSI EP28-A3c. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA: DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.3.179.15. Reed AH, Henry RJ, Mason WB. 1971; Influence of statistical method used on the resulting estimate of normal range. Clin Chem. 17:275–84. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/17.4.275. PMID: 5552364.
Article16. Parrish AR. 2017; The impact of aging on epithelial barriers. Tissue Barriers. 5:e1343172. DOI: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1343172. PMID: 28686506. PMCID: PMC5788442.
Article17. Dai Y, Qu W, Sang S, Tao S, Li Y, Wang Y, et al. 2018; Reference intervals of cytokeratin-19 fragment (CYFRA 21-1) in healthy adults in China. Clin Lab. 64:123–33. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2017.170708. PMID: 29479889.
Article18. Kao CH, Hsieh JF, Ho YJ, Tsai SC, Lee JK. 1999; Cytokeratin fragment 19 (CYFRA 21-1) in healthy smokers. Anticancer Res. 19:4545–6.19. Karnak D, Ulubay G, Kayacan O, Beder S, Ibis E, Oflaz G. 2001; Evaluation of Cyfra 21-1: a potential tumor marker for non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung. 179:57–65. DOI: 10.1007/s004080000047. PMID: 11479694.
Article20. Kim J, Jung H, Kim D, Lee S, Kim M, Park K. 2018; Lack of clinical utility for CYFRA 21-1 in medical screening. Korean J Fam Pract. 8:73–9. DOI: 10.21215/kjfp.2018.8.1.73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Establishment of Reference Intervals of Tumor Markers in Korean Adults
- Pathologic Correlation of Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Cytokeratin 19 Fragment in Resected Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer
- Influence of Waist Circumference Index of Metabolic Syndrome on the Establishment of Reference Intervals
- Establishing Reference Intervals for Complete Blood Cell Count in Healthy Korean Elderly Individuals
- Establishment of Reference Intervals for Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor I in Korean Adult Population