J Stroke.
2024 Jan;26(1):75-86. 10.5853/jos.2023.01529.
Effect of Intravenous Thrombolysis Prior to Mechanical Thrombectomy According to the Location of M1 Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Neurology, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea
- KMID: 2551349
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2023.01529
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
The additive effects of intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) before mechanical thrombectomy (MT) remain unclear. We aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of IVT prior to MT depending on the location of M1 occlusion.
Methods
We reviewed the cases of patients who underwent MT for emergent large-vessel occlusion of the M1 segment. Baseline characteristics as well as clinical and periprocedural variables were compared according to the location of M1 occlusion (i.e., proximal and distal M1 occlusion). The main outcome was the achievement of functional independence (modified Rankin Scale score, 0–2) at 3 months after stroke. The main outcomes were compared between the proximal and distal groups based on the use of IVT before MT.
Results
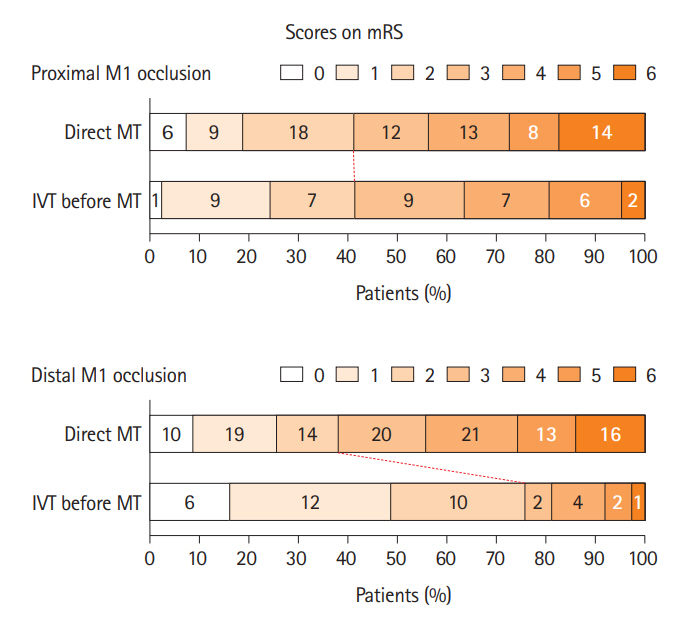
Among 271 patients (proximal occlusion, 44.6%; distal occlusion, 55.4%), 33.9% (41/121) with proximal occlusion and 24.7% (37/150) with distal occlusion underwent IVT prior to MT. Largeartery atherosclerosis was more common in patients with proximal M1 occlusion; cardioembolism was more common in those with distal M1 occlusion. In patients with proximal M1 occlusion, there was no association between IVT before MT and functional independence. In contrast, there was a significant association between the use of IVT prior to MT (odds ratio=5.30, 95% confidence interval=1.56–18.05, P=0.007) and functional independence in patients with distal M1 occlusion.
Conclusion
IVT before MT was associated with improved functional outcomes in patients with M1 occlusion, especially in those with distal M1 occlusion but not in those with proximal M1 occlusion.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 2016; 387:1723–1731.2. Yang P, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Treurniet KM, Chen W, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy with or without intravenous alteplase in acute stroke. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1981–1993.3. LeCouffe NE, Kappelhof M, Treurniet KM, Rinkel LA, Bruggeman AE, Berkhemer OA, et al. A randomized trial of intravenous alteplase before endovascular treatment for stroke. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385:1833–1844.4. Suzuki K, Matsumaru Y, Takeuchi M, Morimoto M, Kanazawa R, Takayama Y, et al. Effect of mechanical thrombectomy without vs with intravenous thrombolysis on functional outcome among patients with acute ischemic stroke: the SKIP randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021; 325:244–253.5. Zi W, Qiu Z, Li F, Sang H, Wu D, Luo W, et al. Effect of endovascular treatment alone vs intravenous alteplase plus endovascular treatment on functional independence in patients with acute ischemic stroke: the DEVT randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021; 325:234–243.6. Trifan G, Biller J, Testai FD. Mechanical thrombectomy vs bridging therapy for anterior circulation large vessel occlusion stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology. 2022; 98:e1361–e1373.7. Hansen CK, Christensen A, Ovesen C, Havsteen I, Christensen H. Stroke severity and incidence of acute large vessel occlusions in patients with hyper-acute cerebral ischemia: results from a prospective cohort study based on CT-angiography (CTA). Int J Stroke. 2015; 10:336–342.8. Santos EM, Marquering HA, den Blanken MD, Berkhemer OA, Boers AM, Yoo AJ, et al. Thrombus permeability is associated with improved functional outcome and recanalization in patients with ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2016; 47:732–741.9. Yoo J, Baek JH, Park H, Song D, Kim K, Hwang IG, et al. Thrombus volume as a predictor of nonrecanalization after intravenous thrombolysis in acute stroke. Stroke. 2018; 49:2108–2115.10. Heo JH, Nam HS, Kim YD, Choi JK, Kim BM, Kim DJ, et al. Pathophysiologic and therapeutic perspectives based on thrombus histology in stroke. J Stroke. 2020; 22:64–75.11. Zhou Y, Xing P, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of occlusion site on the safety and efficacy of intravenous alteplase before endovascular thrombectomy: a prespecified subgroup analysis of DIRECT-MT. Stroke. 2022; 53:7–16.12. Kim YS, Kim BJ, Noh KC, Lee KM, Heo SH, Choi HY, et al. Distal versus proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion: different mechanisms. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019; 47:238–244.13. Friedrich B, Gawlitza M, Schob S, Hobohm C, Raviolo M, Hoffmann KT, et al. Distance to thrombus in acute middle cerebral artery occlusion: a predictor of outcome after intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2015; 46:692–696.14. Lee KY, Han SW, Kim SH, Nam HS, Ahn SW, Kim DJ, et al. Early recanalization after intravenous administration of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator as assessed by preand post-thrombolytic angiography in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke. 2007; 38:192–193.15. Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Lancet. 1998; 352:1245–1251.16. Lee JH, Park KY, Shin JH, Cha JK, Kim HY, Kwon JH, et al. Symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation and its predictors in acute ischemic stroke with atrial fibrillation. Eur Neurol. 2010; 64:193–200.17. Menon BK, Al-Ajlan FS, Najm M, Puig J, Castellanos M, Dowlatshahi D, et al. Association of clinical, imaging, and thrombus characteristics with recanalization of visible intracranial occlusion in patients with acute ischemic stroke. JAMA. 2018; 320:1017–1026.18. Seners P, Turc G, Maïer B, Mas JL, Oppenheim C, Baron JC. Incidence and predictors of early recanalization after intravenous thrombolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2016; 47:2409–2412.19. Behrens L, Möhlenbruch M, Stampfl S, Ringleb PA, Hametner C, Kellert L, et al. Effect of thrombus size on recanalization by bridging intravenous thrombolysis. Eur J Neurol. 2014; 21:1406–1410.20. Kaesmacher J, Kleine JF. Bridging therapy with i. v. rtPA in MCA occlusion prior to endovascular thrombectomy: a double-edged sword? Clin Neuroradiol. 2018; 28:81–89.21. Bilgic AB, Gocmen R, Arsava EM, Topcuoglu MA. The effect of clot volume and permeability on response to intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020; 29:104541.22. Krajícˇková D, Krajina A, Šteiner I, Vyšata O, Herzig R, Lojík M, et al. Fibrin clot architecture in acute ischemic stroke treated with mechanical thrombectomy with stent-retrievers – Cohort study. Circ J. 2018; 82:866–873.23. Molina CA, Montaner J, Arenillas JF, Ribo M, Rubiera M, Alvarez-Sabín J. Differential pattern of tissue plasminogen activator-induced proximal middle cerebral artery recanalization among stroke subtypes. Stroke. 2004; 35:486–490.24. Ng FC, Coulton B, Chambers B, Thijs V. Persistently elevated microvascular resistance postrecanalization. Stroke. 2018; 49:2512–2515.25. Stone GW, Webb J, Cox DA, Brodie BR, Qureshi M, Kalynych A, et al. Distal microcirculatory protection during percutaneous coronary intervention in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005; 293:1063–1072.26. Ali A, Cox D, Dib N, Brodie B, Berman D, Gupta N, et al. Rheolytic thrombectomy with percutaneous coronary intervention for infarct size reduction in acute myocardial infarction: 30-day results from a multicenter randomized study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:244–252.27. Vlaar PJ, Svilaas T, van der Horst IC, Diercks GF, Fokkema ML, de Smet BJ, et al. Cardiac death and reinfarction after 1 year in the thrombus aspiration during percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarction study (TAPAS): a 1-year follow-up study. Lancet. 2008; 371:1915–1920.28. Flint AC, Avins AL, Eaton A, Uong S, Cullen SP, Hsu DP, et al. Risk of distal embolization from tPA (tissue-type plasminogen activator) administration prior to endovascular stroke treatment. Stroke. 2020; 51:2697–2704.29. Kim JS, Kim YJ, Lee KB, Cha JK, Park JM, Hwang Y, et al. Low-versus standard-dose intravenous alteplase in the context of bridging therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a Korean ENCHANTED study. J Stroke. 2018; 20:131–139.30. Desilles JP, Loyau S, Syvannarath V, Gonzalez-Valcarcel J, Cantier M, Louedec L, et al. Alteplase reduces downstream microvascular thrombosis and improves the benefit of large artery recanalization in stroke. Stroke. 2015; 46:3241–3248.31. Ko HC. The clinical outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy for proximal M1 occlusion involving lenticulostriate perforators: is it worse than distal M1 occlusion? Retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021; 100:e27036.32. Kaschner MG, Lande R, Rubbert C, Caspers J, Lee JI, Gliem M, et al. Predictors for basal ganglia viability after mechanical thrombectomy in proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion. Clin Imaging. 2019; 57:1–6.33. Loh Y, Towfighi A, Liebeskind DS, MacArthur DL, Vespa P, Gonzalez NR, et al. Basal ganglionic infarction before mechanical thrombectomy predicts poor outcome. Stroke. 2009; 40:3315–3320.34. Renú Jornet A, Urra X, Laredo C, Montejo C, Rudilosso S, Llull L, et al. Benefit from mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke with fast and slow progression. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020; 12:132–135.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and radiological outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy in simultaneous anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery occlusion
- Intravenous Thrombolysis and Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Minor Symptom
- Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke with occlusion of the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery: A literature review
- Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in 11-year-old Patient
- Mechanical Thrombolysis Using Coil in Acute Occlusion of Fenestrate M1 Segment