J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2022 Jun;24(2):137-143. 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.07.014.
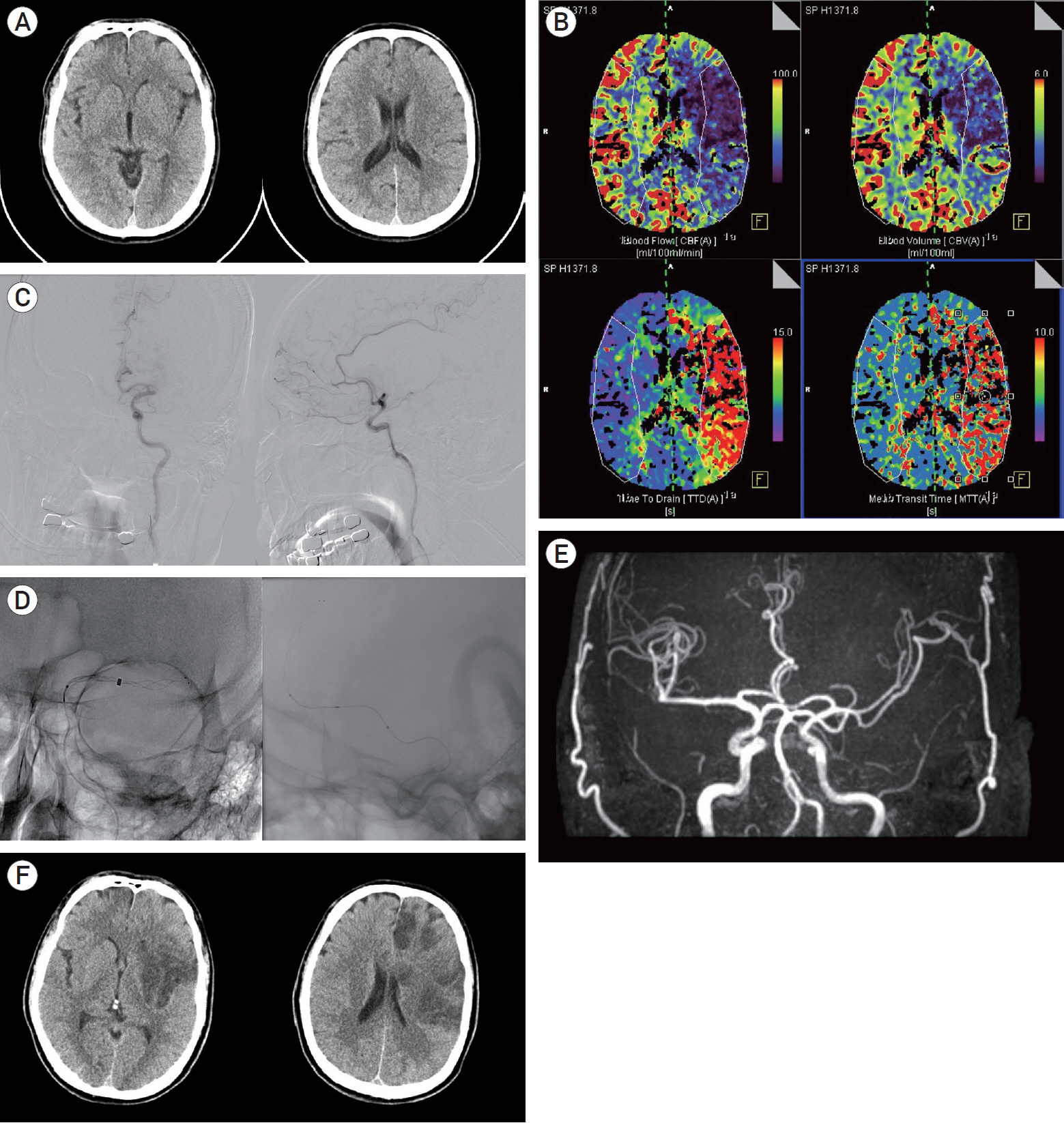
Clinical and radiological outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy in simultaneous anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of neurosurgery, Inje university, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of neurosurgery, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2531656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.07.014
Abstract
Objective
Simultaneous anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion is rare. We investigated the clinical and radiological outcomes of patients with simultaneous ACA and MCA occlusion treated with mechanical thrombectomy.
Methods
We analyzed the clinical and radiological outcomes of 12 patients with simultaneous ACA and MCA occlusion treated with mechanical thrombectomy from January 2018 to December 2020. The clinical outcome was assessed using the modified Rankin Score (mRS) after 3 months of thrombectomy. The radiological outcome was assessed using the thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) score.
Results
The median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score at hospital arrival was 18 (interquartile range, 16–20). M1 was the most common occlusion lesion (n=8), and A3 was the most common lesion in the ACA (n=6). Six patients were first treated for MCA occlusion and later for ACA occlusion (MCA group). Other patients were first treated for ACA occlusion and later for MCA occlusion (ACA group). There was no difference in clinical outcomes between the MCA and ACA groups (p=0.180). Successful recanalization (TICI ≥2b) of MCA was achieved in 10 patients (83.3%). Successful recanalization of ACA was achieved in 10 patients (83.3%). Successful recanalization of both ACA and MCA occlusion was observed in eight patients (66.7%). Three patients (25%) had good clinical outcomes (mRS ≤2).
Conclusions
In our series, simultaneous ACA and MCA occlusion showed relatively poor successful recanalization rates and poor clinical outcomes despite treatment with mechanical thrombectomy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi B-S, Lee H, Jin S-C. Contralateral Mechanical Thrombectomy of Partial Deployed Stent Retrieval for Acute Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Occlusion. World Neurosurgery. 2019; Sep. 129:318–21.
Article2. Frahm D, Wunderlich S, Schubert MI, Poppert H, Kleine JF, Prothmann S. Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Occlusion of the Carotid-T: A Retrospective Single Centre Study in 51 Patients. Clinical Neuroradiology. 2016; Mar. 26(1):23–9.
Article3. Gacs G, Fox AJ, Barnett HJ, Vinuela F. Occurrence and mechanisms of occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery. Stroke. 1983; Nov-Dec. 14(6):952–9.
Article4. Goyal M, Cimflova P, Ospel JM, Chapot R. Endovascular treatment of anterior cerebral artery occlusions. Journal of Neurointerventional Surgery. 2021; Jun. 13(11):
Article5. Kim SH, Lee H, Kim SB, Kim ST, Baek JW, Heo YJ, et al. Hybrid mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke using an intermediate aspiration catheter and Trevo stent simultaneously. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 2020; Jun. 76:9–14.
Article6. Liebeskind DS. Collateral circulation. Stroke. 2003; Jul. 34(9):2279–84.
Article7. Nogles TE, Galuska MA. Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing;2021.8. Noh Y, Jung CK, Hong J-H, Jeong J-H, Chang JY, Kim BJ, et al. Recanalization Rate and Clinical Outcome in Acute Carotid-T Occlusion. European Neurology. 2015; Sep. 74(1-2):36–42.
Article9. Osborn AG, Jacobs JM. Diagnostic cerebral angiography. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999.10. Pfaff J, Herweh C, Pham M, Schieber S, Ringleb PA, Bendszus M, et al. Mechanical Thrombectomy of Distal Occlusions in the Anterior Cerebral Artery: Recanalization Rates, Periprocedural Complications, and Clinical Outcome. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. 2016; Apr. 37(4):673–8.
Article11. Shoamanesh A, Masoud H, Furey K, Duerfeldt K, Lau H, Romero JR, et al. Larger A1/M1 diameter ratio predicts embolic anterior cerebral artery territorial stroke. Stroke. 2014; Sep. 45(9):2798–800.
Article12. Uno J, Kameda K, Otsuji R, Ren N, Nagaoka S, Kazushi M, et al. Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Anterior Cerebral Artery Occlusion. World Neurosurgery. 2018; Dec. 120:e957–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How to Escape Stentriever Wedging in an Open-cell Carotid Stent during Mechanical Thrombectomy for Tandem Cervical Internal Carotid Artery and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke with occlusion of the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery: A literature review
- Delayed Development of Symptomatic Arterial Stenosis after a Mechanical Thrombectomy for an Acute Embolic Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery
- Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in 11-year-old Patient
- Microsurgical anatomy of the Anterior Cerebral-anterior Communicating Artery