Cancer Res Treat.
2024 Jan;56(1):48-60. 10.4143/crt.2023.453.
Lazertinib versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment for EGFR-mutated Locally Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC: LASER301 Korean Subset
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 2Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Center for Lung Cancer, Research Institute and Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 7CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
- 8Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 9Division of Hemato-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University, College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 10Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 11Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 13Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
- 14Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 15Division of Oncology/Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 16Department of Hematology-Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 17Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 18Division of Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 19Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 20Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 21Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 22Yuhan Corporation, Seoul, Korea
- 23Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2023.453
Abstract
- Purpose
This subgroup analysis of the Korean subset of patients in the phase 3 LASER301 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of lazertinib versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for epidermal growth factor receptor mutated (EGFRm) non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Materials and Methods
Patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFRm NSCLC were randomized 1:1 to lazertinib (240 mg/day) or gefitinib (250 mg/day). The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS).
Results
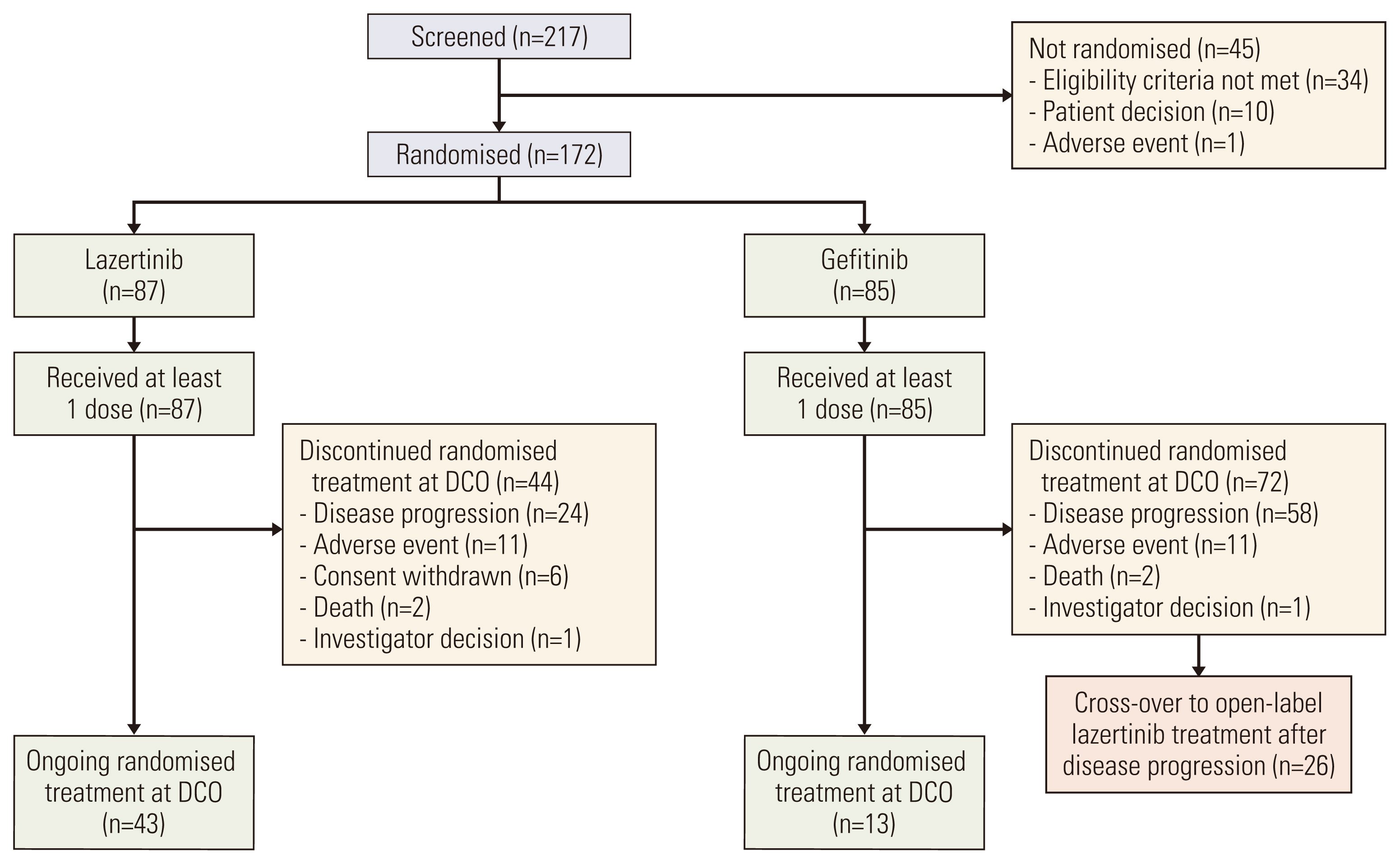
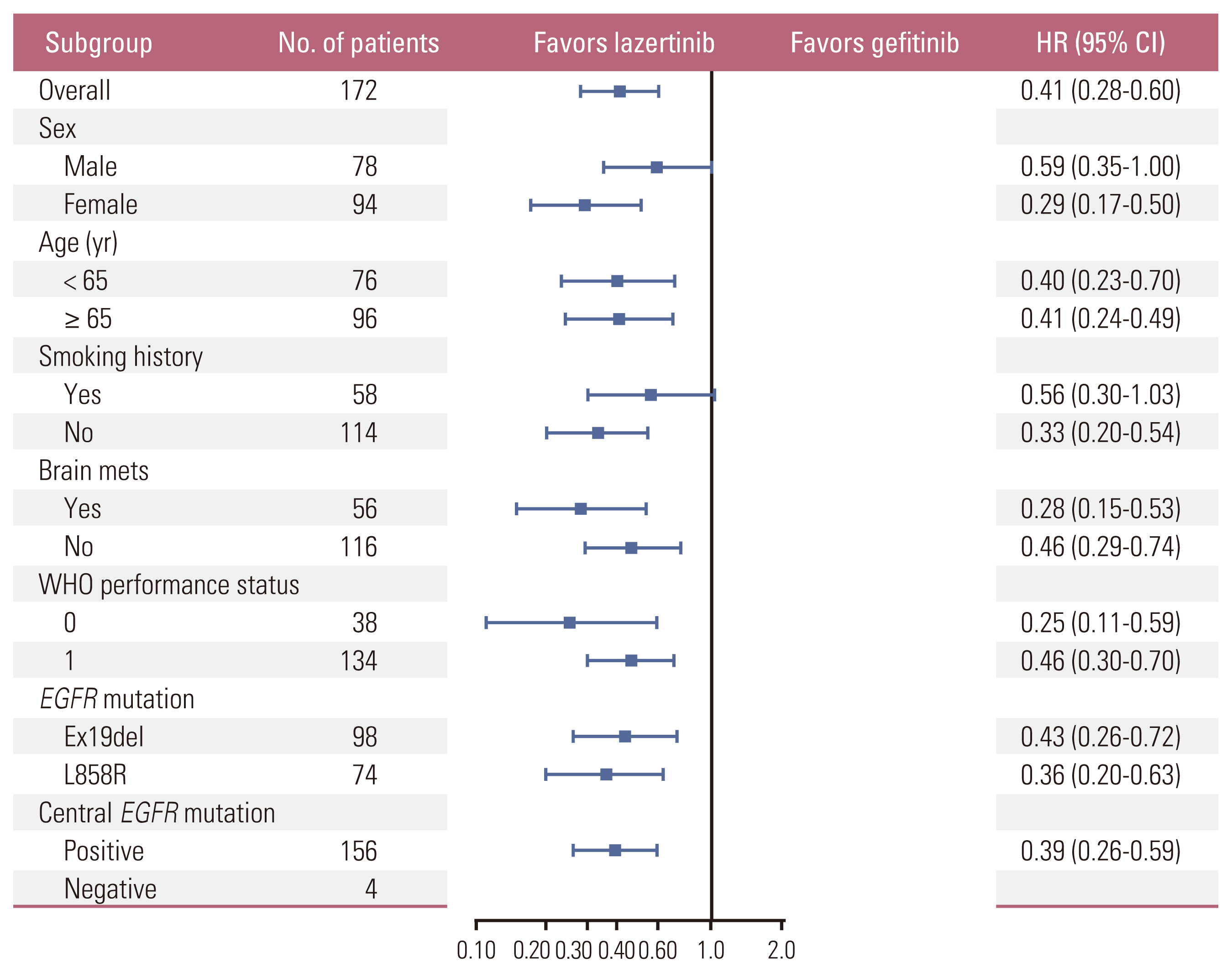
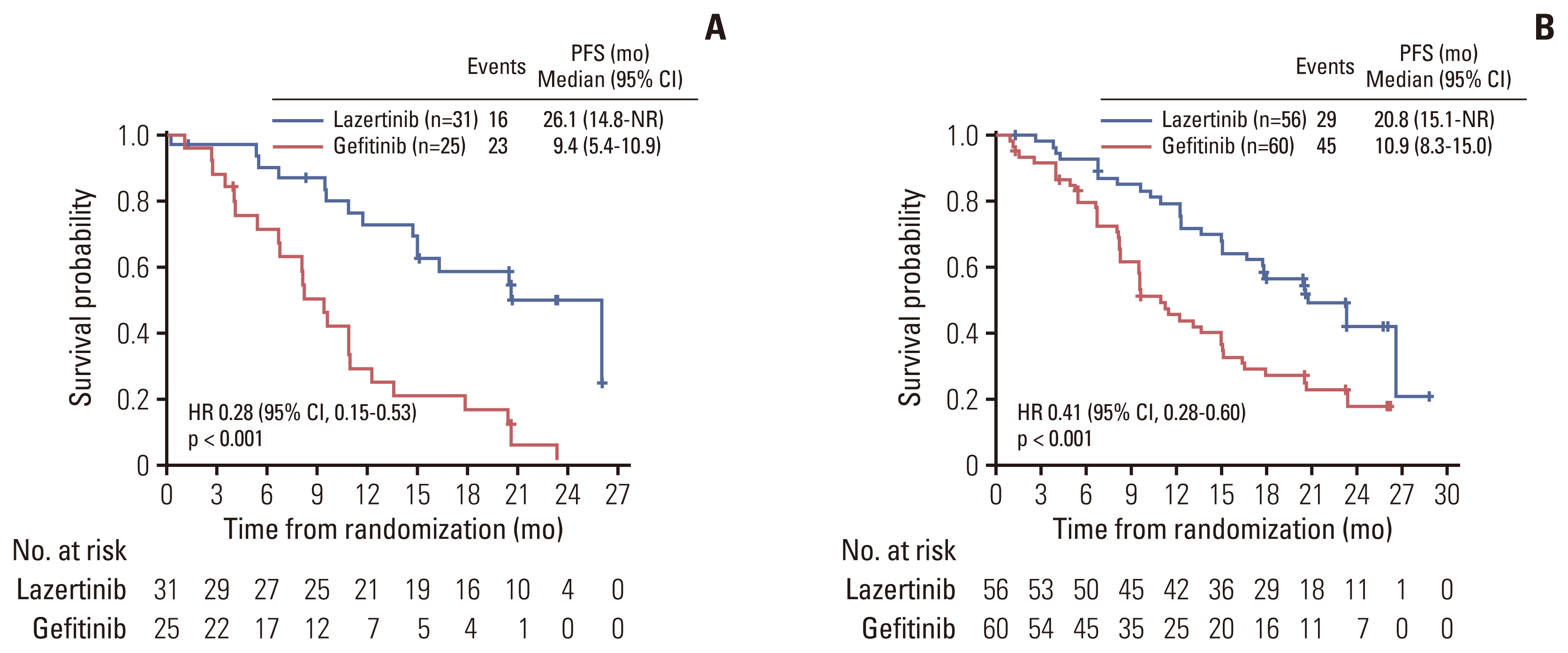
In total, 172 Korean patients were enrolled (lazertinib, n=87; gefitinib, n=85). Baseline characteristics were balanced between the treatment groups. One-third of patients had brain metastases (BM) at baseline. Median PFS was 20.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 16.7 to 26.1) for lazertinib and 9.6 months (95% CI, 8.2 to 12.3) for gefitinib (hazard ratio [HR], 0.41; 95% CI, 0.28 to 0.60). This was supported by PFS analysis based on blinded independent central review. Significant PFS benefit with lazertinib was consistently observed across predefined subgroups, including patients with BM (HR, 0.28; 95% CI, 0.15 to 0.53) and those with L858R mutations (HR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.20 to 0.63). Lazertinib safety data were consistent with its previously reported safety profile. Common adverse events (AEs) in both groups included rash, pruritus, and diarrhoea. Numerically fewer severe AEs and severe treatment–related AEs occurred with lazertinib than gefitinib.
Conclusion
Consistent with results for the overall LASER301 population, this analysis showed significant PFS benefit with lazertinib versus gefitinib with comparable safety in Korean patients with untreated EGFRm NSCLC, supporting lazertinib as a new potential treatment option for this patient population.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kang MJ, Won YJ, Lee JJ, Jung KW, Kim HJ, Kong HJ, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2019. Cancer Res Treat. 2022; 54:330–44.2. Lee JG, Kim HC, Choi CM. Recent trends of lung cancer in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2021; 84:89–95.3. KOrean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Cancer incident cases and incidence rates (1999-2020) [Internet]. Daejeon: Statistics Korea;c2023 [cited 2023 Jun 10]. Available from: https://kosis.kr/ .4. Gazdar AF. Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2009; 28 (Suppl 1):S24–31.5. Midha A, Dearden S, McCormack R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: a systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am J Cancer Res. 2015; 5:2892–911.6. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2380–8.7. Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:213–22.8. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:735–42.9. Westover D, Zugazagoitia J, Cho BC, Lovly CM, Paz-Ares L. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:i10–9.10. Remon J, Besse B. Brain metastases in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer patients: incidence and treatment. Front Oncol. 2018; 8:88.11. Rangachari D, Yamaguchi N, VanderLaan PA, Folch E, Mahadevan A, Floyd SR, et al. Brain metastases in patients with EGFR-mutated or ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2015; 88:108–11.12. Nakagawa K, Nadal E, Garon EB, Nishio M, Seto T, Yamamoto N, et al. RELAY subgroup analyses by EGFR Ex19del and Ex21L858R mutations for ramucirumab plus erlotinib in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021; 27:5258–71.13. Sheng M, Wang F, Zhao Y, Li S, Wang X, Shou T, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 or exon 21 mutations after tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 72:1–11.14. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.15. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Republic of Korea. LECLAZA (lazertinib): Republic of Korea prescribing information [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;c2021 [cited 2022 Dec 10]. Available from: https://nedrug.mfds.go.kr/pbp/CCBBB01/getItemDetail?itemSeq=202100467 .16. Yun J, Hong MH, Kim SY, Park CW, Kim S, Yun MR, et al. YH25448, an irreversible EGFR-TKI with potent intracranial activity in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019; 25:2575–87.17. Ahn MJ, Han JY, Lee KH, Kim SW, Kim DW, Lee YG, et al. Lazertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the dose escalation and dose expansion parts of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:1681–90.18. Cho BC, Han JY, Kim SW, Lee KH, Cho EK, Lee YG, et al. A phase 1/2 study of lazertinib 240 mg in patients with advanced EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC after previous EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. 2022; 17:558–67.19. Cho BC, Ahn MJ, Kang JH, Soo RA, Reungwetwattana T, Yang JC, et al. Lazertinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results from LASER301. J Clin Oncol. 2023; 41:4208–17.20. Cho BC, Han JY, Lee KH, Lee YG, Kim DW, Min YJ, et al. EP08.02-025 lazertinib as a frontline treatment in patients with EGFR mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results from the phase I/II trial. J Thoracic Oncol. 2022; 17(9 Suppl):408–9.21. Ohe Y, Imamura F, Nogami N, Okamoto I, Kurata T, Kato T, et al. Osimertinib versus standard-of-care EGFR-TKI as first-line treatment for EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Japanese subset. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019; 49:29–36.22. Cho BC, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Sriuranpong V, Imamura F, et al. Osimertinib versus standard of care EGFR TKI as first-line treatment in patients with EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Asian subset. J Thorac Oncol. 2019; 14:99–106.23. Togashi Y, Masago K, Masuda S, Mizuno T, Fukudo M, Ikemi Y, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012; 70:399–405.24. Heon S, Yeap BY, Britt GJ, Costa DB, Rabin MS, Jackman DM, et al. Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:5873–82.25. Jung HA, Hong MH, Lee HW, Lee KH, Kim IH, Min YJ, et al. Totality outcome of afatinib sequential treatment in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer in South Korea (TOAST): Korean Cancer Study Group (KCSG) LU-19–22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022; 11:1369–79.26. Yoon HY, Ryu JS, Sim YS, Kim D, Lee SY, Choi J, et al. Clinical significance of EGFR mutation types in lung adenocarcinoma: a multi-centre Korean study. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0228925.27. Choi YW, Choi JH. Does the efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor differ according to the type of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer? Korean J Intern Med. 2017; 32:422–8.28. Mulloy R, Ferrand A, Kim Y, Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutants from human lung cancers exhibit enhanced catalytic activity and increased sensitivity to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:2325–30.29. Carey KD, Garton AJ, Romero MS, Kahler J, Thomson S, Ross S, et al. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:8163–71.30. Jang SB, Kim KB, Sim S, Cho BC, Ahn MJ, Han JY, et al. Cardiac safety assessment of lazertinib: findings from patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC and preclinical studies. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021; 2:100224.31. Batson S, Mitchell SA, Windisch R, Damonte E, Munk VC, Reguart N. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor combination therapy in first-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2017; 10:2473–82.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lazertinib: on the Way to Its Throne
- Comparison of Gefitinib versus Docetaxel in Patients with Pre-Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Early or Late Gefitinib, Which is Better for Survival?: Retrospective Analysis of 228 Korean Patients with Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC
- Intron 1 Polymorphism, Mutation and the Protein Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Relation to the Gefitinib Sensitivity of Korean Lung Cancer Patients
- Enhanced Sensitivity to Gefitinib after Radiation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells