Child Kidney Dis.
2023 Dec;27(2):121-126. 10.3339/ckd.23.022.
Angiotensin receptor blocker induced fetopathy: two case reports and literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2549744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.23.022
Abstract
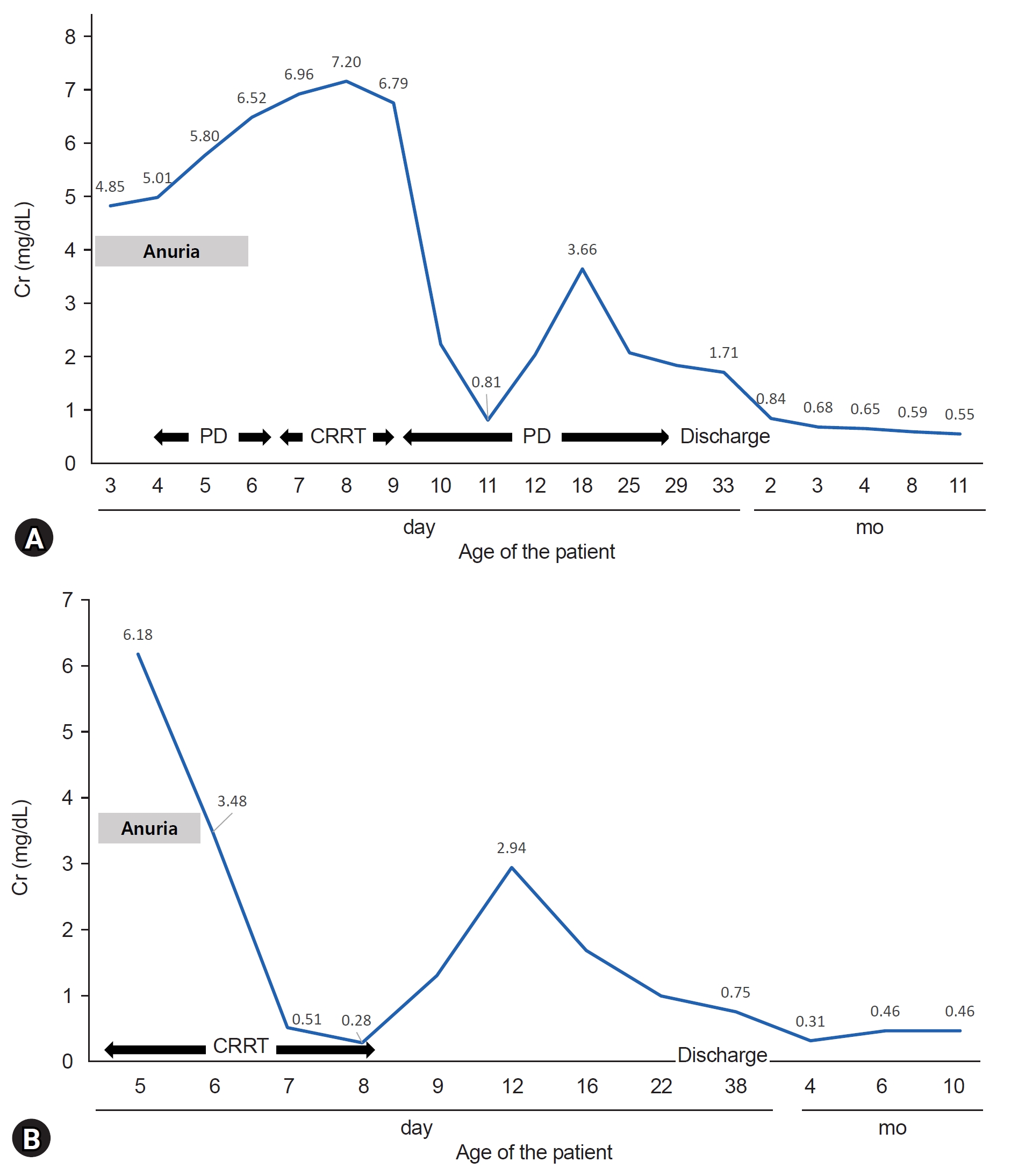
- The administration of angiotensin type 2 receptor blockers (ARBs) during pregnancy is known to cause ARB fetopathy, including renal insufficiency. We aimed to analyze the outcomes of two patients who survived ARB fetopathy and perform an accompanying literature review. Case 1 was exposed antenatally from a gestational age of 30 weeks to valsartan because of maternal pregnancy-induced hypertension. The patient presented with oliguria immediately after birth, and renal replacement therapy was administered for 24 days. Seven years after birth, renal function was indicative of stage 2 chronic kidney disease (CKD) with impaired urinary concentration. Case 2 had a maternal history of hypertension and transient ischemic attack and was treated with olmesartan until 30 weeks of pregnancy. Renal replacement therapy was performed for 4 days since birth. After 8 years, the patient is with CKD stage 2, with intact tubular function. Recent reports suggest that ARB fetopathy might manifest as renal tubular dysgenesis and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, in contrast to mild alterations of glomerular filtration. Tubular dysfunction may induce CKD progression and growth retardation. Patients with ARB fetopathy should be monitored until adulthood. The ARB exposure period might be a critical factor in determining the severity and manifestations of fetopathy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Quan A. Fetopathy associated with exposure to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists. Early Hum Dev. 2006; 82:23–8.
Article2. Miura K, Sekine T, Iida A, Takahashi K, Igarashi T. Salt-losing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by fetal exposure to angiotensin receptor blocker. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24:1235–8.
Article3. Gang MH, Lee YW, Chang MY. Secondary renal tubular dysgenesis in a newborn exposed to angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonist during gestation. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021; 64:136–8.
Article4. Bullo M, Tschumi S, Bucher BS, Bianchetti MG, Simonetti GD. Pregnancy outcome following exposure to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor antagonists: a systematic review. Hypertension. 2012; 60:444–50.
Article5. Oh KT, Namgoong MK, Yoo YM, Lee BK. Angiotensin II receptor blocker fetopathy with persistent pulmonary hypertension, hypocalvaria, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, transient pseudohypoaldosteronism and polycythemia. Perinatology. 2021; 32:48–53.
Article6. Serreau R, Luton D, Macher MA, Delezoide AL, Garel C, Jacqz-Aigrain E. Developmental toxicity of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists during human pregnancy: a report of 10 cases. BJOG. 2005; 112:710–2.
Article7. Berkane N, Carlier P, Verstraete L, Mathieu E, Heim N, Uzan S. Fetal toxicity of valsartan and possible reversible adverse side effects. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2004; 70:547–9.
Article8. Bos-Thompson MA, Hillaire-Buys D, Muller F, Dechaud H, Mazurier E, Boulot P, et al. Fetal toxic effects of angiotensin II receptor antagonists: case report and follow-up after birth. Ann Pharmacother. 2005; 39:157–61.
Article9. Schaefer C. Angiotensin II-receptor-antagonists: further evidence of fetotoxicity but not teratogenicity. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2003; 67:591–4.
Article10. Bass JK, Faix RG. Gestational therapy with an angiotensin II receptor antagonist and transient renal failure in a premature infant. Am J Perinatol. 2006; 23:313–8.
Article11. Simonetti GD, Baumann T, Pachlopnik JM, von Vigier RO, Bianchetti MG. Non-lethal fetal toxicity of the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006; 21:1329–30.
Article12. Georgaki-Angelaki E, Stergiou N, Naoum E, Papassotiriou I, Anagnostakou M. Olmesartan medoxomil-induced acute renal failure in a premature newborn following maternal exposure during pregnancy: a case report and review of the literature. NDT Plus. 2009; 2:295–7.
Article13. Vendemmia M, Garcia-Meric P, Rizzotti A, Boubred F, Lacroze V, Liprandi A, et al. Fetal and neonatal consequences of antenatal exposure to type 1 angiotensin II receptor-antagonists. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005; 18:137–40.
Article14. Spaggiari E, Heidet L, Grange G, Guimiot F, Dreux S, Delezoide AL, et al. Prognosis and outcome of pregnancies exposed to renin-angiotensin system blockers. Prenat Diagn. 2012; 32:1071–6.
Article15. Cooper WO, Hernandez-Diaz S, Arbogast PG, Dudley JA, Dyer S, Gideon PS, et al. Major congenital malformations after first-trimester exposure to ACE inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:2443–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lithium Intoxication Induced by Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker/Thiazide Combination Agent
- A case of angioedema associated with losartan
- Angiotensin receptor blocker add-on therapy in portal hypertension: To use angiotensin receptor blocker or not to use, that is the question
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Fetopathy with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension, Hypocalvaria, Nephrogenic Diabetes Insi pidus, Transient Pseudohypoaldosteronism and Polycythemia
- A Case of Neonate with Acute Renal Failure after Maternal Treatment with Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker