J Rhinol.
2023 Nov;30(3):149-154. 10.18787/jr.2023.00056.
Radiofrequency Ablation and Microdebrider-Assisted Turbinoplasty: 5-Year Postoperative Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Republic of Korea
- 2Dankook Physician Scientist Research Center, Dankook University, Cheonan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2548192
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2023.00056
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Turbinoplasty may be an option in patients with persistent symptoms of allergic rhinitis (AR) despite adequate medication. The two most frequently used surgical techniques for turbinoplasty are radiofrequency ablation and microdebriderassisted turbinoplasty. This study compared the outcomes of these two surgical techniques and assessed the long-term treatment effects.
Methods
This study included patients with AR who underwent turbinoplasty between January 2010 and June 2017. We examined the medication scores, overall treatment satisfaction scores, and medical records. Based on the type of surgery, patients were classified into microdebrider and coblator groups. A telephone survey was conducted to collect data on the 5-year post-treatment efficacy parameters. Scores for allergic symptoms, prescription medicines taken after surgery, and general satisfaction were compared.
Results
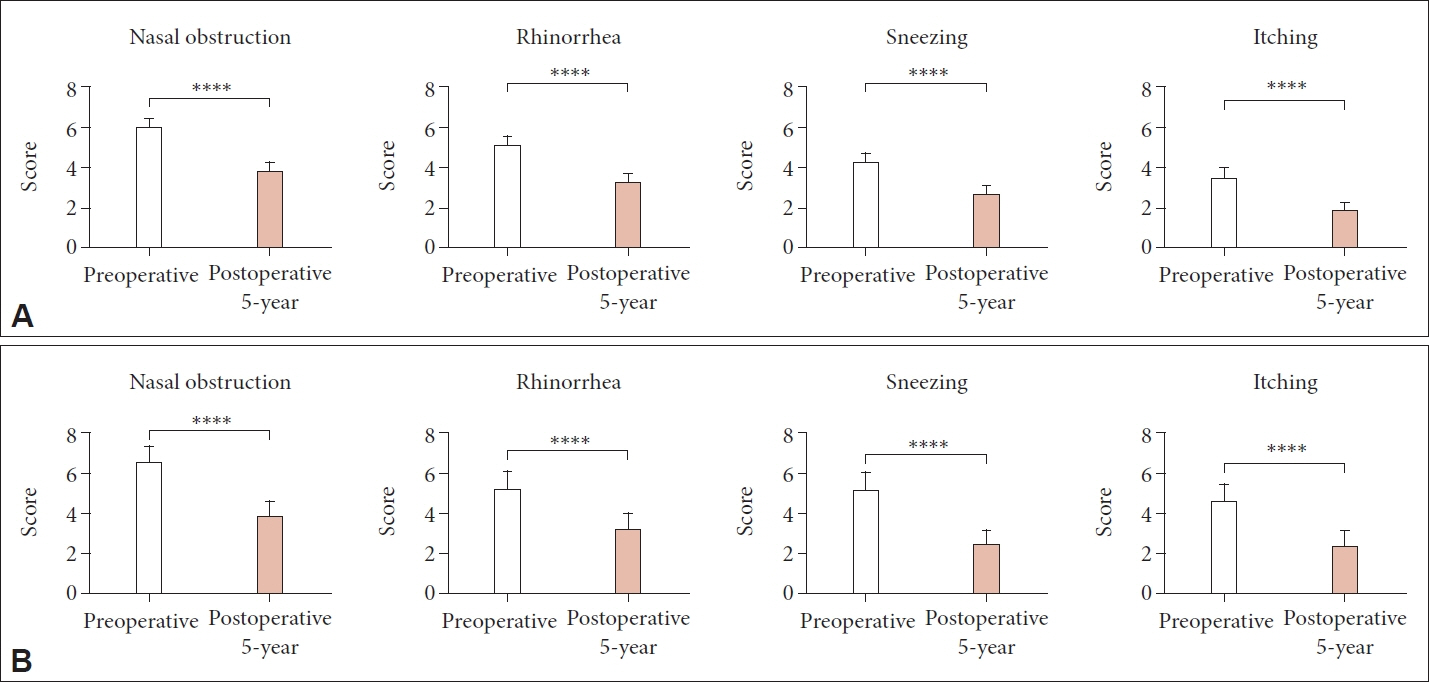
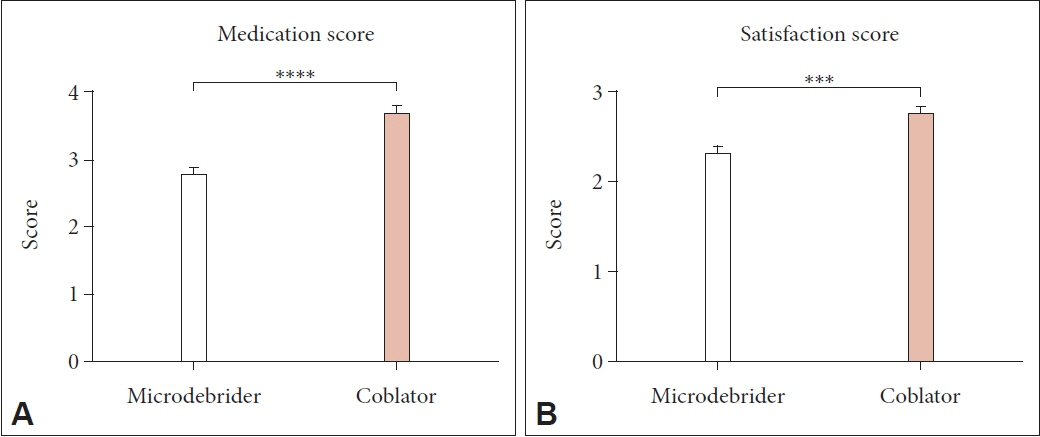
Of the total 241 patients, 192 (79.7%) and 49 (20.3%) underwent microdebrider-assisted turbinoplasty and radiofrequency ablation turbinoplasty, respectively. Both the microdebrider and coblator groups showed remarkable improvements in AR symptoms at the 5-year follow-up (p<0.001). Although the degree of symptom improvement did not differ significantly between the two groups, the coblator group did show significant improvements in medication scores when compared with the microdebrider group (p<0.05), and there were significant differences in postoperative satisfaction scores between the two groups.
Conclusion
In terms of 5-year postoperative outcomes, radiofrequency-ablation turbinoplasty and microdebrider-assisted turbinoplasty were equally beneficial for reducing nasal symptoms and enhancing medication ratings in patients with AR.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Savouré M, Bousquet J, Jaakkola JJK, Jaakkola MS, Jacquemin B, Nadif R. Worldwide prevalence of rhinitis in adults: a review of definitions and temporal evolution. Clin Transl Allergy. 2022; 12(3):e12130.
Article2. Sikorska-Szaflik H, Sozańska B. Quality of life in allergic rhinitis - children’s and their parents› perspective in polish urban and rural population. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020; 18(1):64.3. Meltzer EO. Quality of life in adults and children with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108(1 Suppl):S45–53.4. Lee KC, Cho JM, Kim SK, Lim KR, Lee SY, Park SS. The efficacy of coblator in turbinoplasty. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017; 18(2):82–8.
Article5. Passàli D, Lauriello M, Anselmi M, Bellussi L. Treatment of hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate: long-term results in 382 patients randomly assigned to therapy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 108(6):569–75.
Article6. Abdullah B, Singh S. Surgical interventions for inferior turbinate hypertrophy: a comprehensive review of current techniques and technologies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3441.
Article7. Singh S, Ramli RR, Wan Mohammad Z, Abdullah B. Coblation versus microdebrider-assisted turbinoplasty for endoscopic inferior turbinates reduction. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2020; 47(4):593–601.
Article8. Farmer SE, Quine SM, Eccles R. Efficacy of inferior turbinate coblation for treatment of nasal obstruction. J Laryngol Otol. 2009; 123(3):309–14.
Article9. Chung YJ, Cho IK, Lee KI, Bae SH, Lee JW, Chung PS, et al. Seasonal specificity of seasonal allergens and validation of the ARIA classification in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5(2):75–80.
Article10. Han M, Shin S, Park H, Park KU, Park MH, Song EY. Comparison of three multiple allergen simultaneous tests: RIDA allergy screen, MAST optigen, and polycheck allergy. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:340513.
Article11. Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 140(4):950–8.12. Chhabra N, Houser SM. Surgical options for the allergic rhinitis patient. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012; 20(3):199–204.
Article13. Park DY, Lee YJ, Kim DK, Kim SW, Yang HJ, Kim DH, et al. KAAACI allergic rhinitis guidelines: part 2. Update in non-pharmacological management. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2023; 15(2):145–59.
Article14. Bousquet J, Anto JM, Bachert C, Baiardini I, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Walter Canonica G, et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020; 6(1):95.
Article15. Drazdauskaitė G, Layhadi JA, Shamji MH. Mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020; 21(1):2.
Article16. Mori S, Fujieda S, Igarashi M, Fan GK, Saito H. Submucous turbinectomy decreases not only nasal stiffness but also sneezing and rhinorrhea in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29(11):1542–8.
Article17. Acevedo JL, Camacho M, Brietzke SE. Radiofrequency ablation turbinoplasty versus microdebrider-assisted turbinoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 153(6):951–6.18. Chhabra N, Houser SM. The surgical management of allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2011; 44(3):779–95. , xi.
Article19. Kanesan N, Norhayati MN, Hamid SSA, Abdullah B. Microdebriderassisted inferior turbinoplasty versus other surgical techniques. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2022; 42(5):415–26.
Article20. Lin HC, Lin PW, Friedman M, Chang HW, Su YY, Chen YJ, et al. Long-term results of radiofrequency turbinoplasty for allergic rhinitis refractory to medical therapy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 136(9):892–5.
Article21. Bhandarkar ND, Smith TL. Outcomes of surgery for inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 18(1):49–53.
Article22. Ye T, Zhou B. Update on surgical management of adult inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 23(1):29–33.
Article23. Hegazy HM, ElBadawey MR, Behery A. Inferior turbinate reduction; coblation versus microdebrider - a prospective, randomised study. Rhinology. 2014; 52(4):306–14.
Article24. Pfaar O, Raap U, Holz M, Hörmann K, Klimek L. Pathophysiology of itching and sneezing in allergic rhinitis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2009; 139(3-4):35–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Study on the Long-Term Effectiveness between Coblator- and Microdebrider-Assisted Partial Turbinoplasty
- Surgical treatment for allergic rhinitis
- The Long Term Efficacy of Microdebrider Assisted versus Coblation Assisted Inferior Turbinoplasty
- Treatment of Severe Pregnancy Rhinitis Using Microdebrider-Assisted Inferior Turbinoplasty: A Case Report
- Letter to the Editor “Ten-Year Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Locally Recurrent Papillary Thyroid Cancer”