J Rhinol.
2023 Nov;30(3):139-143. 10.18787/jr.2023.00052.
Effects of a Proton-Pump Inhibitor on Postnasal Drip Symptoms in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2548190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2023.00052
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is an increasingly common disease, characterized by stomach acid reflux reaching the upper airways. Postnasal drip (PND) is a known consequence of LPR, defined as mucus accumulation perceived in the posterior areas of the nose and throat. PND is among the most common causes of persistent cough, hoarseness, sore throat, and other symptoms, affecting the quality of life. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of a proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) on PND symptoms in patients with LPR.
Methods
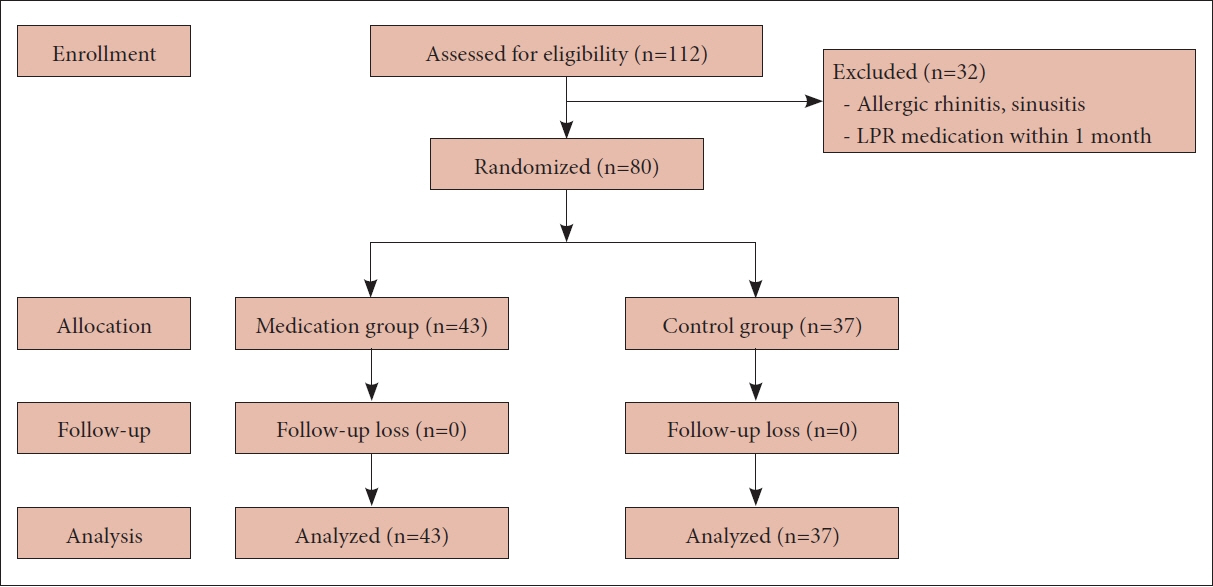
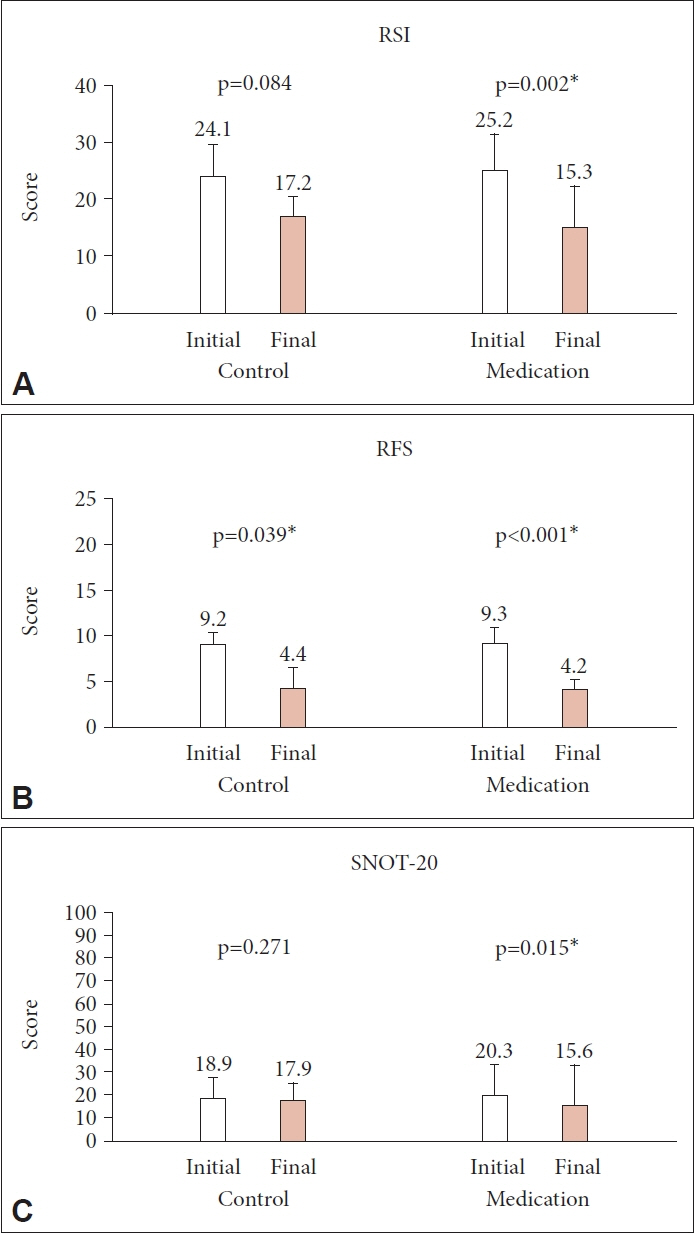
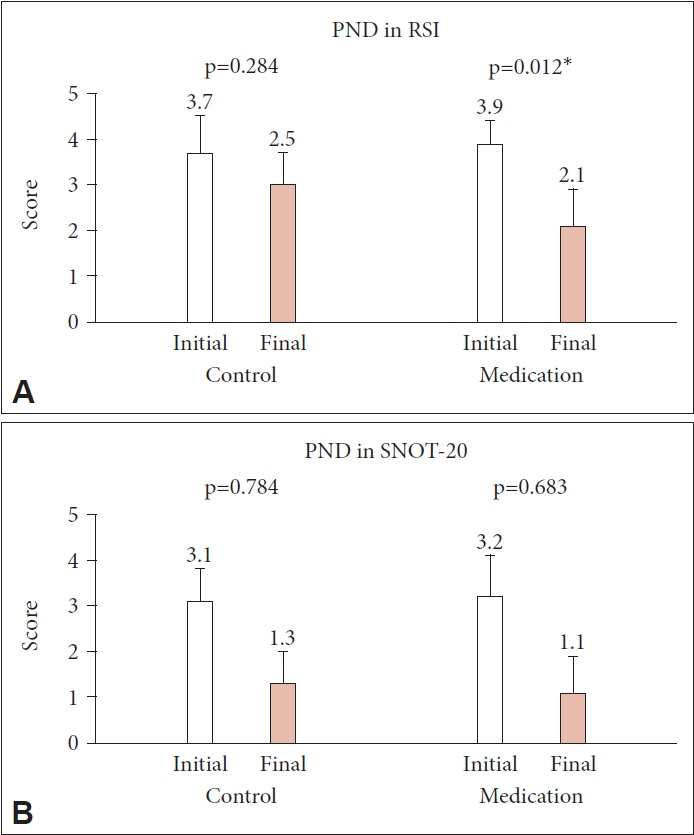
We prospectively enrolled patients diagnosed with LPR at our institution between September 2019 and June 2020. The patients were randomly assigned to either the treatment group (20 mg of ilaprazole daily for 8 weeks) or the control group. The scores for the Reflux Symptom Index (RSI), Reflux Finding Score (RFS), and Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT)-20 were evaluated at baseline and at the end of treatment, focusing on PND symptoms.
Results
Eighty patients (28 men and 52 women; mean age, 48.8 years, range, 22–78 years) were enrolled, with 43 in the treatment group and 37 in the control group. The initial RSI, RFS, and SNOT-20 scores were similar between the two groups, and they decreased significantly only in the treatment group (p=0.002, p<0.001, and p=0.015, respectively). However, the PND symptom scores showed a significant decrease in the treatment group only in the RSI (p=0.012).
Conclusion
PPI treatment for 8 weeks may be effective in improving PND symptoms in patients with LPR.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Koufman JA. Laryngopharyngeal reflux 2002: a new paradigm of airway disease. Ear Nose Throat J. 2002; 81(9 Suppl 2):2–6.2. Ford CN. Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. JAMA. 2005; 294(12):1534–40.3. Shin KS, Tae K, Jeong JH, Jeong SW, Kim KR, Park CW, et al. The role of psychological distress in laryngopharyngeal reflux patients: a prospective questionnaire study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2010; 35(1):25–30.4. Woo JS. Ultra-structural and molecular aspects of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2009; 52(5):394–400.
Article5. Koufman JA, Aviv JE, Casiano RR, Shaw GY. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: position statement of the committee on speech, voice, and swallowing disorders of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 127(1):32–5.
Article6. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope. 2001; 111(8):1313–7.
Article7. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J Voice. 2002; 16(2):274–7.
Article8. Piccirillo JF, Merritt MG Jr, Richards ML. Psychometric and clinimetric validity of the 20-item sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT-20). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 126(1):41–7.
Article9. Kim NH, Kim KS. Postnasal drip syndrome. J Rhinol. 2011; 18(1):16–9.10. Morice AH. Post-nasal drip syndrome--a symptom to be sniffed at? Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 17(6):343–5.
Article11. Boghossian TA, Rashid FJ, Thompson W, Welch V, Moayyedi P, RojasFernandez C, et al. Deprescribing versus continuation of chronic proton pump inhibitor use in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 3(3):CD011969.
Article12. Scarpignato C, Gatta L, Zullo A, Blandizzi C. Effective and safe proton pump inhibitor therapy in acid-related diseases – A position paper addressing benefits and potential harms of acid suppression. BMC Med. 2016; 14(1):179.
Article13. Pawar S, Lim HJ, Gill M, Smith TL, Merati A, Toohill RJ, et al. Treatment of postnasal drip with proton pump inhibitors: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21(6):695–701.
Article14. Koufman JA, Amin MR, Panetti M. Prevalence of reflux in 113 consecutive patients with laryngeal and voice disorders. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 123(4):385–8.
Article15. Wise SK, Wise JC, DelGaudio JM. Association of nasopharyngeal and laryngopharyngeal reflux with postnasal drip symptomatology in patients with and without rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2006; 20(3):283–9.
Article16. Oh JH, Ji YB, Song CM, Jung JH, Jin BJ, Tae K. Correlation between ambulatory 24 hour dual probe pH monitoring and reflux finding score, reflux symptom index in the laryngopharyngeal reflux. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2013; 56(11):706–10.
Article17. Lee JH, Shin HA, Choi HS, Kim CY, Jeong SW, Chang JH. Change of voice quality before and after treatment of short-term therapy with proton pump inhibitor in laryngopharyngeal reflux. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2014; 57(10):703–6.
Article18. Yoo CS, Kim DS, Lee SK, Lee BD, Chang HS, Kang JW. A study for causative diseases of globus pharyngeus patients who have nopathologic conditions in laryngopharynx. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1998; 41(12):1573–8.19. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Amin MR, Koufman JA. Symptoms and findings of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Ear Nose Throat J. 2002; 81(9 Suppl 2):10–3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of a Proton-pump Inhibitor in Unexplained Chronic Cough Patients
- Change of Voice Quality before and after Treatment of Short-Term Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Recent Trends of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease
- Effectiveness of Proton Pump Inhibitor in the Treatment of Contact Granuloma
- Proton Pump Inhibitor for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Intelligent Prescription