Int J Stem Cells.
2023 Nov;16(4):394-405. 10.15283/ijsc23036.
Differentiation and Characterization of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Knockout Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Salivary Gland Epithelial Progenitors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School and Hospital of Stomatology and Central Laboratory, Peking University, Beijing, China
- 2Institute of Molecular Medicine, Peking University, Beijing, China
- KMID: 2548003
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc23036
Abstract
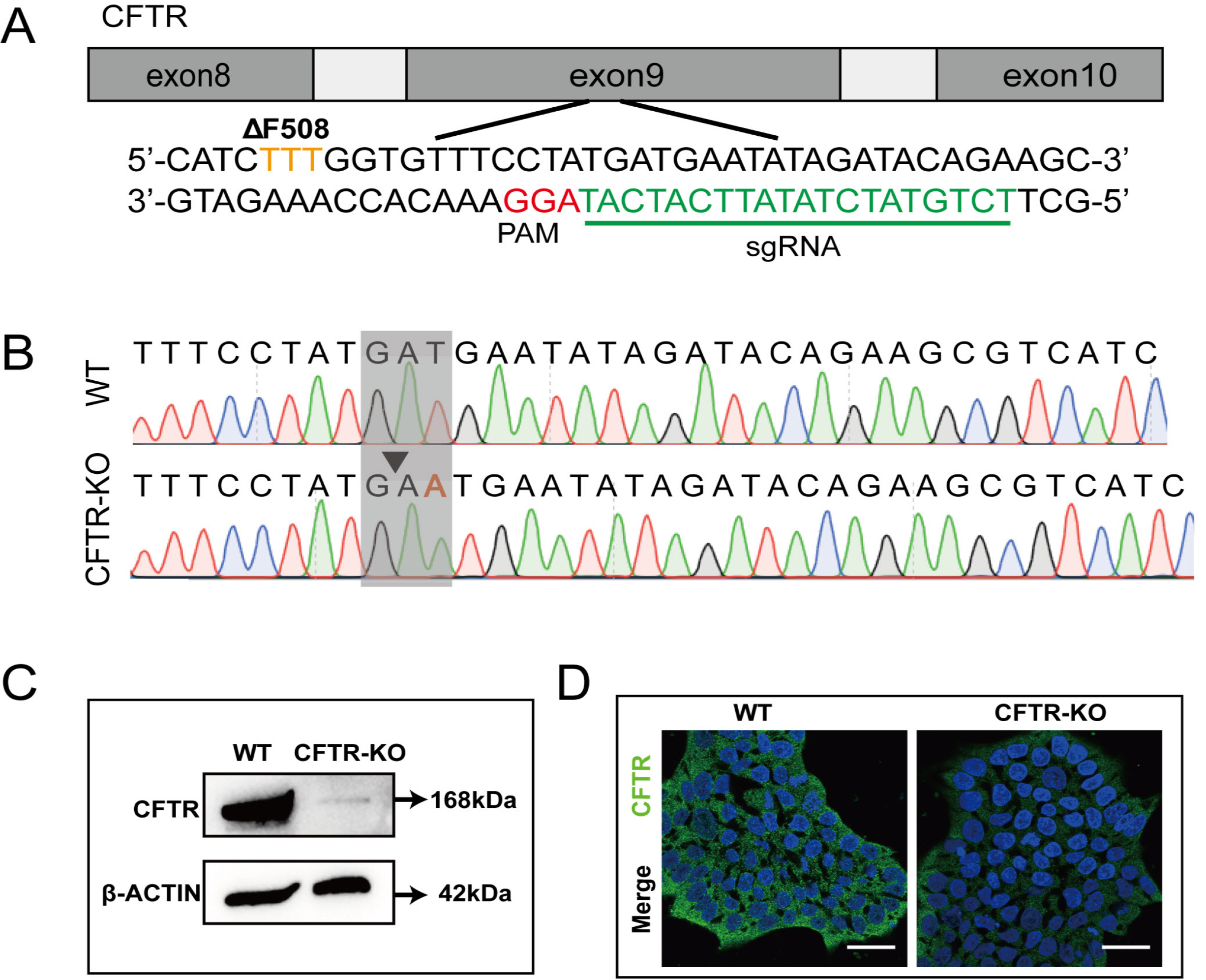
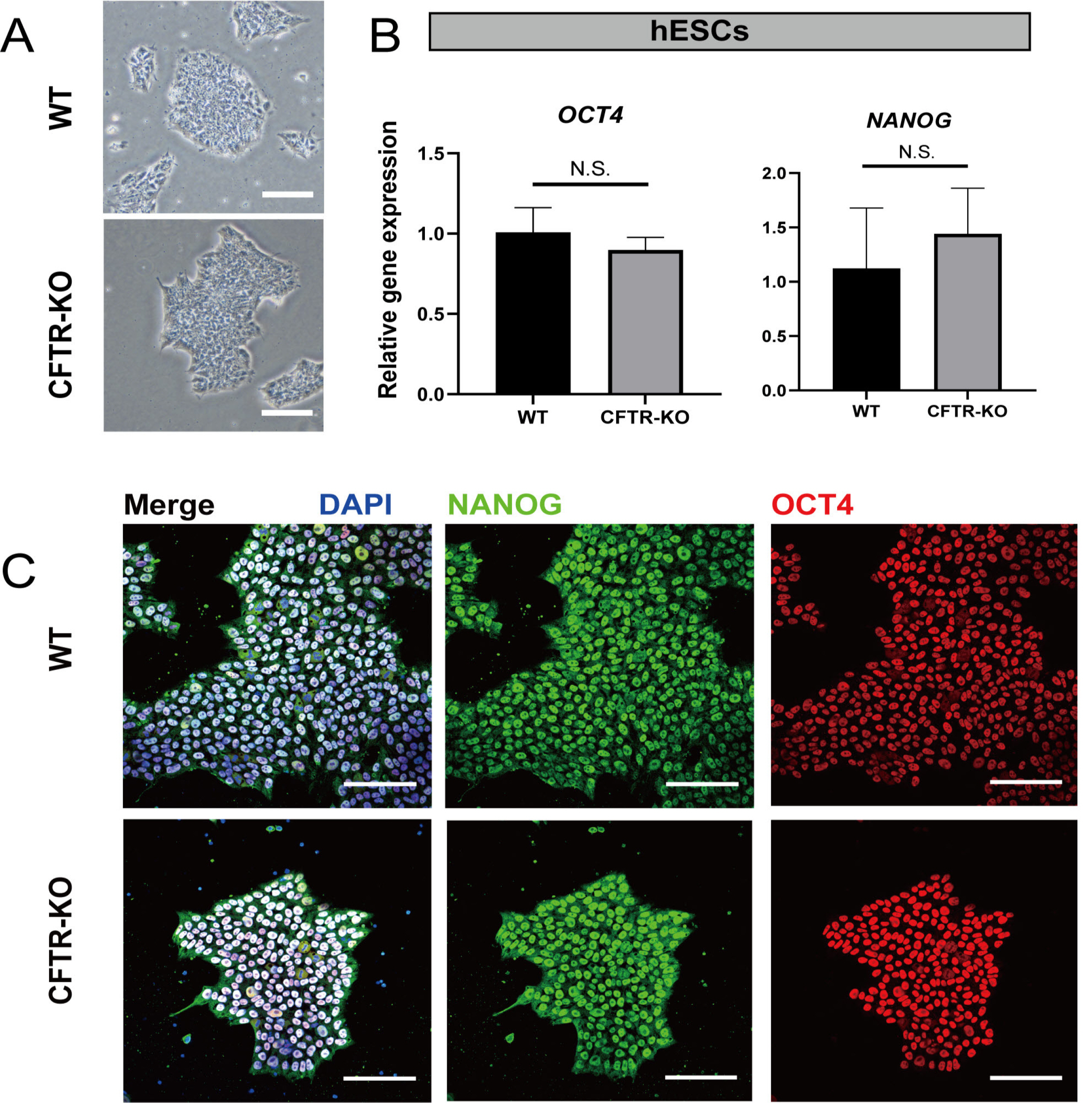
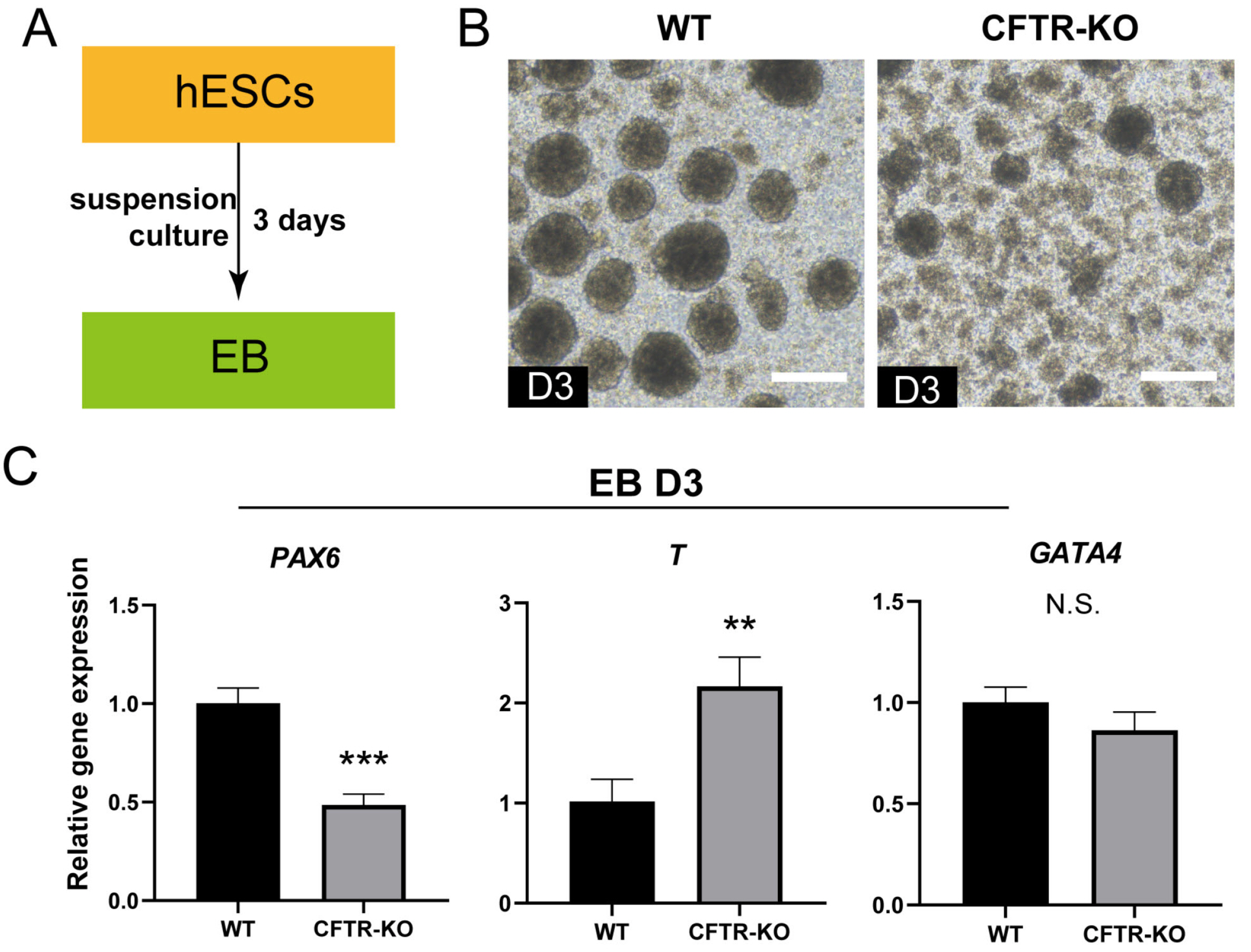
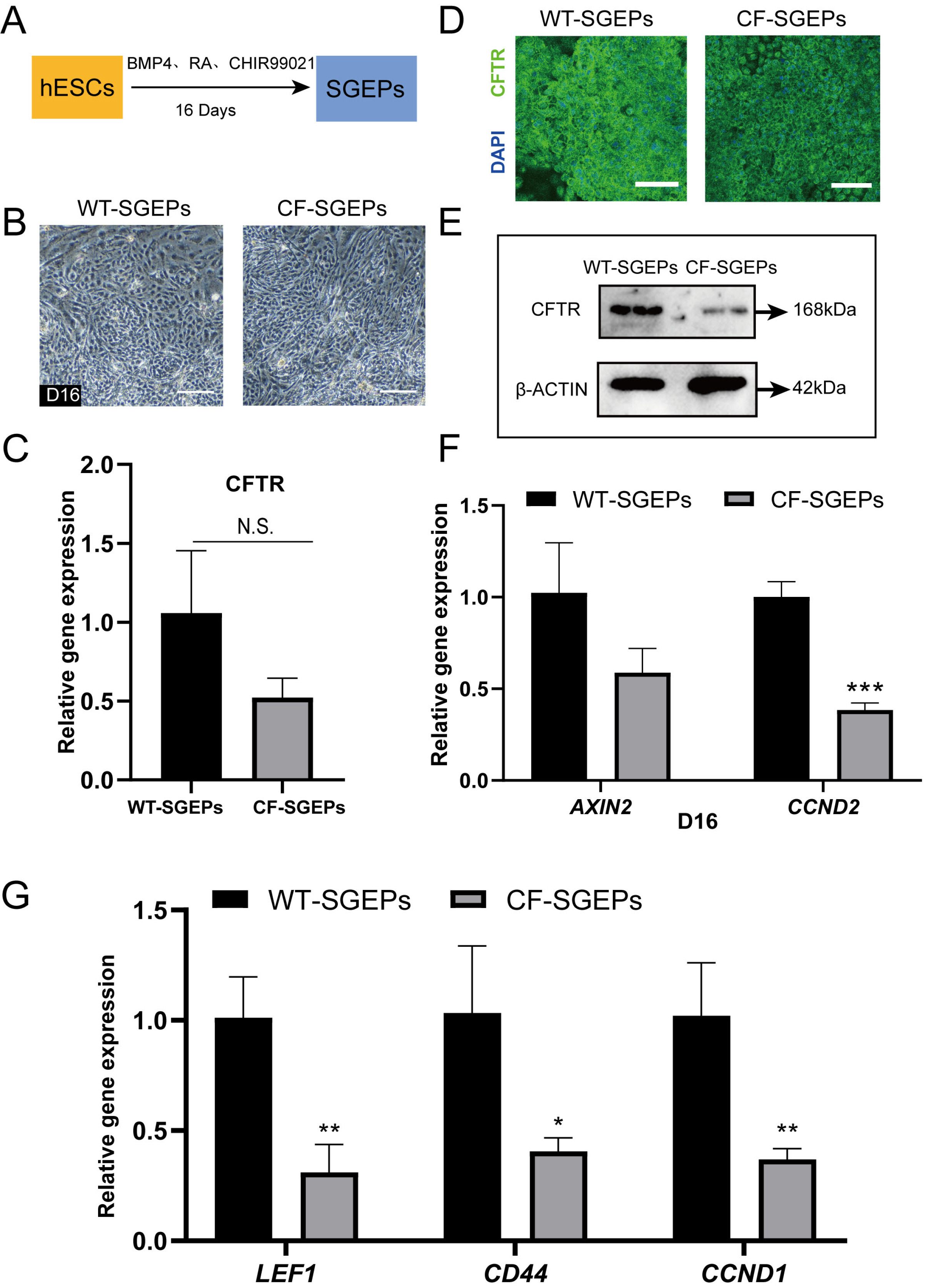
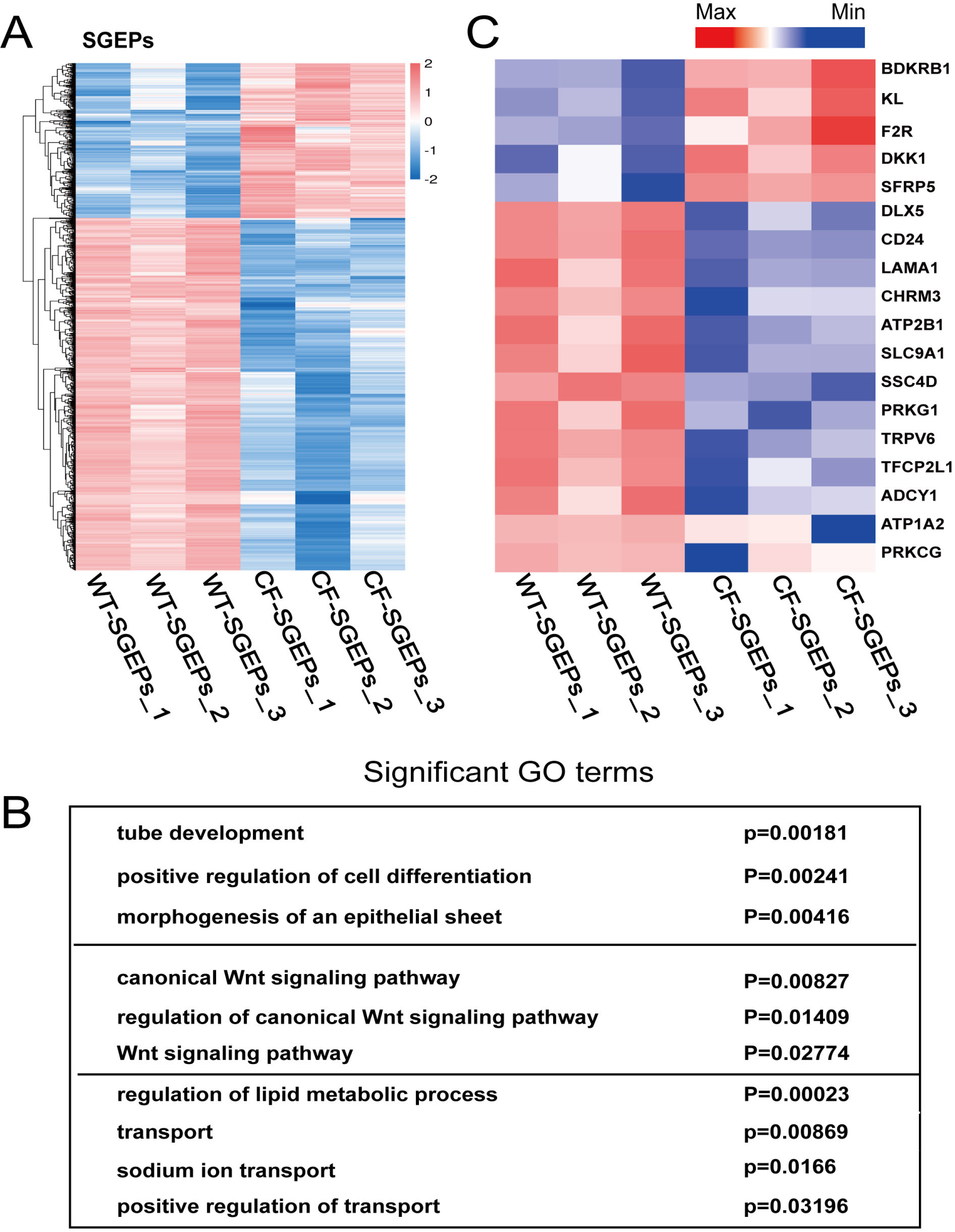
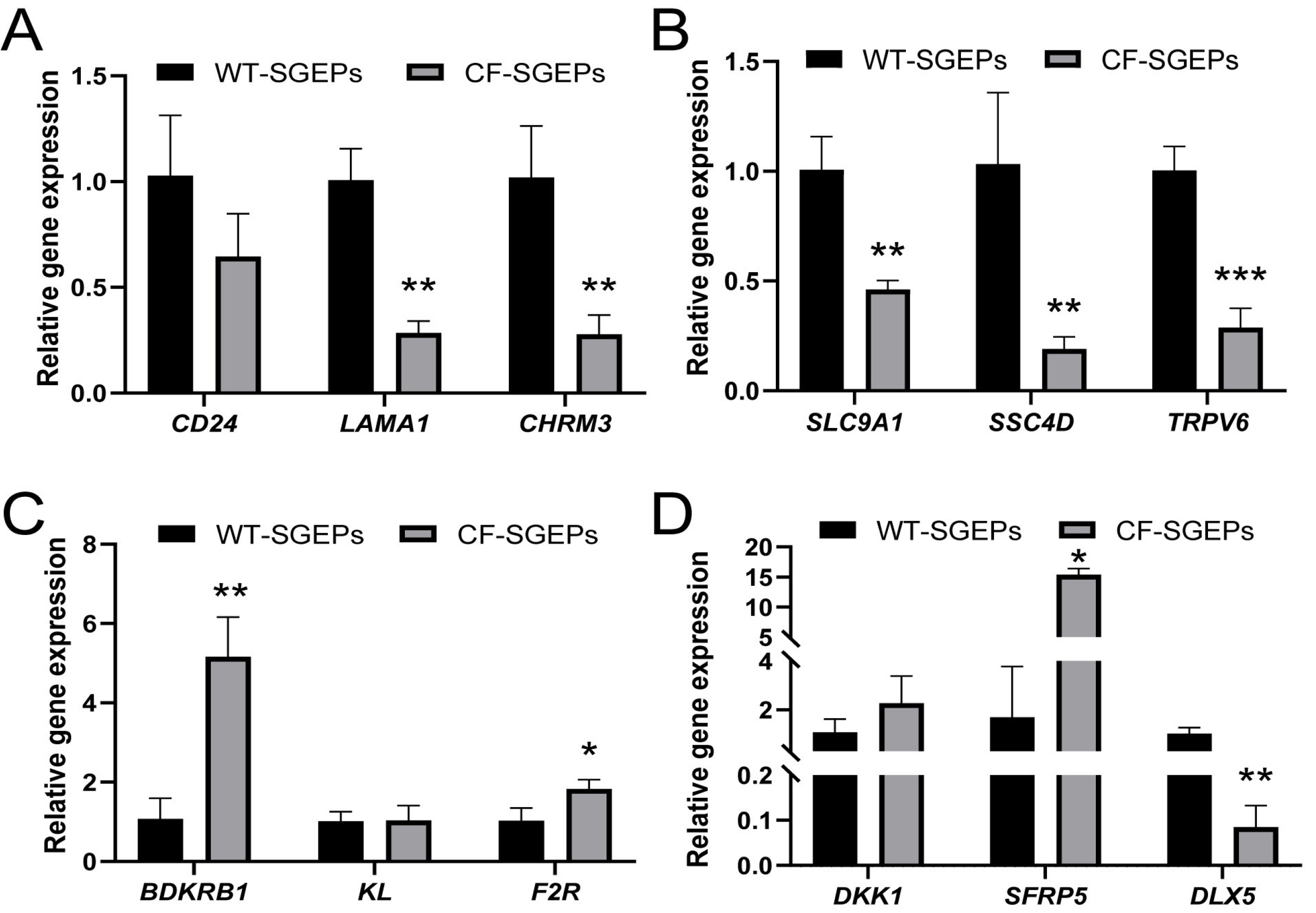
- The differentiation of pluripotent stem cells has been used to study disease mechanisms and development. We previously described a method for differentiating human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into salivary gland epithelial progenitors (SGEPs). Here, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) knockout hPSCs were differentiated into SGEPs derived from CFTR knockout hESCs (CF-SGEPs) using the same protocol to investigate whether the hPSC-derived SGEPs can model the characteristics of CF. CF—a disease that affects salivary gland (SG) function—is caused by mutations of the CFTR gene. Firstly, we successfully generated CFTR knockout hPSCs with reduced CFTR protein expression using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. After 16 days of differentiation, the protein expression of CFTR decreased in SGEPs derived from CFTR knockout hESCs (CF-SGEPs). RNA-Seq revealed that multiple genes modulating SG development and function were down-regulated, and positive regulators of inflammation were up-regulated in CF-SGEPs, correlating with the salivary phenotype of CF patients. These results demonstrated that CFTR suppression disrupted the differentiation of hPSC-derived SGEPs, which modeled the SG development of CF patients. In summary, this study not only proved that the hPSC-derived SGEPs could serve as manipulable and readily accessible cell models for the study of SG developmental diseases but also opened up new avenues for the study of the CF mechanism.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kolagar TA, Farzaneh M, Nikkar N, Khoshnam SE. 2020; Hu-man pluripotent stem cells in neurodegenerative diseases: potentials, advances and limitations. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 15:102–110. DOI: 10.2174/1574888X14666190823142911. PMID: 31441732.2. Liu G, David BT, Trawczynski M, Fessler RG. 2020; Advances in pluripotent stem cells: history, mechanisms, technolo-gies, and applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 16:3–32. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-019-09935-x. PMID: 31760627. PMCID: PMC6987053.
Article3. Lancaster MA, Renner M, Martin CA, et al. 2013; Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature. 501:373–379. DOI: 10.1038/nature12517. PMID: 23995685. PMCID: PMC3817409.
Article4. Drakhlis L, Devadas SB, Zweigerdt R. 2021; Generation of heart-forming organoids from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Protoc. 16:5652–5672. DOI: 10.1038/s41596-021-00629-8. PMID: 34759383.
Article5. McCracken KW, Catá EM, Crawford CM, et al. 2014; Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature. 516:400–404. DOI: 10.1038/nature13863. PMID: 25363776. PMCID: PMC4270898.
Article6. Spence JR, Mayhew CN, Rankin SA, et al. 2011; Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature. 470:105–109. DOI: 10.1038/nature09691. PMID: 21151107. PMCID: PMC3033971.
Article7. Tam WL, Freitas Mendes L, Chen X, et al. 2021; Human pluripotent stem cell-derived cartilaginous organoids promote scaffold-free healing of critical size long bone defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:513. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-021-02580-7. PMID: 34563248. PMCID: PMC8466996. PMID: e0bbc5cdaf7747208d680c993e153392.
Article8. Petersen MBK, Gonçalves CAC, Kim YH, Grapin-Botton A. 2018; Recapitulating and deciphering human pancreas development from human pluripotent stem cells in a dish. Curr Top Dev Biol. 129:143–190. DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2018.02.009. PMID: 29801529.
Article9. Heslop JA, Duncan SA. 2019; The use of human pluripotent stem cells for modeling liver development and disease. Hepatology. 69:1306–1316. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30288. PMID: 30251414.
Article10. Emmerson E, Knox SM. 2018; Salivary gland stem cells: a review of development, regeneration and cancer. Genesis. 56:e23211. DOI: 10.1002/dvg.23211. PMID: 29663717. PMCID: PMC5980780.
Article11. Holmberg KV, Hoffman MP. 2014; Anatomy, biogenesis and regeneration of salivary glands. Monogr Oral Sci. 24:1–13. DOI: 10.1159/000358776. PMID: 24862590. PMCID: PMC4048853.
Article12. Tanaka J, Senpuku H, Ogawa M, et al. 2022; Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived salivary gland organoids model SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication. Nat Cell Biol. 24:1595–1605. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-01007-6. PMID: 36253535.
Article13. Zhang S, Sui Y, Zhang Y, et al. 2023; Derivation of human salivary epithelial progenitors from pluripotent stem cells via activation of RA and Wnt signaling. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 19:430–442. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-022-10431-y. PMID: 35948781.
Article14. Ooi CY, Durie PR. 2016; Cystic fibrosis from the gastroentero-logist's perspective. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:175–185. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.226. PMID: 26790364.
Article15. Sermet-Gaudelus I, Vallée B, Urbin I, et al. 2002; Normal function of the cystic fibrosis conductance regulator protein can be associated with homozygous (Delta)F508 mutation. Pediatr Res. 52:628–635. DOI: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000032981.64413.AD. PMID: 12409506.
Article16. Trapnell BC, Chu CS, Paakko PK, et al. 1991; Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene in the respiratory tract of normal individuals and indivi-duals with cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 88:6565–6569. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6565. PMID: 1713683. PMCID: PMC52127.
Article17. Barbero GJ, Sibinga MS. 1962; Enlargement of the submaxillary salivary glands in cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 29:788–793. DOI: 10.1542/peds.29.5.788. PMID: 13864857.
Article18. da Silva Modesto KB, de Godói Simões JB, de Souza AF, et al. 2015; Salivary flow rate and biochemical composition analysis in stimulated whole saliva of children with cystic fibro-sis. Arch Oral Biol. 60:1650–1654. DOI: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.08.007. PMID: 26351748.
Article19. El Khoury J, Haber E, Nasr M, Hokayem N. 2016; Botulinum neurotoxin A for parotid enlargement in cystic fibrosis: the first case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 74:1771–1773. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.03.038. PMID: 27131031.
Article20. Nedvetsky PI, Emmerson E, Finley JK, et al. 2014; Parasympa-thetic innervation regulates tubulogenesis in the developing salivary gland. Dev Cell. 30:449–462. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.06.012. PMID: 25158854. PMCID: PMC4155578.
Article21. Ran FA, Hsu PD, Wright J, Agarwala V, Scott DA, Zhang F. 2013; Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc. 8:2281–2308. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2013.143. PMID: 24157548. PMCID: PMC3969860.
Article22. Liu Z, Guo J, Wang Y, et al. 2017; CFTR-β-catenin interaction regulates mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation and embryonic development. Cell Death Differ. 24:98–110. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2016.118. PMID: 27834953. PMCID: PMC5260497.
Article23. Nanduri LS, Baanstra M, Faber H, et al. 2014; Purification and ex vivo expansion of fully functional salivary gland stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 3:957–964. DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.09.015. PMID: 25448065. PMCID: PMC4264052. PMID: ff5fb296102c4ee7b2546e2d78fb48d8.
Article24. Kadoya Y, Nomizu M, Sorokin LM, Yamashina S, Yamada Y. 1998; Laminin alpha1 chain G domain peptide, RKRLQVQ-LSIRT, inhibits epithelial branching morphogenesis of cultured embryonic mouse submandibular gland. Dev Dyn. 212:394–402. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199807)212:3<394::AID-AJA7>3.0.CO;2-C.
Article25. Yang TL, Hsiao YC. 2015; Chitosan facilitates structure formation of the salivary gland by regulating the basement membrane components. Biomaterials. 66:29–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.028. PMID: 26189212.
Article26. Nichols DP, Chmiel JF. 2015; Inflammation and its genesis in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 50 Suppl 40:S39–S56. DOI: 10.1002/ppul.23242. PMID: 26335954.
Article27. Sun H, Wang Y, Zhang J, et al. 2018; CFTR mutation enhances Dishevelled degradation and results in impairment of Wnt-dependent hematopoiesis. Cell Death Dis. 9:275. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0311-9. PMID: 29449653. PMCID: PMC5833403.
Article28. Dumortier C, Danopoulos S, Velard F, Al Alam D. 2021; Bone cells differentiation: how CFTR mutations may rule the game of stem cells commitment? Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:611921. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.611921. PMID: 34026749. PMCID: PMC8139249. PMID: 577d821c5fd9461592081e812c559a2c.
Article29. Rowe SM, Miller S, Sorscher EJ. 2005; Cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 352:1992–2001. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra043184. PMID: 15888700.
Article30. Meng X, Clews J, Kargas V, Wang X, Ford RC. 2017; The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and its stability. Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:23–38. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2386-8. PMID: 27734094. PMCID: PMC5209436.
Article31. Zinn VZ, Khatri A, Mednieks MI, Hand AR. 2015; Localization of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator signaling complexes in human salivary gland striated duct cells. Eur J Oral Sci. 123:140–148. DOI: 10.1111/eos.12184. PMID: 25903037. PMCID: PMC4425606.
Article32. Alshahran SA, Almufareh NA, Almarshady B, Alotaibi RK, Al-Qahtani WS. 2020; Effects of consuming Catha edulis Forsk (khat) on the gene manifestation of CHRM1 and CHRM3 in relation to salivary glands, saliva flow rates, pH and dental caries in Yemeni consumers. Open Dent J. 14:482–488. DOI: 10.2174/1874210602014010482.33. Jeong J, Baek H, Kim YJ, et al. 2013; Human salivary gland stem cells ameliorate hyposalivation of radiation-damaged rat salivary glands. Exp Mol Med. 45:e58. DOI: 10.1038/emm.2013.121. PMID: 24232257. PMCID: PMC3849572.
Article34. Fonseca I, Moura Nunes JF, Soares J. 2000; Expression of CD44 isoforms in normal salivary gland tissue: an immunohis-tochemical and ultrastructural study. Histochem Cell Biol. 114:483–488. DOI: 10.1007/s004180000220. PMID: 11201610.
Article35. Gonzalez-Begne M, Nakamoto T, Nguyen HV, Stewart AK, Alper SL, Melvin JE. 2007; Enhanced formation of a HCO3-transport metabolon in exocrine cells of Nhe1-/-mice. J Biol Chem. 282:35125–35132. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M707266200. PMID: 17890222.
Article36. Shen ZJ, Han YC, Nie MW, Xiang RL, Xie HZ. 2021; Analyses of circRNA and mRNA profiles in the submandibular gland in hypertension. Genomics. 113(1 Pt 1):57–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.016. PMID: 33227410.
Article37. Zou DP, Chen YM, Zhang LZ, et al. 2020; SFRP5 inhibits melanin synthesis of melanocytes in vitiligo by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes Dis. 8:677–688. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.06.003. PMID: 34291139. PMCID: PMC8278527.
Article38. Harutyunyan SA, Simonyan KG, Mkrtchyan NM, Kashir-skaya NY, Libik M, Macek M. 2020; Sialadenitis in cystic fibrosis: case report. Doctor.Ru. 19:66–68. Russian. DOI: 10.31550/1727-2378-2020-19-10-66-68.39. Bachvarov DR, Hess JF, Menke JG, Larrivée JF, Marceau F. 1996; Structure and genomic organization of the human B1 receptor gene for kinins (BDKRB1). Genomics. 33:374–381. DOI: 10.1006/geno.1996.0213. PMID: 8660997.
Article40. Lv J, Liu J, Chao G, Zhang S. 2023; PARs in the inflam-mation-cancer transformation of CRC. Clin Transl Oncol. 25:1242–1251. DOI: 10.1007/s12094-022-03052-x. PMID: 36547764.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cystic fibrosis lung disease: Current perspectives
- Localization of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator in Nasal Polyp Epithelial Cell
- Uridine-5'-Triphosphate Stimulates Chloride Secretion via Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator and Ca2+-Activated Chloride Channels in Cultured Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cells
- Molecular Mechanism of Pancreatic Bicarbonate Secretion
- Cystic fibrosis in a female adolescent carrying c.263T>G (p.Leu88X) and c.2977G>T (p.Asp993Tyr) mutation