Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Oct;55(4):1152-1170. 10.4143/crt.2023.493.
Final Report on Real-World Effectiveness of Sequential Afatinib and Osimertinib in EGFR-Positive Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Analysis of the RESET Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine and Biomedical Research Institute, Busan, Korea
- 5Division of Pulmonology, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 14Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 15Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
- 16Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 17Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2547790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2023.493
Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to report the final analysis of time-on-treatment (TOT) and overall survival (OS) in patients with advanced-stage epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)+ non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who received sequential afatinib and osimertinib and to compare the outcomes with other second-line regimens (comparator group).
Materials and Methods
In this updated report, the existing medical records were reviewed and rechecked. TOT and OS were updated and analyzed according to clinical features using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. TOT and OS were compared with those of the comparator group, in which most patients received pemetrexed-based treatments. A multivariable Cox proportional hazard model was used to evaluate features that could affect survival outcomes.
Results
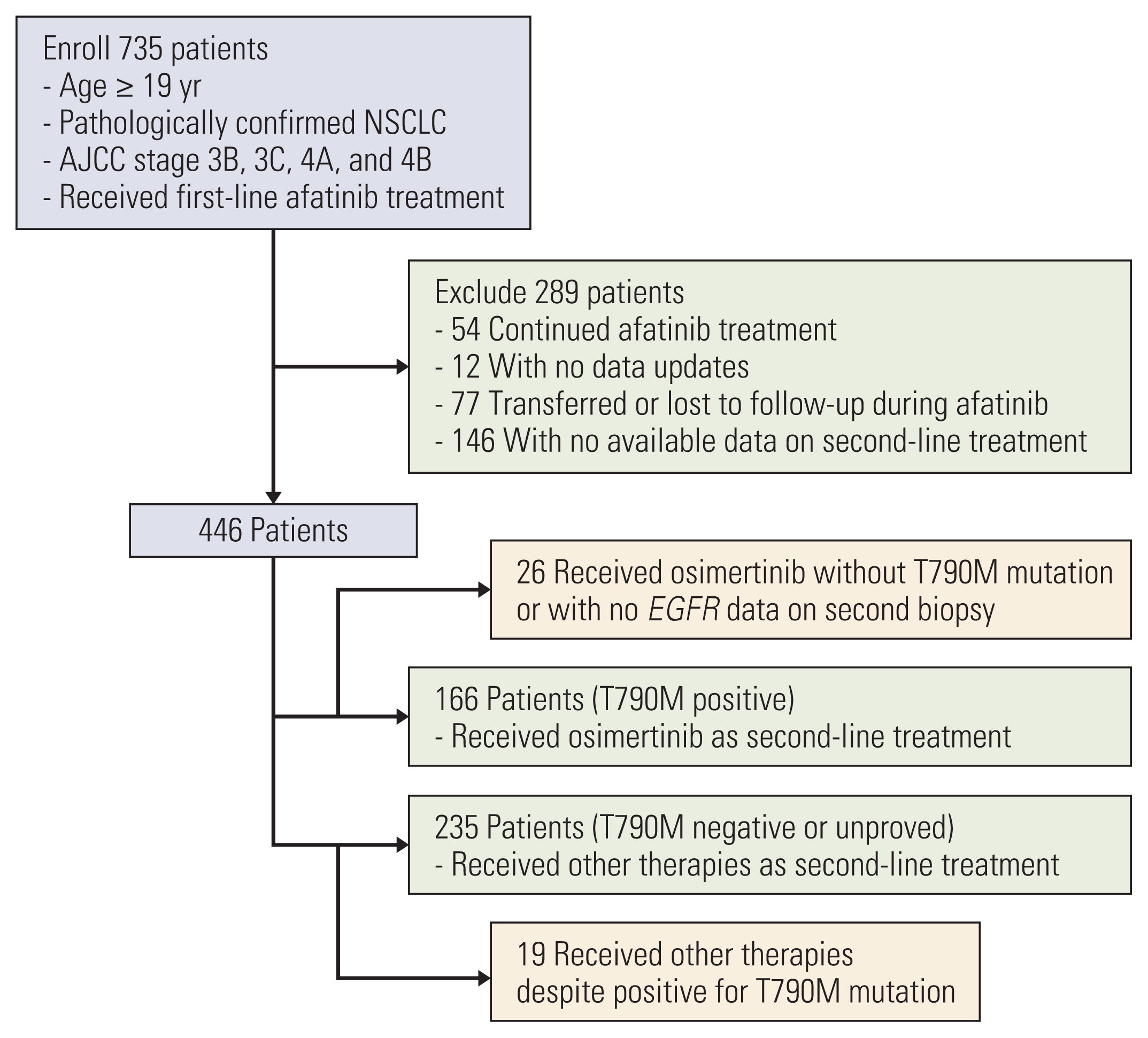
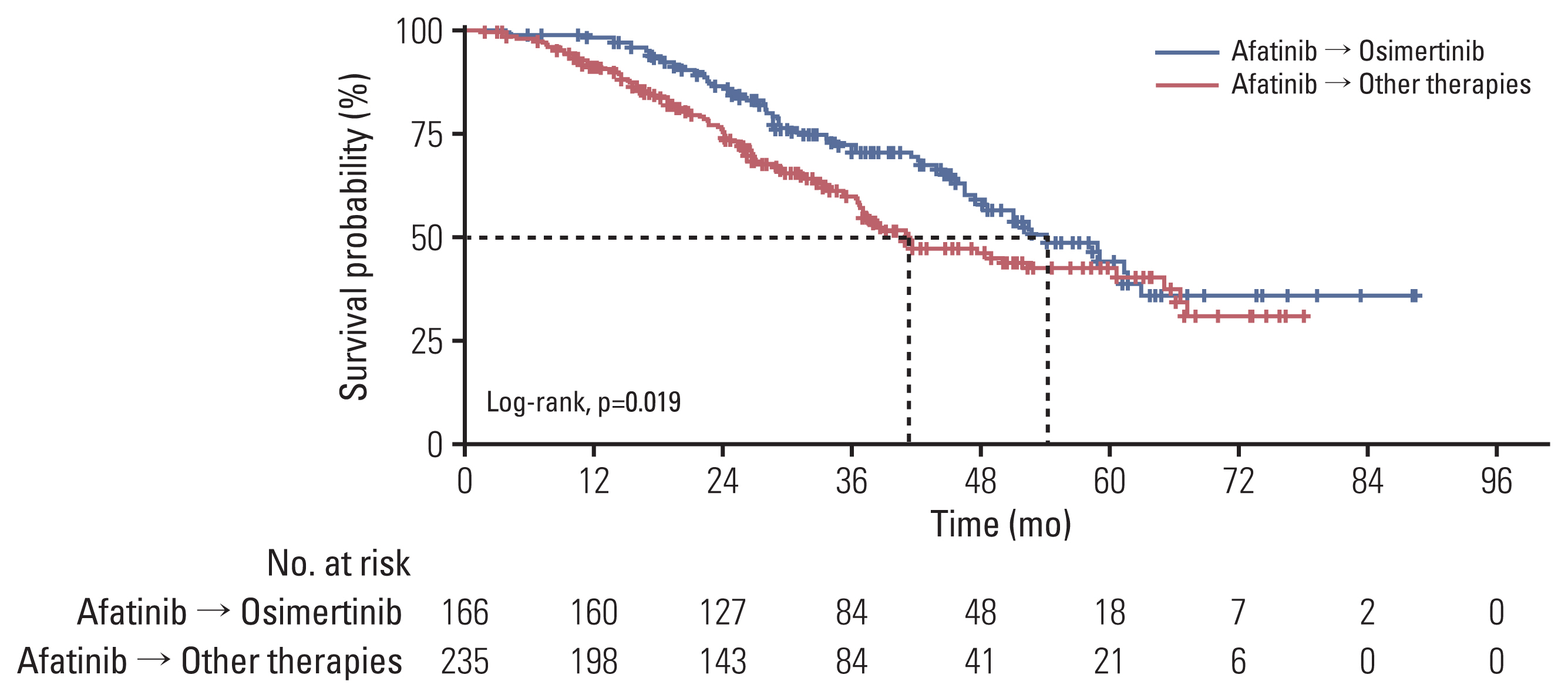
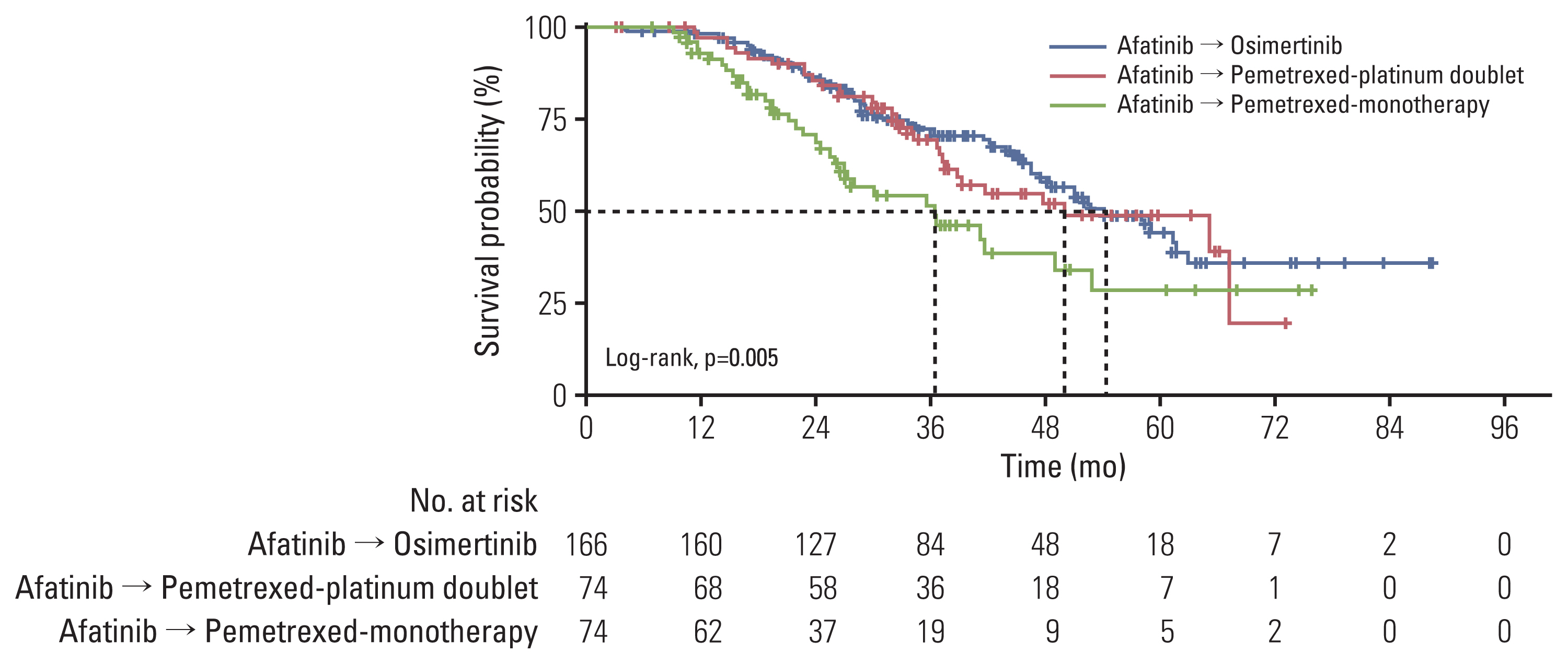
The median observation time was 31.0 months. The follow-up period was extended to 20 months. A total of 401 patients who received first-line afatinib were analyzed (166 with T790M+ and second-line osimertinib, and 235 with unproven T790M and other second-line agents). Median TOTs on afatinib and osimertinib were 15.0 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 14.0 to 16.1) and 11.9 months (95% CI, 8.9 to 14.6), respectively. The median OS in the osimertinib group was 54.3 months (95% CI, 46.7 to 61.9), much longer than that in the comparator group. In patients who received osimertinib, the OS was longest with Del19+ (median, 59.1; 95% CI, 48.7 to 69.5).
Conclusion
This is one of the largest real-world studies reporting the encouraging activity of sequential afatinib and osimertinib in Asian patients with EGFR+ NSCLC who acquired the T790M mutation, particularly Del19+.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Pineros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J Cancer. 2021; 149:778–89.2. Zhang Y, Luo G, Etxeberria J, Hao Y. Global patterns and trends in lung cancer incidence: a population-based study. J Thorac Oncol. 2021; 16:933–44.3. Cheng TY, Cramb SM, Baade PD, Youlden DR, Nwogu C, Reid ME. The international epidemiology of lung cancer: latest trends, disparities, and tumor characteristics. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:1653–71.4. Lortet-Tieulent J, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Rutherford M, Weiderpass E, Bray F. International trends in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype: adenocarcinoma stabilizing in men but still increasing in women. Lung Cancer. 2014; 84:13–22.5. Lee JG, Kim HC, Choi CM. Recent trends of lung cancer in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2021; 84:89–95.6. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.7. Ke EE, Zhou Q, Zhang QY, Su J, Chen ZH, Zhang XC, et al. A higher proportion of the EGFR T790M mutation may contribute to the better survival of patients with exon 19 deletions compared with those with L858R. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:1368–75.8. Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:629–40.9. Paz-Ares L, Tan EH, O’Byrne K, Zhang L, Hirsh V, Boyer M, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28:270–7.10. Hochmair MJ, Morabito A, Hao D, Yang CT, Soo RA, Yang JC, et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: final analysis of the GioTag study. Future Oncol. 2020; 16:2799–808.11. Popat S, Jung HA, Lee SY, Hochmair MJ, Lee SH, Escriu C, et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC and acquired T790M: a global non-interventional study (UpSwinG). Lung Cancer. 2021; 162:9–15.12. Kim T, Jang TW, Choi CM, Kim MH, Lee SY, Park CK, et al. Sequential treatment of afatinib and osimertinib or other regimens in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: results from a real-world study in South Korea. Cancer Med. 2021; 10:5809–22.13. Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:213–22.14. Akamatsu H, Katakami N, Okamoto I, Kato T, Kim YH, Imamura F, et al. Osimertinib in Japanese patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA3 trial. Cancer Sci. 2018; 109:1930–8.15. Smit EF, Burgers SA, Biesma B, Smit HJ, Eppinga P, Dingemans AM, et al. Randomized phase II and pharmacogenetic study of pemetrexed compared with pemetrexed plus carboplatin in pretreated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:2038–45.16. Miura S, Jung HA, Lee SY, Lee SH, Lee MK, Lee YC, et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in Asian patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-dmall vell lung cancer and acquired T790M: combined analysis of two global non-interventional studies. Onco Targets Ther. 2022; 15:873–82.17. Kogure Y, Shigematsu F, Oki M, Saka H. T790M correlates with longer progression-free survival in non-small cell lung carcinomas harboring EGFR mutations. In Vivo. 2018; 32:1199–204.18. Gaut D, Sim MS, Yue Y, Wolf BR, Abarca PA, Carroll JM, et al. Clinical implications of the T790M mutation in disease characteristics and treatment response in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Lung Cancer. 2018; 19:e19–28.19. Chmielecki J, Foo J, Oxnard GR, Hutchinson K, Ohashi K, Somwar R, et al. Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with evolutionary cancer modeling. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3:90ra59.20. Regales L, Balak MN, Gong Y, Politi K, Sawai A, Le C, et al. Development of new mouse lung tumor models expressing EGFR T790M mutants associated with clinical resistance to kinase inhibitors. PLoS One. 2007; 2:e810.21. Leonetti A, Sharma S, Minari R, Perego P, Giovannetti E, Tiseo M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2019; 121:725–37.22. Yonesaka K, Kobayashi Y, Hayashi H, Chiba Y, Mitsudomi T, Nakagawa K. Dual blockade of EGFR tyrosine kinase using osimertinib and afatinib eradicates EGFR-mutant Ba/F3 cells. Oncol Rep. 2019; 41:1059–66.23. Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:41–50.24. Kang MJ, Won YJ, Lee JJ, Jung KW, Kim HJ, Kong HJ, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2019. Cancer Res Treat. 2022; 54:330–44.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Afatinib for Lung Cancer on Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy of Rebiopsy and EGFR Mutation Test of Tissue and Plasma Samples in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- The Role of Brain Radiotherapy before First-Line Afatinib Therapy, Compared to Gefitinib or Erlotinib, in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Efficacy and Safety of Afatinib for EGFR-mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, Compared with Gefitinib or Erlotinib
- Real-World Study of Osimertinib in Korean Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor T790M Mutation–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer