Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Oct;82(4):194-197. 10.4166/kjg.2023.090.
Case of Abdominal Colicky Pain Caused by Hepatic Paragonimiasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Gumi, Korea
- KMID: 2547290
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.090
Abstract
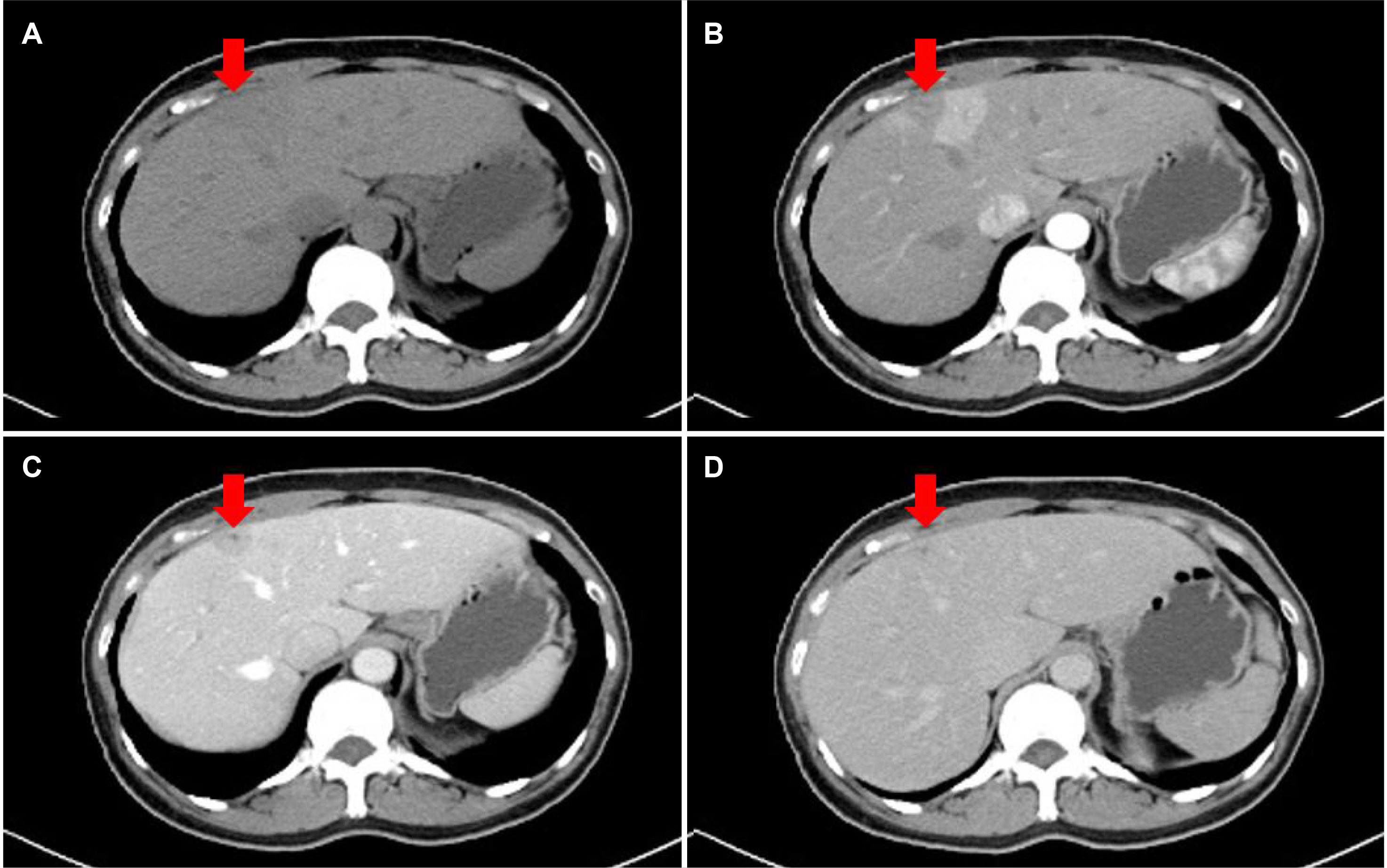
- In Korea, the prevalence of paragonimiasis has decreased markedly since 1970 and is now rarely encountered. Although the lung is the primary site of paragonimiasis, ectopic infestation can occur in other sites. The central nervous system is the most commonly involved ectopic site, accounting for only approximately 1% of all paragonimiasis patients. Therefore, the liver is an extremely rare site of ectopic infestation. The authors experienced the case of a 55-year-old female with hepatic paragonimiasis who presented with abdominal colicky pain.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cartwright SL, Knudson MP. 2008; Evaluation of acute abdominal pain in adults. Am Fam Physician. 77:971–978.2. Kim TS, Cho SH, Huh S, et al. 2009; A nationwide survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Republic of Korea, 2004. Korean J Parasitol. 47:37–47. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.1.37. PMID: 19290090. PMCID: PMC2655332.
Article3. Cho SY, Kong Y, Kang SY. 1997; Epidemiology of paragonimiasis in Korea. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 28 Suppl 1:32–36.4. Mukae H, Taniguchi H, Matsumoto N, et al. 2001; Clinicoradiologic features of pleuropulmonary Paragonimus westermani on Kyusyu Island, Japan. Chest. 120:514–520. DOI: 10.1378/chest.120.2.514. PMID: 11502652.
Article5. Chai JY. 2013; Paragonimiasis. Handb Clin Neurol. 114:283–296. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53490-3.00023-6. PMID: 23829919.
Article6. Yokogawa M. 1965; Paragonimus and paragonimiasis. Adv Parasitol. 3:99–158. DOI: 10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60364-4. PMID: 5334823.
Article7. Ogakwu M, Nwokolo C. 1973; Radiological findings in pulmonary paragonimiasis as seen in Nigeria: a review based on one hundred cases. Br J Radiol. 46:699–705. DOI: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-549-699. PMID: 4726120.
Article8. Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Mukae H, Nawa Y. 2002; Paragonimiasis: a Japanese perspective. Clin Chest Med. 23:409–420. DOI: 10.1016/S0272-5231(01)00006-5. PMID: 12092035.
Article9. Ye X, Xiong X, Cheng N, Lu J, Lin Y. 2017; Hepatic paragonimiasis: a single-center retrospective analysis of 32 cases in Mainland China. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 5:282–287. DOI: 10.1093/gastro/gox008. PMID: 29230298. PMCID: PMC5691780.
Article10. Kim EA, Juhng SK, Kim HW, et al. 2004; Imaging findings of hepatic paragonimiasis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 19:759–762. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.759. PMID: 15483359. PMCID: PMC2816346.
Article11. Cha SH, Chang KH, Cho SY, et al. 1994; Cerebral paragonimiasis in early active stage: CT and MR features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 162:141–145. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.162.1.8273653. PMID: 8273653.
Article12. Chi JG, Choi WY, Lee OR, Chung CS. 1982; [Changes of liver and diaphragm in experimental paragonimiasis]. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi. 20:160–168. Korean. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.1982.20.2.160. PMID: 12902688.
Article13. Hu X, Feng R, Zheng Z, Liang J, Wang H, Lu J. 1982; Hepatic damage in experimental and clinical paragonimiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 31:1148–1155. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1148. PMID: 7149101.
Article14. Chen J, Chen Z, Lin J, et al. 2013; Cerebral paragonimiasis: a retrospective analysis of 89 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 115:546–551. DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.06.025. PMID: 22795301.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging Findings of Hepatic Paragonimiasis: A Case Report
- Paragonimiasis in the Abdominal Cavity and Subcutaneous Tissue: Report of 3 Cases
- A Case of Hepatic Paragonimiasis Combined with Intrahepatic Bile Duct Stones
- A Case of Pulmonary Paragonimiasis with Involvement of the Abdominal Muscle in a 9-Year-Old Girl
- Ectopic Paragonimiasis Presented as Multiple Colonic and Liver Masses