Acute Crit Care.
2023 Aug;38(3):308-314. 10.4266/acc.2023.00115.
Outcomes of patients with COVID-19 requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy in the United States
- Affiliations
-
- 1Critical Care Medicine, WellStar Health System, Marietta, GA, USA
- 2Internal Medicine, WellStar Health System, Marietta, GA, USA
- KMID: 2547024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.00115
Abstract
- Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Some patients develop severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and kidney failure requiring the combination of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).
Methods
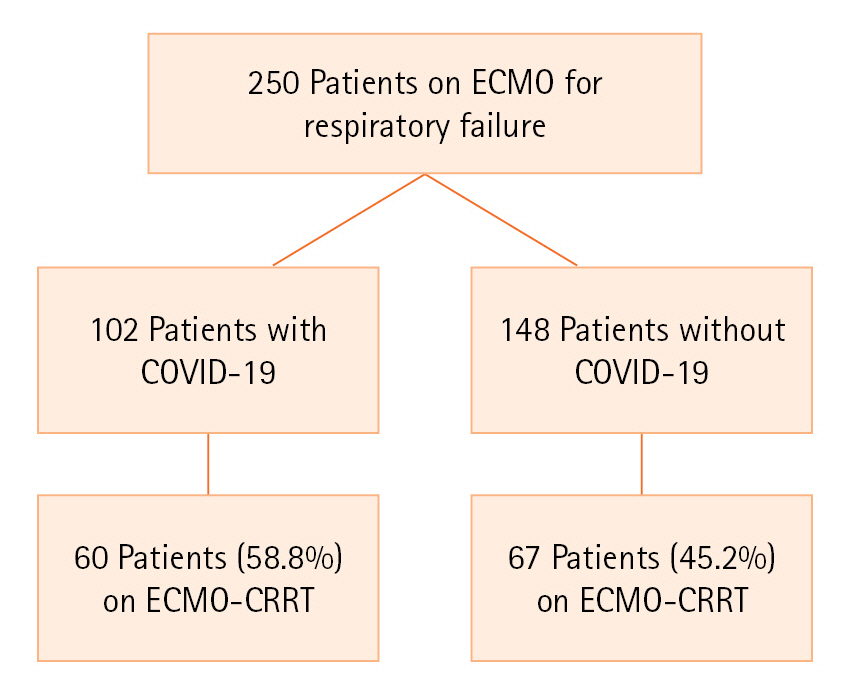
Retrospective cohort study of 127 consecutive patients requiring combined ECMO and CRRT support in intensive care units at an ECMO center in Marietta, GA, United States.
Results
Sixty and 67 patients with and without COVID-19, respectively, required ECMO-CRRT support. After adjusting for confounding variables, patients with COVID-19 had increased mortality at 30 days (hazard ratio [HR], 5.19; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.51–10.7; P<0.001) and 90 days (HR, 6.23; 95% CI, 2.60–14.9; P<0.001).
Conclusions
In this retrospective study, patients with COVID-19 who required ECMO-CRRT had increased mortality when compared to patients without COVID-19.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shih E, Squiers JJ, DiMaio JM, George T, Banwait J, Monday K, et al. Outcomes of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19 versus influenza. Ann Thorac Surg. 2022; 113:1445–51.
Article2. Cau A, Cheng MP, Lee T, Levin A, Lee TC, Vinh DC, et al. Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy in COVID-19 versus other respiratory viruses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2021; 8:20543581211052185.
Article3. Metnitz PG, Krenn CG, Steltzer H, Lang T, Ploder J, Lenz K, et al. Effect of acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy on outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2002; 30:2051–8.
Article4. ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012; 307:2526–33.5. El Mouhayyar C, Dewald J, Cabrales J, Tighiouart H, Moraco AH, Jaber BL, et al. Factors associated with severity of acute kidney injury and adverse outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Nephron. 2022; 146:584–92.
Article6. Silver SA, Beaubien-Souligny W, Shah PS, Harel S, Blum D, Kishibe T, et al. The prevalence of acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Med. 2021; 3:83–98.
Article7. Burke E, Haber E, Pike CW, Sonti R. Outcomes of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill with COVID-19. Med Intensiva. 2021; 45:325–31.
Article8. Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. Addendum: a pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020; 588:E6.
Article9. Naicker S, Yang CW, Hwang SJ, Liu BC, Chen JH, Jha V. The novel coronavirus 2019 epidemic and kidneys. Kidney Int. 2020; 97:824–8.
Article10. Sabaghian T, Kharazmi AB, Ansari A, Omidi F, Kazemi SN, Hajikhani B, et al. COVID-19 and acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022; 9:705908.
Article11. Thongprayoon C, Cheungpasitporn W, Lertjitbanjong P, Aeddula NR, Bathini T, Watthanasuntorn K, et al. Incidence and impact of acute kidney injury in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:981.
Article12. Lumlertgul N, Wright R, Hutson G, Milicevic JK, Vlachopanos G, Lee KC, et al. Long-term outcomes in patients who received veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and renal replacement therapy: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Intensive Care. 2022; 12:70.
Article13. Fleming GM, Askenazi DJ, Bridges BC, Cooper DS, Paden ML, Selewski DT, et al. A multicenter international survey of renal supportive therapy during ECMO: the Kidney Intervention During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (KIDMO) group. ASAIO J. 2012; 58:407–14.14. Kielstein JT, Heiden AM, Beutel G, Gottlieb J, Wiesner O, Hafer C, et al. Renal function and survival in 200 patients undergoing ECMO therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013; 28:86–90.
Article15. Al-Fares A, Pettenuzzo T, Del Sorbo L. Extracorporeal life support and systemic inflammation. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019; 7(Suppl 1):46.
Article16. Borasino S, Kalra Y, Elam AR, Carlisle O’Meara L, Timpa JG, Goldberg KG, et al. Impact of hemolysis on acute kidney injury and mortality in children supported with cardiac extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2018; 50:217–24.
Article17. Kilburn DJ, Shekar K, Fraser JF. The complex relationship of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and acute kidney injury: causation or association? Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:1094296.
Article18. Ling RR, Ramanathan K, Sim JJ, Wong SN, Chen Y, Amin F, et al. Evolving outcomes of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2022; 26:147.19. Diaz J, Hebert CA, Schwartz G, Lingle KJ, Szerlip HM. Use of synchronous kidney and lung extracorporeal support for severe COVID-19: a single-center retrospective study. Clin Nephrol. 2022; 98:182–7.
Article20. Bertini P, Guarracino F, Falcone M, Nardelli P, Landoni G, Nocci M, et al. ECMO in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022; 36(8 Pt A):2700–6.
Article21. Fanelli V, Giani M, Grasselli G, Mojoli F, Martucci G, Grazioli L, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19 and influenza H1N1 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2022; 26:34.
Article22. Brown JR, Kramer RS, Coca SG, Parikh CR. Duration of acute kidney injury impacts long-term survival after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010; 90:1142–8.
Article23. Distelmaier K, Wiedemann D, Binder C, Haberl T, Zimpfer D, Heinz G, et al. Duration of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support and survival in cardiovascular surgery patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018; 155:2471–6.
Article24. Singbartl K, Formeck CL, Kellum JA. Kidney-immune system crosstalk in AKI. Semin Nephrol. 2019; 39:96–106.
Article25. Woodrow G, Turney JH. Cause of death in acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1992; 7:230–4.
Article26. Odutayo A, Wong CX, Farkouh M, Altman DG, Hopewell S, Emdin CA, et al. AKI and long-term risk for cardiovascular events and mortality. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017; 28:377–87.
Article27. Thomas JM, Dado DN, Basel AP, Aden JK, Thomas SB, Piper L, et al. Adjunct use of continuous renal replacement therapy with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation achieves negative fluid balance and enhances oxygenation which improves survival in critically ill patients without kidney failure. Blood Purif. 2022; 51:477–84.
Article28. Hadadi A, Farrokhpour H, Rashedi S, Kafan S, Sotoudehnia M, Rahimzadeh H, et al. Long-term impact of the COVID-19 associated AKI: the relationship between kidney recovery and mortality in a 10-month follow-up cohort study. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2022; 47:486–91.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An adolescent female with intentional ingestion of a large amount of metformin requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy
- Simultaneous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, Renal Replacement Therapy, and Plasma Exchange for Thrombocytopenia-Associated Multiple Organ Failure
- Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Infants and Neonates
- Outcomes of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in COVID-19: A Single-Center Study
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Two Cases