Lab Med Online.
2021 Jan;11(1):64-68. 10.47429/lmo.2021.11.1.64.
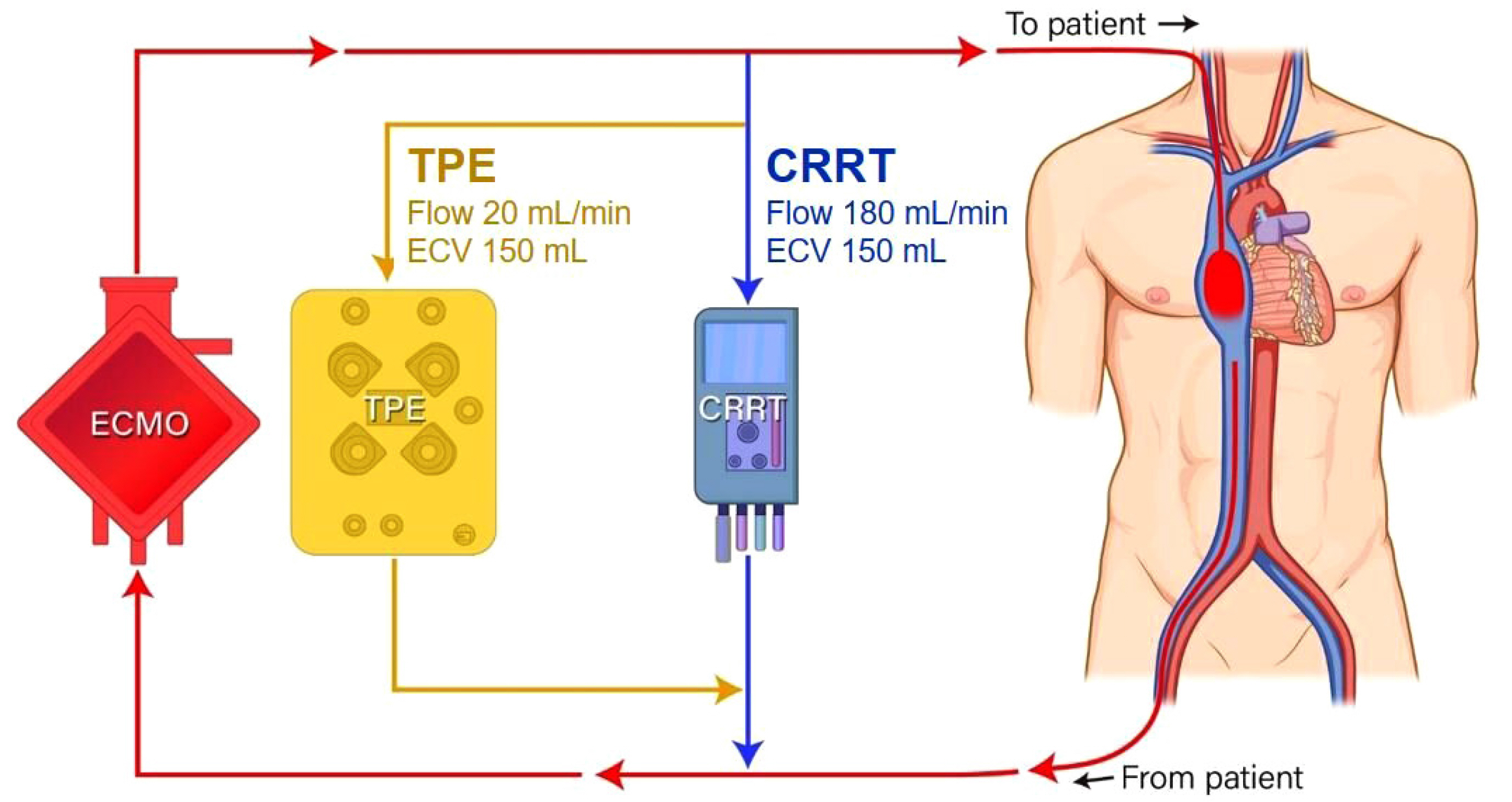
Simultaneous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, Renal Replacement Therapy, and Plasma Exchange for Thrombocytopenia-Associated Multiple Organ Failure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525783
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2021.11.1.64
Abstract
- Thrombocytopenia-associated multiple organ failure (TAMOF) is a distinct type of sepsis related to thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolysis, and multiple organ failure. TAMOF belongs to a spectrum of syndromes related to disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Treatment modalities for TAMOF include therapeutic plasma exchange along with other extracorporeal organ support. To the best of our knowledge, we report the first case of triple-modality treatment for TAMOF in Korea, which involved extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, continuous renal replacement therapy, and therapeutic plasma exchange in a patient with TAMOF.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, et al. 1995; Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults: a multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. JAMA. 274:968–74. DOI: 10.1001/jama.1995.03530120060042. PMID: 7674528.2. Venkata C, Kashyap R, Farmer JC, Afessa B. 2013; Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with sepsis: incidence, risk factors, and its association with clinical outcome. J Intensive Care. 1:9. DOI: 10.1186/2052-0492-1-9. PMID: 25810916. PMCID: PMC4373028.3. Bridges BC, Hardison D, Pietsch J. 2013; A case series of the successful use of ECMO, continuous renal replacement therapy, and plasma exchange for thrombocytopenia-associated multiple organ failure. J Pediatr Surg. 48:1114–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.02.061. PMID: 23701790.4. Nguyen TC, Carcillo JA. 2006; Bench-to-bedside review: thrombocytopenia-associated multiple organ failure - a newly appreciated syndrome in the critically ill. Crit Care. 10:235. DOI: 10.1186/cc5064. PMID: 17096864. PMCID: PMC1794442.5. Seczyńska B, Królikowski W, Nowak I, Jankowski M, Szułdrzyński K, Szczeklik W. 2014; Continuous renal replacement therapy during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients treated in medical intensive care unit: technical considerations. Ther Apher Dial. 18:523–34. DOI: 10.1111/1744-9987.12188. PMID: 25195931.6. Chen H, Yu RG, Yin NN, Zhou JX. 2014; Combination of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Crit Care. 18:675. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-014-0675-x. PMID: 25482187. PMCID: PMC4277651.7. Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, Blanchette VS, Kelton JG, Nair RC, et al. 1991; Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. New Engl J Med. 325:393–7. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199108083250604. PMID: 2062330.8. Brunskill SJ, Tusold A, Benjamin S, Stanworth SJ, Murphy MF. 2007; A systematic review of randomized controlled trials for plasma exchange in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Med. 17:17–35. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.2006.00720.x. PMID: 17266701.9. Padmanabhan A, Connelly-Smith L, Aqui N, Balogun RA, Klingel R, Meyer E, et al. 2019; Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice - evidence-based approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue. J Clin Apher. 34:171–354. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21705. PMID: 31180581.10. Darmon M, Azoulay E, Thiery G, Ciroldi M, Galicier L, Parquet N, et al. 2006; Time course of organ dysfunction in thrombotic microangiopathy patients receiving either plasma perfusion or plasma exchange. Crit Cate Med. 34:2127–33. DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000227659.14644.3E. PMID: 16763519.11. Chong M, Lopez-Magallon AJ, Saenz L, Sharma MS, Althouse AD, Morell VO, et al. 2017; Use of therapeutic plasma exchange during extracorporeal life support in critically ill cardiac children with thrombocytopenia-associated multi-organ failure. Front Pediatr. 5:254. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2017.00254. PMID: 29250516. PMCID: PMC5716972.12. Jhang J, Middlesworth W, Shaw R, Charette K, Papa J, Jefferson R, et al. 2007; Therapeutic plasma exchange performed in parallel with extra corporeal membrane oxygenation for antibody mediated rejection after heart transplantation. J Clin Apher. 22:333–8. DOI: 10.1002/jca.20151. PMID: 18080271.13. Dyer M, Neal MD, Rollins-Raval MA, Raval JS. 2014; Simultaneous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and therapeutic plasma exchange procedures are tolerable in both pediatric and adult patients. Transfusion. 54:1158–65. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12418. PMID: 24117674.14. Dechmann-Sültemeyer T, Linkeschova R, Lenzen K, Kuril Z, Grabensee B, Voiculescu A. 2009; Tandem plasmapheresis and haemodialysis as a safe procedure in 82 patients with immune-mediated disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 24:252–7. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfn434. PMID: 18682492.15. Pérez-Sáez MJ, Toledo K, Ojeda R, Crespo R, Soriano S, Álvarez de Lara MA, et al. 2011; Tandem plasmapheresis and hemodialysis: efficacy and safety. Ren Fail. 33:765–9. DOI: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.599912. PMID: 21770855.16. Paglialonga F, Ardissino G, Biasuzzi A, Testa S, Edefonti A. 2012; Tandem plasma-exchange and haemodialysis in a paediatric dialysis unit. Pediat Nephrol. 27:493–5. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-011-2066-8. PMID: 22134881.17. Farah M, Levin A, Kiaii M, Vickars L, Werb R. 2013; Combination hemodialysis and centrifugal therapeutic plasma exchange: 18 years of Canadian experience. Hemodials Int. 17:256–65. DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2012.00737.x. PMID: 22928813.18. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. 2016; The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315:801–10. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. PMID: 26903338. PMCID: PMC4968574.19. Sidebotham D, Allen SJ, McGeorge A, Ibbott N, Willcox T. 2012; Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adults: practical aspects of circuits, cannulae, and procedures. J Cardiothoac Vasc Anesth. 26:893–909. DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2012.02.001. PMID: 22503344.20. Filler G, Clark WF, Huang SH. 2014; Tandem hemodialysis and plasma exchange. Pediatr Nephrol. 29:2077–82. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-013-2620-7. PMID: 24022368.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment of Traumatic Lung Injury: 2 Cases
- An adolescent female with intentional ingestion of a large amount of metformin requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy
- Successful Retrieval of a Fractured Guidewire during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenator Insertion
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy for Treatment of Calcium Channel Blockers, Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers, and Metformin Overdose
- Catastrophic catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy rescued by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in recurrent malignant pheochromocytoma