Pediatr Emerg Med J.
2023 Oct;10(4):118-123. 10.22470/pemj.2023.00752.
Clinical aspects of patients visiting the emergency department with febrile seizure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2546285
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.22470/pemj.2023.00752
Abstract
- Purpose
We aimed to analyze the clinical characteristics, recurrence, neurological outcomes, and the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in children who visited 2 emergency departments (EDs) with febrile seizure (FS).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical records of 3,172 episodes, involving 2,510 children aged 6-60 months whose diagnoses were FSs at the EDs in 2 hospitals from 2013 through 2022. Through the review, we analyzed clinical characteristics and associated factors for the recurrence of FS. As a sub-analysis, the variables were compared between before (2017-2019) and during (2020-2022) the pandemic.
Results
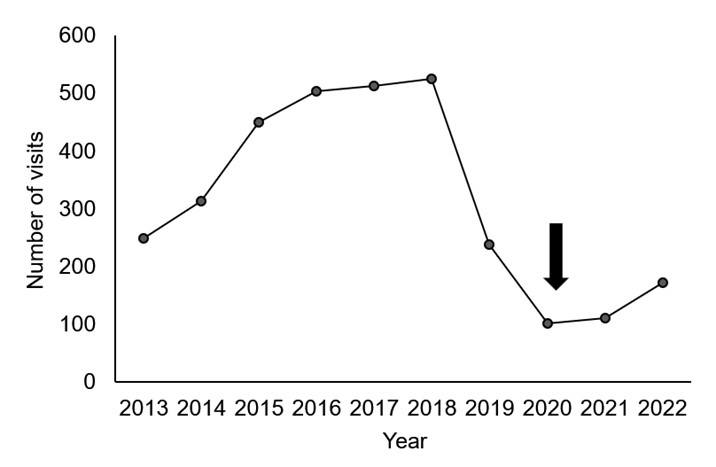
A total of 3,172 FS-related visits to the EDs were found in 2,510 children. Of these, 890 children (35.5%) underwent recurrences of FS. The recurrence of FS was associated with boys (63.3% vs. 57.8%; P = 0.007), seizures lasting longer than 5 minutes (16.6% vs. 12.7%; P = 0.007), family history of FS (23.7% vs. 16.2%; P < 0.001), complex FS (13.3% vs. 8.0%; P < 0.001), and epilepsy diagnosed thereafter (9.1% vs. 3.0%; P < 0.001). During the pandemic, we noted a decrease in the number of FS-related visits to the EDs (from 1,274 to 383), an increase in the percentage of complex FS (9.3% vs. 13.8%; P = 0.012), and a decrease in the percentage of recurrent FS (49.4% vs. 33.4%; P < 0.001), compared to before the pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study identified factors associated with recurrence of FS, and confirmed the increase in complex FS with the decrease in the recurrence during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. These findings could be helpful when caring for children with FS in EDs.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Campbell A, McIntosh C. Forfar and Arneil’s textbook of pediatrics. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone;1992. p. 754–5.2. Subcommittee on Febrile Seizures; American Academy of Pediatrics. Neurodiagnostic evaluation of the child with a simple febrile seizure. Pediatrics. 2011; 127:389–94.3. Shinnar S, Glauser TA. Febrile seizures. J Child Neurol. 2002. 17 Suppl 1:S44–52.4. Baumer JH; Paediatric Accident and Emergency Research Group. Evidence based guideline for post-seizure management in children presenting acutely to secondary care. Arch Dis Child. 2004; 89:278–80.5. Nelson KB, Ellenberg JH. Prognosis in children with febrile seizures. Pediatrics. 1978; 61:720–7.6. Berg AT, Shinnar S, Darefsky AS, Holford TR, Shapiro ED, Salomon ME, et al. Predictors of recurrent febrile seizures. A prospective cohort study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1997; 151:371–8.7. Berg AT, Shinnar S, Hauser WA, Leventhal JM. Predictors of recurrent febrile seizures: a meta-analytic review. J Pediatr. 1990; 116:329–37.8. Kim SH. Predictors of recurrent febrile seizure. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2014; 22:149–54. Korean.9. Berg AT, Shinnar S, Hauser WA, Alemany M, Shapiro ED, Salomon ME, et al. A prospective study of recurrent febrile seizures. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327:1122–7.10. Noh JH, Koh ID, Song KS, Cha BH. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of multiple recurrent febrile seizures among children. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2015; 23:7–12.11. Sadleir LG, Scheffer IE. Febrile seizures. BMJ. 2007; 334:307–11.12. Bae EJ, Kim IC, Park WI, Kim BS, Lee HJ, Lee KJ. Risk factors for recurrence of febrile seizure in children. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2001; 9:368–374. Korean.13. Aicardi J. Epilepsy in children. 2nd ed. Lippincott-Raven;1996. p. 253–75.14. Patel N, Ram D, Swiderska N, Mewasingh LD, Newton RW, Offringa M. Febrile seizures. BMJ. 2015; 351:h4240.15. Syndi Seinfeld D, Pellock JM. Recent research on febrile seizures: a review. J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2013; 4:19519.16. Lee IG. Recent advances in febrile convulsion. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000; 43:1021–8. Korean.17. Mikkonen K, Uhari M, Pokka T, Rantala H. Diurnal and seasonal occurrence of febrile seizures. Pediatr Neurol. 2015; 52:424–7.18. Pavlidou E, Tzitiridou M, Kontopoulos E, Panteliadis CP. Which factors determine febrile seizure recurrence? A prospective study. Brain Dev. 2008; 30:7–13.19. Nelson KB, Ellenberg JH. Predictors of epilepsy in children who have experienced febrile seizures. N Engl J Med. 1976; 295:1029–33.20. Verity CM, Golding J. Risk of epilepsy after febrile convulsions: a national cohort study. BMJ. 1991; 303:1373–6.21. Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Shirts SB, Kurland LT. Factors prognostic of unprovoked seizures after febrile convulsions. N Engl J Med. 1987; 316:493–8.22. Pavlidou E, Panteliadis C. Prognostic factors for subsequent epilepsy in children with febrile seizures. Epilepsia. 2013; 54:2101–7.23. Kim DH, Nguyen TM, Kim JH. Infectious respiratory diseases decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18:6008.24. Park KH, Choe YJ, Shim Y, Eun BL, Byeon JH. Decrease in incidence of febrile seizure following social distancing measures: a national cohort study in South Korea. Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2021; 28:144–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Selection of High Risk Group According to Risk Factors of Recurrent Febrile Seizures
- A Study on the Etiology and Clinical Aspects of Febrile Seizures according to Their Types
- Clinical characteristics of the respiratory virus in children with febrile convulsion
- Relationship between Admission and Clinical Features of Children who visited the Emergency Department with Seizures
- Risk factors for repeated febrile seizures during the same febrile illness