Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 Sep;27(5):493-511. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.493.
Inhibition of the interaction between Hippo/YAP and Akt signaling with ursolic acid and 3′3-diindolylmethane suppresses esophageal cancer tumorigenesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 54907, Korea
- 2Department of Oral Physiology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 02447, Korea
- 3School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
- 4Department of Anatomy, Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 54907, Korea
- 5Department of Systems Biology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77030, USA
- KMID: 2545539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.493
Abstract
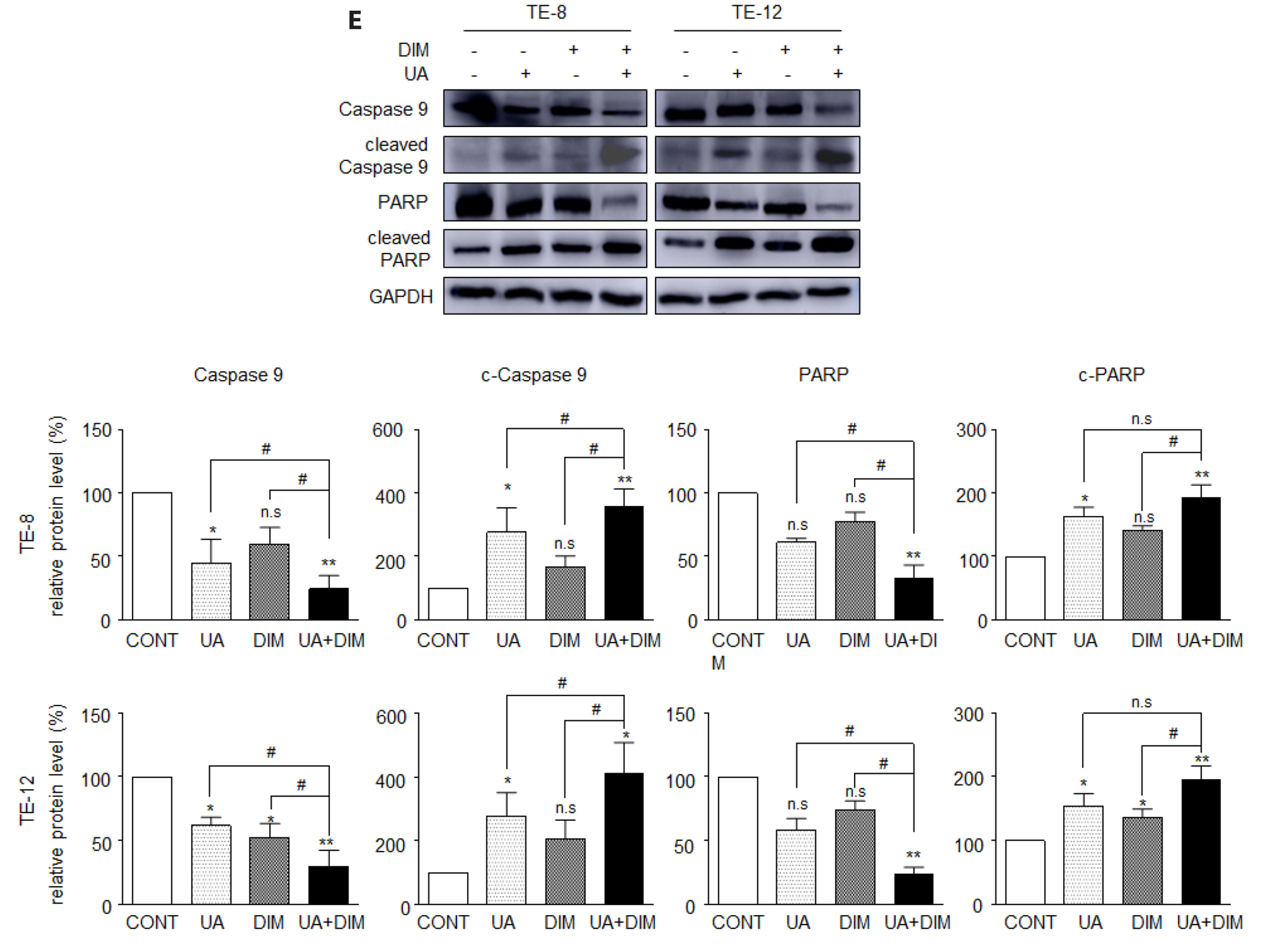
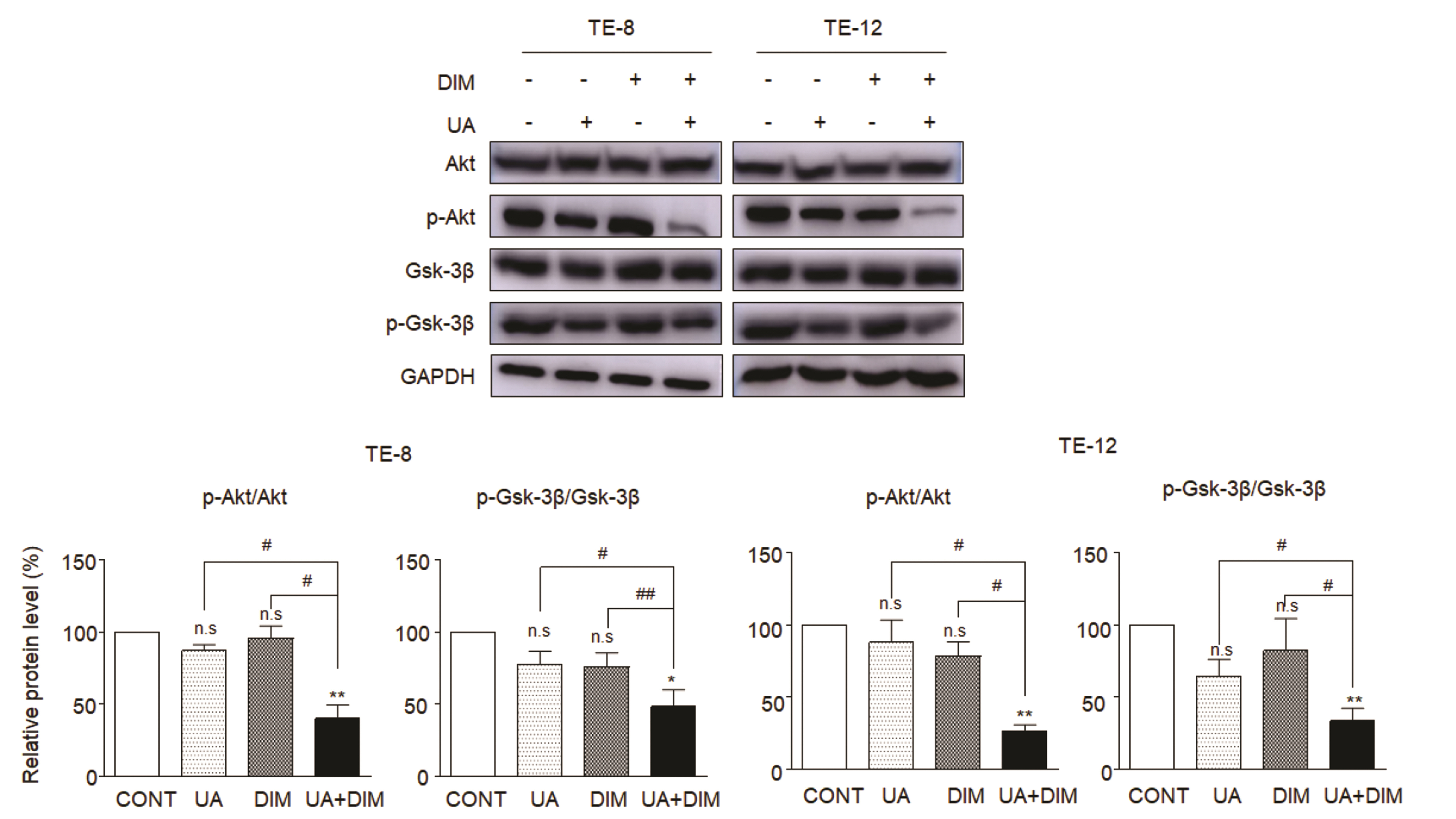
- Hippo/YAP signaling hinders cancer progression. Inactivation of this pathway contributes to the development of esophageal cancer by activation of Akt. However, the possible interaction between Akt and Hippo/YAP pathways in esophageal cancer progression is unclear. In this study, we found that ursolic acid (UA) plus 3′3-diindolylmethane (DIM) efficiently suppressed the oncogenic Akt/Gsk-3β signaling pathway while activating the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway in esophageal cancer cells. Moreover, the addition of the Akt inhibitor LY294002 and the PI3K inhibitor 3-methyladenine enhanced the inhibitory effects of UA plus DIM on Akt pathway activation and further stimulated the Hippo pathway, including the suppression of YAP nuclear translocation in esophageal cancer cells. Silencing YAP under UA plus DIM conditions significantly increased the activation of the tumor suppressor PTEN in esophageal cancer cells, while decreasing p-Akt activation, indicating that the Akt signaling pathway could be down-regulated in esophageal cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Furthermore, in a xenograft nude mice model, UA plus DIM treatment effectively diminished esophageal tumors by inactivating the Akt pathway and stimulating the Hippo signaling pathway. Thus, our study highlights a feedback loop between the PI3K/Akt and Hippo signaling pathways in esophageal cancer cells, implying that a low dose of UA plus DIM could serve as a promising chemotherapeutic combination strategy in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Uhlenhopp DJ, Then EO, Sunkara T, Gaduputi V. 2020; Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin J Gastroenterol. 13:1010–1021. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-020-01237-x. PMID: 32965635.
Article2. Then EO, Lopez M, Saleem S, Gayam V, Sunkara T, Culliford A, Gaduputi V. 2020; Esophageal cancer: an updated surveillance epidemiology and end results database analysis. World J Oncol. 11:55–64. DOI: 10.14740/wjon1254. PMID: 32284773. PMCID: PMC7141161.
Article3. Shin A, Won YJ, Jung HK, Kong HJ, Jung KW, Oh CM, Choe S, Lee J. 2018; Trends in incidence and survival of esophageal cancer in Korea: analysis of the Korea Central Cancer Registry Database. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 33:1961–1968. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14289. PMID: 29802647. PMCID: PMC6334276.
Article4. Sun D, Cao M, Li H, He S, Chen W. 2020; Cancer burden and trends in China: a review and comparison with Japan and South Korea. Chin J Cancer Res. 32:129–139. DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.02.01. PMID: 32410791. PMCID: PMC7219092.
Article5. Cummings D, Wong J, Palm R, Hoffe S, Almhanna K, Vignesh S. 2021; Epidemiology, diagnosis, staging and multimodal therapy of esophageal and gastric tumors. Cancers (Basel). 13:582. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13030582. PMID: 33540736. PMCID: PMC7867245. PMID: f2dd64f9294344139bdb6b4ab170b9c1.
Article6. Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrández Arenas Á, Lanas Arbeloa Á. 2015; Esophageal cancer: risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J Gastroenterol. 21:7933–7943. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.7933. PMID: 26185366. PMCID: PMC4499337.
Article7. Luan S, Zeng X, Zhang C, Qiu J, Yang Y, Mao C, Xiao X, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Yuan Y. 2021; Advances in drug resistance of esophageal cancer: from the perspective of tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:664816. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.664816. PMID: 33816512. PMCID: PMC8017339. PMID: 35de3603f9c64442b10a87332ef70935.
Article8. Lindner K, Eichelmann AK, Matuszcak C, Hussey DJ, Haier J, Hummel R. 2018; Complex epigenetic regulation of chemotherapy resistance and biohlogy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 19:499. Erratum in: Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:921. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20040921. PMID: 30791591. PMCID: PMC6412518. PMID: dacafc1a8d7341df99f259a2fdc05199.
Article9. Krasna MJ. 2010; Multimodality therapy for esophageal cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 24:1134–1138. PMID: 21141694.10. Islami F, Ren JS, Taylor PR, Kamangar F. 2009; Pickled vegetables and the risk of oesophageal cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 101:1641–1647. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605372. PMID: 19862003. PMCID: PMC2778505.
Article11. Higdon JV, Delage B, Williams DE, Dashwood RH. 2007; Cruciferous vegetables and human cancer risk: epidemiologic evidence and mechanistic basis. Pharmacol Res. 55:224–236. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.01.009. PMID: 17317210. PMCID: PMC2737735.
Article12. Khwaza V, Oyedeji OO, Aderibigbe BA. 2020; Ursolic acid-based derivatives as potential anti-cancer agents: an update. Int J Mol Sci. 21:5920. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21165920. PMID: 32824664. PMCID: PMC7460570. PMID: 60ea6e8af8944627b70f910451c0984a.
Article13. Alam M, Ali S, Ahmed S, Elasbali AM, Adnan M, Islam A, Hassan MI, Yadav DK. 2021; Therapeutic potential of ursolic acid in cancer and diabetic neuropathy diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 22:12162. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212162. PMID: 34830043. PMCID: PMC8621142. PMID: e17bd67e0fb74c92a8e8c2850d80e840.
Article14. Kassi E, Papoutsi Z, Pratsinis H, Aligiannis N, Manoussakis M, Moutsatsou P. 2007; Ursolic acid, a naturally occurring triterpenoid, demonstrates anticancer activity on human prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 133:493–500. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-007-0193-1. PMID: 17516089.
Article15. Navin R, Kim SM. 2016; Therapeutic interventions using ursolic acid for cancer treatment. Med Chem (Los Angeles). 6:339–344. DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444.1000367.
Article16. Figueroa-Suárez MZ, González Christen J, Cardoso-Taketa AT, Gutiérrez Villafuerte MDC, Rodríguez-López V. 2019; Anti-inflammatory and antihistaminic activity of triterpenoids isolated from Bursera cuneata (Schldl.) Engl. J Ethnopharmacol. 238:111786. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.013. PMID: 30872171.
Article17. Habtemariam S. 2019; Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of neuroprotection by ursolic acid: addressing brain injury, cerebral ischemia, cognition deficit, anxiety, and depression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:8512048. DOI: 10.1155/2019/8512048. PMID: 31223427. PMCID: PMC6541953.
Article18. do Nascimento PG, Lemos TL, Bizerra AM, Arriaga ÂM, Ferreira DA, Santiago GM, Braz-Filho R, Costa JG. 2014; Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ursolic acid and derivatives. Molecules. 19:1317–1327. DOI: 10.3390/molecules19011317. PMID: 24451251. PMCID: PMC6271190. PMID: 25fcb9a47785495fb68e2ddcc5134986.
Article19. Hassan HM, Jiang ZH, Asmussen C, McDonald E, Qin W. 2014; Antibacterial activity of northern Ontario medicinal plant extracts. Can J Plant Sci. 94:417–424. DOI: 10.4141/cjps2013-258.
Article20. Lee NR, Meng RY, Rah SY, Jin H, Ray N, Kim SH, Park BH, Kim SM. 2020; Reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy by ursolic acid inhibits growth and metastasis of esophageal cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:9409. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249409. PMID: 33321911. PMCID: PMC7764507. PMID: 32da4af9afe64e46a080552397a0fd6a.
Article21. Yang K, Chen Y, Zhou J, Ma L, Shan Y, Cheng X, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ji X, Chen L, Dai H, Zhu B, Li C, Tao Z, Hu X, Yin W. 2019; Ursolic acid promotes apoptosis and mediates transcriptional suppression of CT45A2 gene expression in non-small-cell lung carcinoma harbouring EGFR T790M mutations. Br J Pharmacol. 176:4609–4624. DOI: 10.1111/bph.14793. PMID: 31322286. PMCID: PMC6965687.
Article22. Huang CY, Lin CY, Tsai CW, Yin MC. 2011; Inhibition of cell proliferation, invasion and migration by ursolic acid in human lung cancer cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 25:1274–1280. DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2011.04.014. PMID: 21539908.
Article23. Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin CC. 2004; Proliferative inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of apoptosis by ursolic acid in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Life Sci. 75:2303–2316. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.04.027. PMID: 15350828.
Article24. Kim SH, Jin H, Meng RY, Kim DY, Liu YC, Chai OH, Park BH, Kim SM. 2019; Activating Hippo pathway via Rassf1 by ursolic acid suppresses the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:4709. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194709. PMID: 31547587. PMCID: PMC6801984. PMID: 098852b82a354918a8075acbca83ab19.
Article25. Kim ES, Moon A. 2015; Ursolic acid inhibits the invasive phenotype of SNU-484 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 9:897–902. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2735. PMID: 25621065.
Article26. Liu T, Ma H, Shi W, Duan J, Wang Y, Zhang C, Li C, Lin J, Li S, Lv J, Lin L. 2017; Inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway by ursolic acid suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 51:555–562. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4035. PMID: 28714512.
Article27. Zhou W, Lin L, Cheng Y, Liu Y. 2017; Ursolic acid improves liver transplantation and inhibits apoptosis in miniature pigs using donation after cardiac death. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:331–338. DOI: 10.1159/000480413. PMID: 28854432. PMID: 3807e3e23c2b462a9ee8951cbd5259df.
Article28. Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F, Nema T, Vali S, Abbasi T, Kapoor S, Sharma A, Kumar AP, Ho PC, Hui KM, Sethi G. 2011; Ursolic acid inhibits multiple cell survival pathways leading to suppression of growth of prostate cancer xenograft in nude mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:713–727. DOI: 10.1007/s00109-011-0746-2. PMID: 21465181.
Article29. Ye Y, Fang Y, Xu W, Wang Q, Zhou J, Lu R. 2016; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane induces anti-human gastric cancer cells by the miR-30e-ATG5 modulating autophagy. Biochem Pharmacol. 115:77–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.06.018. PMID: 27372603.
Article30. Li XJ, Park ES, Park MH, Kim SM. 2013; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane suppresses the growth of gastric cancer cells via activation of the Hippo signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 30:2419–2426. DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2717. PMID: 24008339.
Article31. Jin H, Park MH, Kim SM. 2015; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane potentiates paclitaxel-induced antitumor effects on gastric cancer cells through the Akt/FOXM1 signaling cascade. Oncol Rep. 33:2031–2036. DOI: 10.3892/or.2015.3758. PMID: 25633416.
Article32. Zhu P, Yu H, Zhou K, Bai Y, Qi R, Zhang S. 2020; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition through repressing RhoA/ROCK1-mediated COX2/PGE2 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:113. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01618-7. PMID: 32546278. PMCID: PMC7298755. PMID: 55aa1451e2f54bc69fa9687a08cc3b69.33. Kim SJ, Lee JS, Kim SM. 2012; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane suppresses growth of human esophageal squamous cancer cells by G1 cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep. 27:1669–1673. DOI: 10.3892/or.2012.1662. PMID: 22293900.
Article34. Li XJ, Leem SH, Park MH, Kim SM. 2013; Regulation of YAP through an Akt-dependent process by 3, 3'-diindolylmethane in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:1992–1998. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2121. PMID: 24100865.
Article35. Kong D, Banerjee S, Huang W, Li Y, Wang Z, Kim HR, Sarkar FH. 2008; Mammalian target of rapamycin repression by 3,3'-diindolylmethane inhibits invasion and angiogenesis in platelet-derived growth factor-D-overexpressing PC3 cells. Cancer Res. 68:1927–1934. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3241. PMID: 18339874. PMCID: PMC3757473.
Article36. Rahman KW, Sarkar FH. 2005; Inhibition of nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-{kappa}B contributes to 3,3'-diindolylmethane-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:364–371. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.364.65.1. PMID: 15665315.
Article37. Han Y. 2019; Analysis of the role of the Hippo pathway in cancer. J Transl Med. 17:116. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1869-4. PMID: 30961610. PMCID: PMC6454697. PMID: 8a32b04a45634498900b8618a3e93fb5.
Article38. He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS, Xu WW, Li B. 2021; Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:425. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5. PMID: 34916492. PMCID: PMC8677728. PMID: 37774d4ae5334c1a9a597cb056b37cdb.
Article39. Luo Q, Du R, Liu W, Huang G, Dong Z, Li X. 2022; PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, regulatory mechanisms and opportunities for targeted therapy. Front Oncol. 12:852383. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.852383. PMID: 35392233. PMCID: PMC8980269. PMID: 3457337e85a54ddeb424fb2bdb7d8419.
Article40. Javadinia SA, Shahidsales S, Fanipakdel A, Mostafapour A, Joudi-Mashhad M, Ferns GA, Avan A. 2018; The esophageal cancer and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling regulatory microRNAs: a novel marker for prognosis, and a possible target for immunotherapy. Curr Pharm Des. 24:4646–4651. DOI: 10.2174/1381612825666190110143258. PMID: 30636576.
Article41. Zhu C, Li L, Zhao B. 2015; The regulation and function of YAP transcription co-activator. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:16–28. DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gmu110. PMID: 25487920.
Article42. Misra JR, Irvine KD. 2018; The Hippo signaling network and its biological functions. Annu Rev Genet. 52:65–87. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031621. PMID: 30183404. PMCID: PMC6322405.
Article43. Yu FX, Zhao B, Guan KL. 2015; Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell. 163:811–828. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.044. PMID: 26544935. PMCID: PMC4638384.
Article44. Tumaneng K, Schlegelmilch K, Russell RC, Yimlamai D, Basnet H, Mahadevan N, Fitamant J, Bardeesy N, Camargo FD, Guan KL. 2012; YAP mediates crosstalk between the Hippo and PI(3)K-TOR pathways by suppressing PTEN via miR-29. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1322–1329. DOI: 10.1038/ncb2615. PMID: 23143395. PMCID: PMC4019071.
Article45. Qian X, He L, Hao M, Li Y, Li X, Liu Y, Jiang H, Xu L, Li C, Wu W, Du L, Yin X, Lu Q. 2021; YAP mediates the interaction between the Hippo and PI3K/Akt pathways in mesangial cell proliferation in diabetic nephropathy. Acta Diabetol. 58:47–62. DOI: 10.1007/s00592-020-01582-w. PMID: 32816106.
Article46. Ye X, Deng Y, Lai ZC. 2012; Akt is negatively regulated by Hippo signaling for growth inhibition in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 369:115–123. DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.014. PMID: 22732571.
Article47. Borreguero-Muñoz N, Fletcher GC, Aguilar-Aragon M, Elbediwy A, Vincent-Mistiaen ZI, Thompson BJ. 2019; The Hippo pathway integrates PI3K-Akt signals with mechanical and polarity cues to control tissue growth. PLoS Biol. 17:e3000509. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000509. PMID: 31613895. PMCID: PMC6814241. PMID: 49700236fbce48088ee3945b33c7f241.
Article48. Hu LL, Su T, Luo RC, Zheng YH, Huang J, Zhong ZS, Nie J, Zheng LP. 2019; Hippo pathway functions as a downstream effector of AKT signaling to regulate the activation of primordial follicles in mice. J Cell Physiol. 234:1578–1587. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27024. PMID: 30078193.
Article49. Lin Z, Zhou P, von Gise A, Gu F, Ma Q, Chen J, Guo H, van Gorp PR, Wang DZ, Pu WT. 2015; Pi3kcb links Hippo-YAP and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival. Circ Res. 116:35–45. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.304457. PMID: 25249570. PMCID: PMC4282610.
Article50. Xu W, Yang Z, Xie C, Zhu Y, Shu X, Zhang Z, Li N, Chai N, Zhang S, Wu K, Nie Y, Lu N. 2018; PTEN lipid phosphatase inactivation links the hippo and PI3K/Akt pathways to induce gastric tumorigenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:198. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0795-2. PMID: 30134988. PMCID: PMC6104022. PMID: fa829ec5bd6b4945a08ad9b0211c1d69.
Article51. Worby CA, Dixon JE. 2014; PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. 83:641–669. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-082411-113907. PMID: 24905788.
Article52. Zou R, Xu Y, Feng Y, Shen M, Yuan F, Yuan Y. 2020; YAP nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation is regulated by mechanical signaling, protein modification, and metabolism. Cell Biol Int. 44:1416–1425. DOI: 10.1002/cbin.11345. PMID: 32190949.
Article53. Kitagawa Y, Uno T, Oyama T, Kato K, Kato H, Kawakubo H, Kawamura O, Kusano M, Kuwano H, Takeuchi H, Toh Y, Doki Y, Naomoto Y, Nemoto K, Booka E, Matsubara H, Miyazaki T, Muto M, Yanagisawa A, Yoshida M. 2019; Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: part 1. Esophagus. 16:1–24. Erratum in: Esophagus. 2022;19:726. DOI: 10.1007/s10388-018-0641-9. PMID: 30171413. PMCID: PMC6510883.
Article54. Meng RY, Jin H, Nguyen TV, Chai OH, Park BH, Kim SM. 2021; Ursolic acid accelerates paclitaxel-induced cell death in esophageal cancer cells by suppressing Akt/FOXM1 signaling cascade. Int J Mol Sci. 22:11486. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111486. PMID: 34768915. PMCID: PMC8584129. PMID: d28bd70cecc64f66bf6cb2ef10fc4235.
Article55. Biersack B. 2020; 3,3'-Diindolylmethane and its derivatives: nature-inspired strategies tackling drug resistant tumors by regulation of signal transduction, transcription factors and microRNAs. Cancer Drug Resist. 3:867–878. DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2020.53. PMID: 35582221. PMCID: PMC8992569.
Article56. Lin W, Ye H. 2020; Anticancer activity of ursolic acid on human ovarian cancer cells via ROS and MMP mediated apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and downregulation of PI3K/AKT pathway. J BUON. 25:750–756. PMID: 32521863.57. Meng Y, Lin ZM, Ge N, Zhang DL, Huang J, Kong F. 2015; Ursolic acid induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Am J Chin Med. 43:1471–1486. DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X15500834. PMID: 26503559.
Article58. Wong RS. 2011; Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:87. DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-87. PMID: 21943236. PMCID: PMC3197541. PMID: 14037097dac24b9dae7629da9c125275.
Article59. Tahtamouni L, Ahram M, Koblinski J, Rolfo C. 2019; Molecular regulation of cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019:1356508. DOI: 10.1155/2019/1356508. PMID: 31218208. PMCID: PMC6536998. PMID: a0407114b4874fdb92140eab9fe3e998.
Article60. Shin JY, Kim JO, Lee SK, Chae HS, Kang JH. 2010; LY294002 may overcome 5-FU resistance via down-regulation of activated p-AKT in Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:425. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-425. PMID: 20704765. PMCID: PMC3087326. PMID: e37d2abf32d94d3ca2610f5c88c54213.
Article61. Datta S, Cano M, Satyanarayana G, Liu T, Wang L, Wang J, Cheng J, Itoh K, Sharma A, Bhutto I, Kannan R, Qian J, Sinha D, Handa JT. 2023; Mitophagy initiates retrograde mitochondrial-nuclear signaling to guide retinal pigment cell heterogeneity. Autophagy. 19:966–983. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2109286. PMID: 35921555. PMCID: PMC9980637.
Article62. Domoto T, Pyko IV, Furuta T, Miyashita K, Uehara M, Shimasaki T, Nakada M, Minamoto T. 2016; Glycogen synthase kinase-3β is a pivotal mediator of cancer invasion and resistance to therapy. Cancer Sci. 107:1363–1372. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13028. PMID: 27486911. PMCID: PMC5084660.
Article63. Duda P, Akula SM, Abrams SL, Steelman LS, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Ratti S, Candido S, Libra M, Montalto G, Cervello M, Gizak A, Rakus D, McCubrey JA. 2020; Targeting GSK3 and associated signaling pathways involved in cancer. Cells. 9:1110. DOI: 10.3390/cells9051110. PMID: 32365809. PMCID: PMC7290852. PMID: 4013e82b8ba443de968a8ae058a04c3d.
Article64. Fu Y, Sun S, Sun H, Peng J, Ma X, Bao L, Ji R, Luo C, Gao C, Zhang X, Jin Y. 2019; Scutellarin exerts protective effects against atherosclerosis in rats by regulating the Hippo-FOXO3A and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 234:18131–18145. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28446. PMID: 30891776.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepatic Hippo signaling inhibits development of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Resveratrol suppresses breast cancer cell invasion by inactivating a RhoA/YAP signaling axis
- Hippo Signal Transduction Mechanisms in T Cell Immunity
- Alisol A Inhibited the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting the Hippo Signaling Pathway
- Downregulation of LINC01508 contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via the regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway