J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2023 Sep;66(5):503-510. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0249.
Is Tranexamic Acid an Effective Prevention in the Formation of Epidural Fibrosis? Histological Evaluation in the Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Istanbul Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
- 2Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Istanbul Haydarpasa Numune Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
- 3Department of Pathology, Istanbul Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
- KMID: 2545341
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0249
Abstract
Objective
: The present study aimed to determine the topical and systemic efficacy of tranexamic acid (TXA) on epidural fibrosis in a rat laminectomy model.
Methods
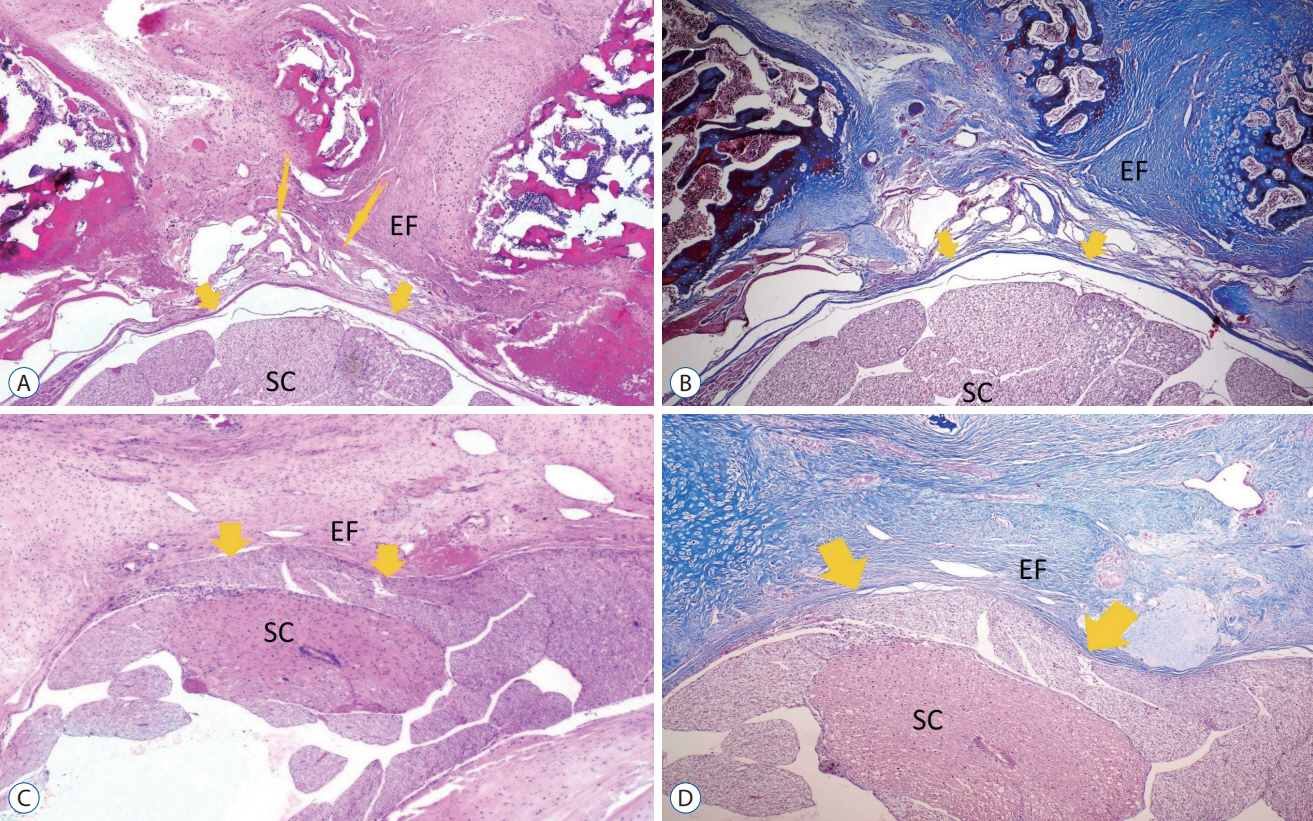
: Thirty-two 12-month-old adult Sprague-Dawley rats were used in this study. Each rat underwent bilateral laminectomy at the L1 and L2 vertebral levels. Rats were divided into four groups : in group I (control group, n=8), a laminectomy was performed and saline solution was applied into the surgical space. In group II (topical group, n=8), laminectomy was performed and 30 mg/ kg TXA was applied to the surgical site before skin closure. In group III (systemic group, n=8), 30 mg/kg TXA was administered intravenously via the tail vein in the same session as the surgical procedure. In group IV (topical and systemic group, n=8), TXA was administered 30 mg/kg both topical and intravenous. The rats were sacrificed at 4 weeks postoperatively. Masson’s trichrome and hematoxylin and eosin were used to assess acute inflammatory cells, chronic inflammatory cells, vascular proliferation, and epidural fibrosis.
Results
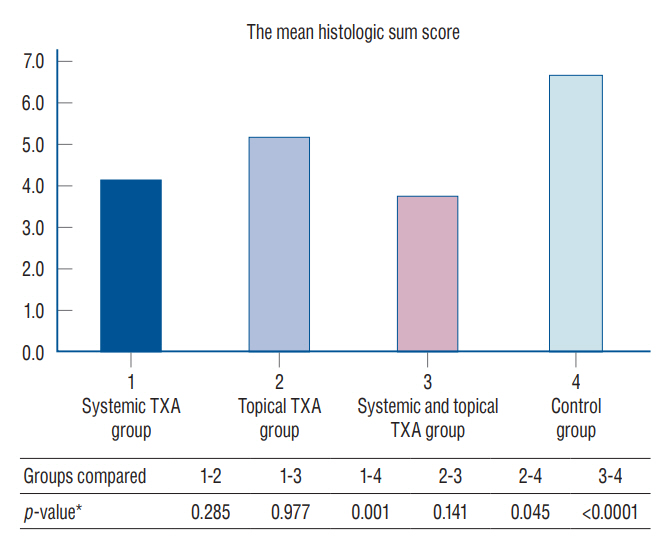
: Epidural fibrosis, acute inflammation, chronic inflammation, and sum histologic score value were significantly lower in the systemic TXA group, systemic and topical TXA groups than in the control group (p<0.05). In addion, the sum histologic score was significantly lower in the topical TXA group than in the control group (p<0.05).
Conclusion
: In this study, epidural fibrosis formation was prevented more by systemic application, but the topical application was found to be effective when compared to the control group. As a result, we recommend the systemic and topical use of TXA to prevent epidural fibrosis during spinal surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Burton CV, Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Yong-Hing K, Heithoff KB. Causes of failure of surgery on the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (157):191–199. 1981.2. Butala BP, Shah VR, Bhosale GP, Shah RB. Medication error: subarachnoid injection of tranexamic acid. Indian J Anaesth. 56:168–170. 2012.3. Çirci E, Özalay M, Caylak B, Bacanli D, Derincek A, Tuncay IC. The effect of oophorectomy on epidural fibrosis after laminectomy: an experimental study in rats. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 47:193–200. 2013.4. Coskun E, Süzer T, Topuz O, Zencir M, Pakdemirli E, Tahta K. Relationships between epidural fibrosis, pain, disability, and psychological factors after lumbar disc surgery. Eur Spine J. 9:218–223. 2000.5. Cravens GT, Brown MJ, Brown DR, Wass CT. Antifibrinolytic therapy use to mitigate blood loss during staged complex major spine surgery: postoperative visual color changes after tranexamic acid administration. Anesthesiology. 105:1274–1276. 2006.6. Erdogan U, Tanik C, Tanriverdi O, Gunaldi O, Yilmaz I, Arslanhan A, et al. Immunohistochemical grading of epidural fibrosis with CD105 antibody. World Neurosurg. 125:e297–e303. 2019.7. Fritsch EW, Heisel J, Rupp S. The failed back surgery syndrome: reasons, intraoperative findings, and long-term results: a report of 182 operative treatments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:626–633. 1996.8. Gybel M, Kristensen K, Roseva-Nielsen N. Cardiac arrest caused by massive pulmonary embolism during treatment with tranexamic acid. Ugeskr Laeger. 175:1426–1427. 2013.9. He Y, Revel M, Loty B. A quantitative model of post-laminectomy scar formation. Effects of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:557–563. discussion 579-580. 1995.10. Henry DA, Carless PA, Moxey AJ, O’Connell D, Stokes BJ, McClelland B, et al. Anti-fibrinolytic use for minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (1):CD001886. 2011.11. Hui S, Peng Y, Tao L, Wang S, Yang Y, Du Y, et al. Tranexamic acid given into wound reduces postoperative drainage, blood loss, and hospital stay in spinal surgeries: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 16:401. 2021.12. Kasimcan MO, Bakar B, Aktaş S, Alhan A, Yilmaz M. Effectiveness of the biophysical barriers on the peridural fibrosis of a postlaminectomy rat model: an experimental research. Injury. 42:778–781. 2011.13. Koo JR, Lee YK, Kim YS, Cho WY, Kim HK, Won NH. Acute renal cortical necrosis caused by an antifibrinolytic drug (tranexamic acid). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 14:750–752. 1999.14. Lecker I, Wang DS, Whissell PD, Avramescu S, Mazer CD, Orser BA. Tranexamic acid-associated seizures: causes and treatment. Ann Neurol. 79:18–26. 2016.15. Li J, Wang L, Bai T, Liu Y, Huang Y. Combined use of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid efficiently reduces blood loss in patients aged over 60 operated with a 2-level lumbar fusion. J Orthop Surg Res. 15:339. 2020.16. Li Y, Zhang Y, Fang X. Acute normovolemic hemodilution in combination with tranexamic acid is an effective strategy for blood management in lumbar spinal fusion surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 17:71. 2022.17. Luo W, Sun RX, Jiang H, Ma XL. The efficacy and safety of topical administration of tranexamic acid in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 13:96. 2018.18. Mitchell RN, Cotran RS. Tissue repair: Cell regeneration and fibrosis. In : Kumar V, Cotran RS, Robbin S, editors. Basic pathology. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;2003. p. 61–78.19. Mohseni K, Jafari A, Nobahar MR, Arami A. Polymyoclonus seizure resulting from accidental injection of tranexamic acid in spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 108:1984–1986. 2009.20. Mohsenipour I, Daniaux M, Aichner F, Twerdy K. Prevention of local scar formation after operative discectomy for lumbar disc herniation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 140:9–13. 1998.21. Murkin JM, Falter F, Granton J, Young B, Burt C, Chu M. High-dose tranexamic acid is associated with nonischemic clinical seizures in cardiac surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 110:350–353. 2010.22. Robertson JT. Role of peridural fibrosis in the failed back: a review. Eur Spine J 5 Suppl. 1:S2–S6. 1996.23. Ross JS, Robertson JT, Frederickson RC, Petrie JL, Obuchowski N, Modic MT, et al. Association between peridural scar and recurrent radicular pain after lumbar discectomy: magnetic resonance evaluation. ADCON-L European Study Group. Neurosurgery. 38:855–861. discussion 861-853. 1996.24. Roy M, Burggraf M, Lendemans S, de Groot H, Rohrig R. Tranexamic acid prolongs survival after controlled hemorrhage in rats. J Surg Res. 208:104–110. 2017.25. Sae-Jung S, Jirarattanaphochai K, Sumananont C, Wittayapairoj K, Sukhonthamarn K. Interrater reliability of the postoperative epidural fibrosis classification: a histopathologic study in the rat model. Asian Spine J. 9:587–594. 2015.26. Sahin E, Berk H, Ozkal S, Keskinoglu P, Balci P, Balci A. Effect of local tranexamic acid on the quality of bone healing in a rat spinal fusion model. Spine Surg Relat Res. 6:151–158. 2022.27. Salam A, King C, Orhan O, Mak V. The great deception: tranexamic acid and extensive pulmonary emboli. BMJ Case Rep. 2013:bcr2012007808. 2013.28. Schlag MG, Hopf R, Redl H. Convulsive seizures following subdural application of fibrin sealant containing tranexamic acid in a rat model. Neurosurgery. 47:1463–1467. 2000.29. Schwarzkopf R, Dang P, Luu M, Mozaffar T, Gupta R. Topical tranexamic acid does not affect electrophysiologic or neurovascular sciatic nerve markers in an animal model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 473:1074–1082. 2015.30. Sen O, Kizilkilic O, Aydin MV, Yalcin O, Erdogan B, Cekinmez M, et al. The role of closed-suction drainage in preventing epidural fibrosis and its correlation with a new grading system of epidural fibrosis on the basis of MRI. Eur Spine J. 14:409–414. 2005.31. Shrestha IK, Ruan TY, Lin L, Tan M, Na XQ, Qu QC, et al. The efficacy and safety of high-dose tranexamic acid in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 16:53. 2021.32. Winter SF, Santaguida C, Wong J, Fehlings MG. Systemic and topical use of tranexamic acid in spinal surgery: a systematic review. Global Spine J. 6:284–295. 2016.33. Xu D, Zhuang Q, Li Z, Ren Z, Chen X, Li S. A randomized controlled trial on the effects of collagen sponge and topical tranexamic acid in posterior spinal fusion surgeries. J Orthop Surg Res. 12:166. 2017.34. Zhang C, Kong X, Liu C, Liang Z, Zhao H, Tong W, et al. ERK2 small interfering RNAs prevent epidural fibrosis via the efficient inhibition of collagen expression and inflammation in laminectomy rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:395–400. 2014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is irrational use of tranexamic acid justified in anesthesia practice?
- Treatment Effect of Tranexamic Acid in Plasma D-dimer Level Elevated Anti-histamine Resistant Chronic Urticaria Patients
- Melasma Showing Response to Combination Therapy with Oral Tranexamic Acid and the Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
- Efficacy of Tranexamic Acid during Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparative Study between Intravenous Use and Topical Use
- Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding in a patient with factor VII deficiency: a case controlled with tranexamic acid