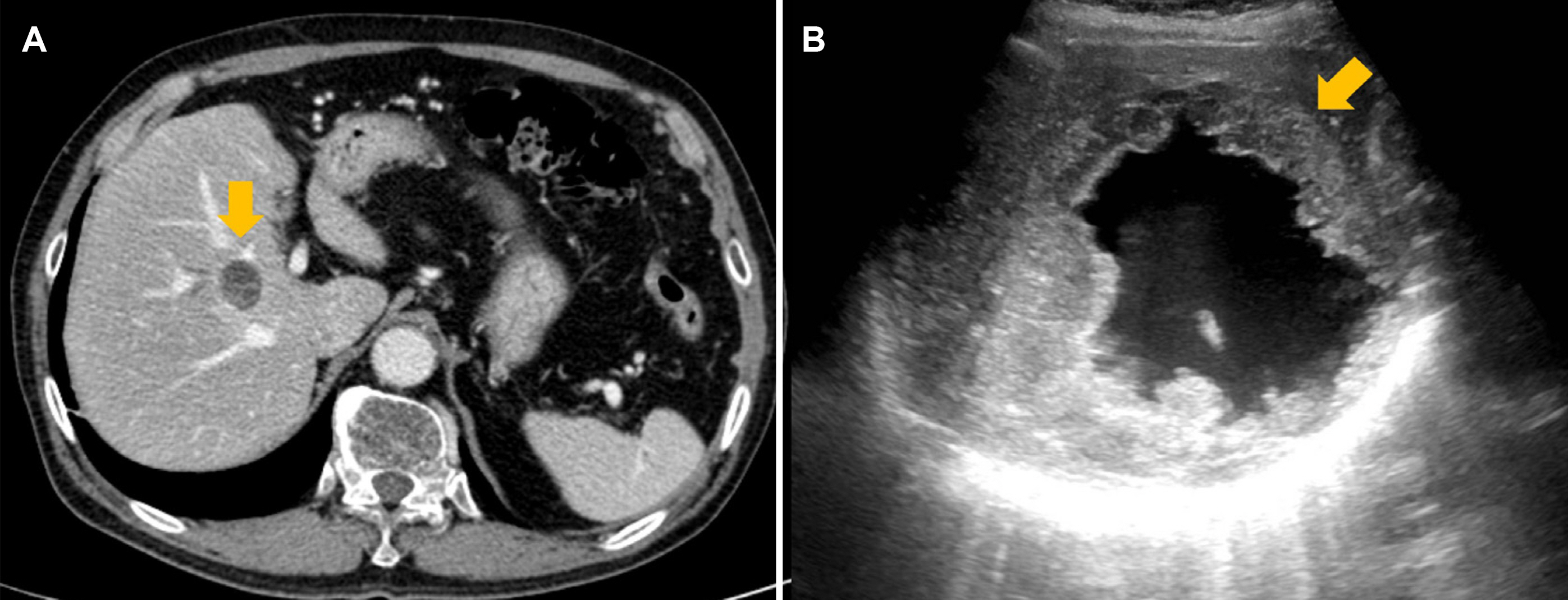
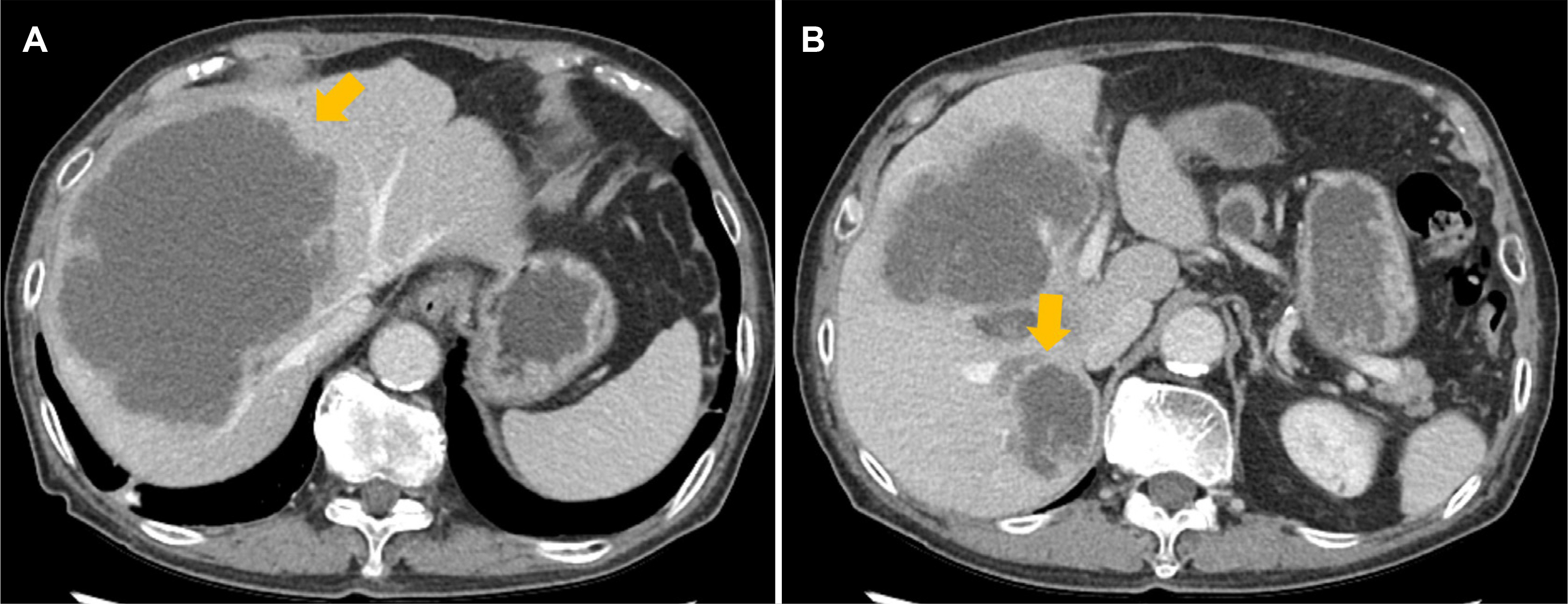
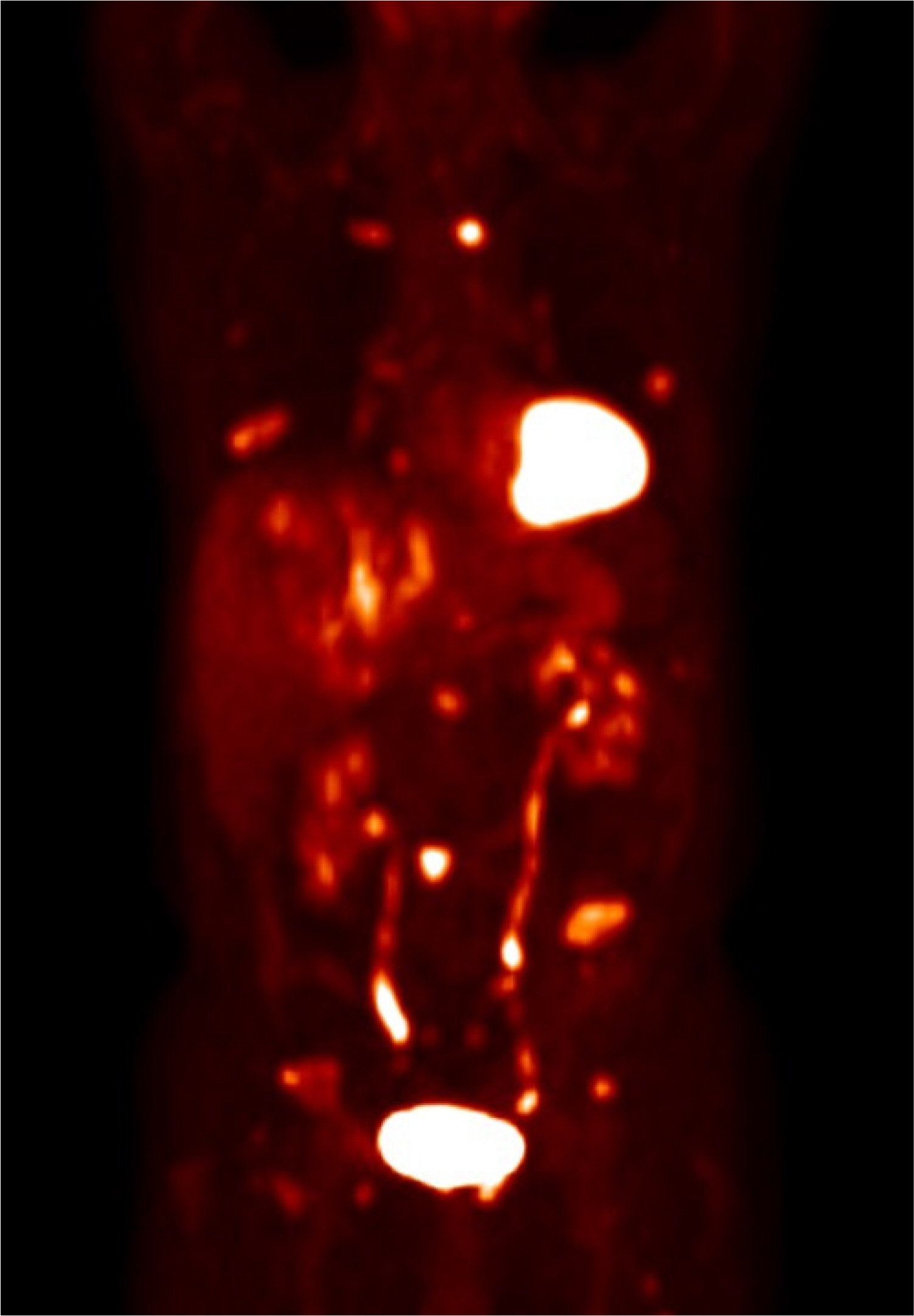
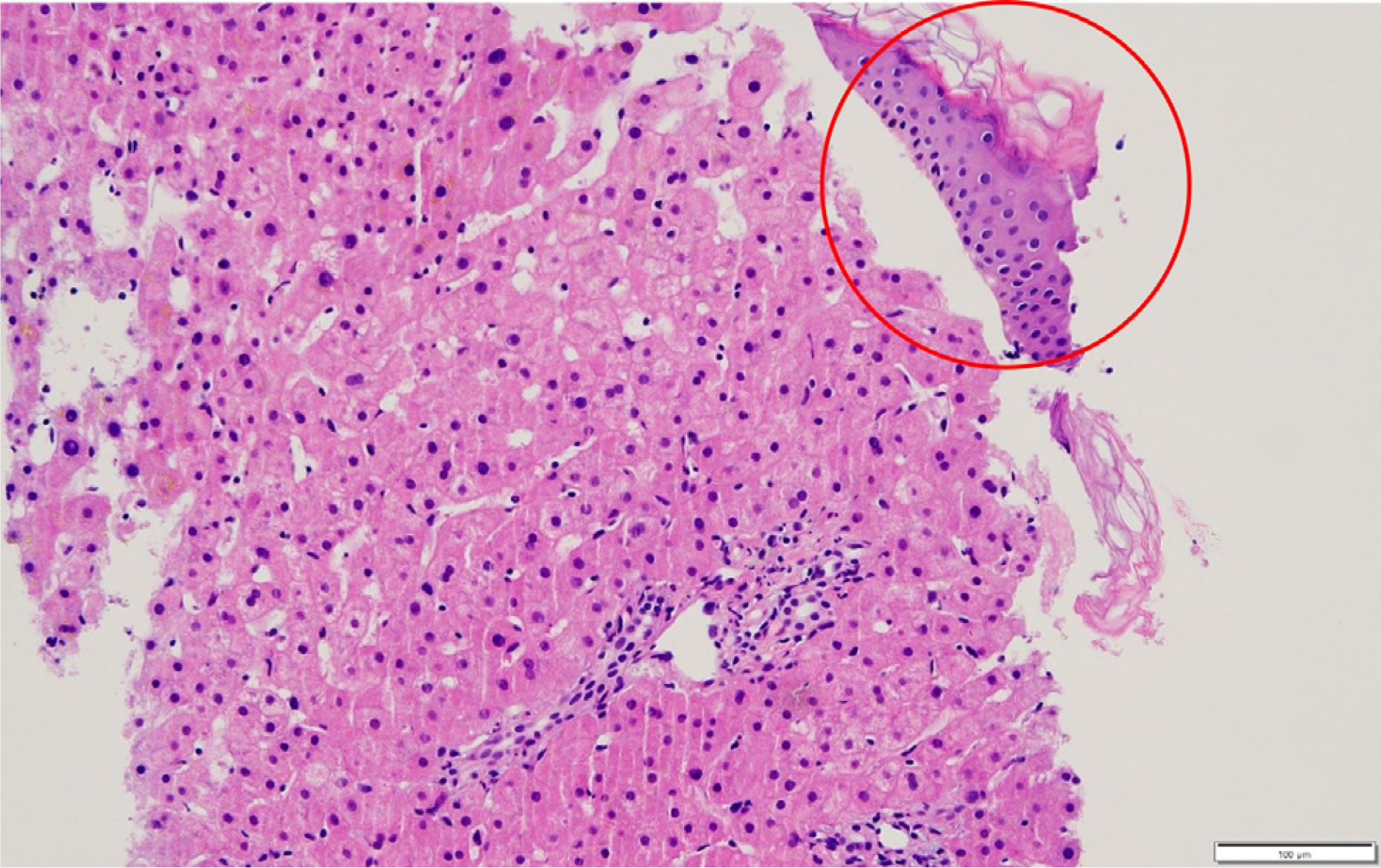
Korean J Gastroenterol.
2023 Jul;82(1):40-42. 10.4166/kjg.2023.077.
Malignant Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2544939
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.077
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sakai Y, Ohtsuka M, Sugiyama H, et al. 2021; Current status of diagnosis and therapy for intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. World J Gastroenterol. 27:1569–1577. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i15.1569. PMID: 33958844. PMCID: PMC8058653.2. Nakanuma YBO, Esposito I, Klimstra DS, Komuta M, Zen Y. 2019. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. WHO Classification of Tumours. Medical history and perspective. 5th ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer;Lyon:3. Nakanuma Y, Uesaka K, Miyayama S, Yamaguchi H, Ohtsuka M. 2017; Intraductal neoplasms of the bile duct. A new challenge to biliary tract tumor pathology. Histol Histopathol. 32:1001–1015.4. Lee S, Kim MJ, Kim S, Choi D, Jang KT, Park YN. 2019; Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: Assessment of invasive carcinoma and long-term outcomes using MRI. J Hepatol. 70:692–699. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.005. PMID: 30553839.5. Liu Y, Zhong X, Yan L, Zheng J, Liu Z, Liang C. 2015; Diagnostic performance of CT and MRI in distinguishing intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct from cholangiocarcinoma with intraductal papillary growth. Eur Radiol. 25:1967–1974. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-015-3618-2. PMID: 25716939.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intrahepatic and extrahepatic intraductal papillary neoplasms of bile duct
- Extrahepatic Bile Duct Duplication with Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm: A Case Report
- A huge intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct treated by right trisectionectomy after right portal vein embolization
- Photodynamic Therapy Followed by Left Hepatectomy Used to Treat an Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Bile Duct
- Unexpected Metastasis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Bile Duct into Thoracic Cavity with Direct Extension: Case Report