J Pathol Transl Med.
2023 Jul;57(4):189-195. 10.4132/jptm.2023.05.24.
A review of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis regression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA
- KMID: 2544326
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.05.24
Abstract
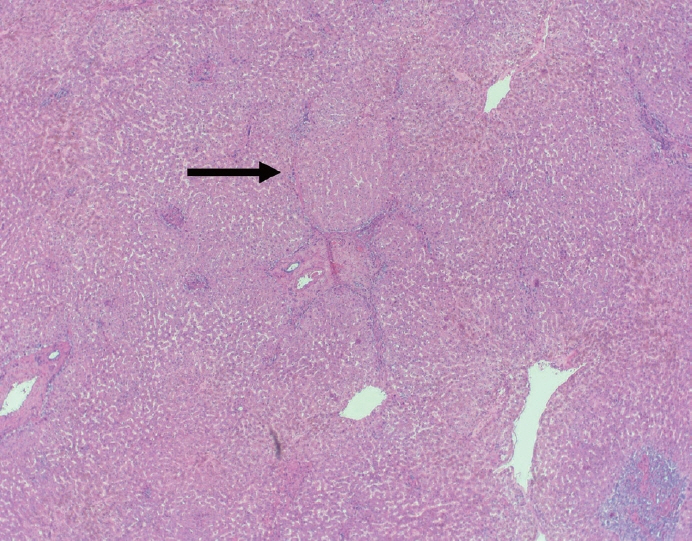
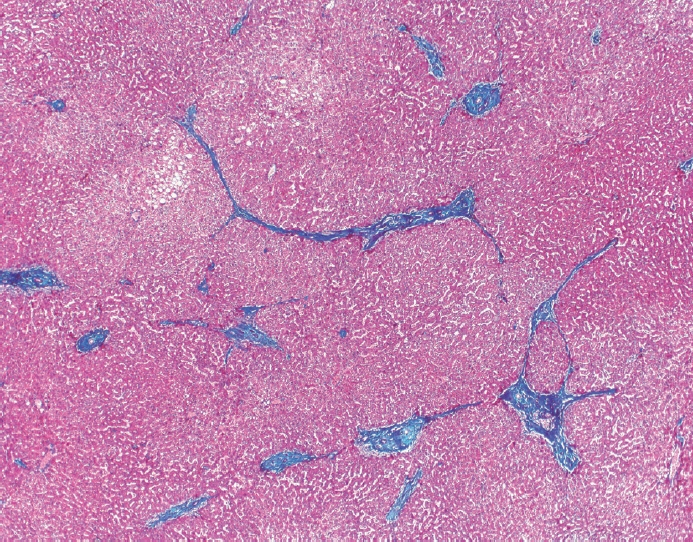
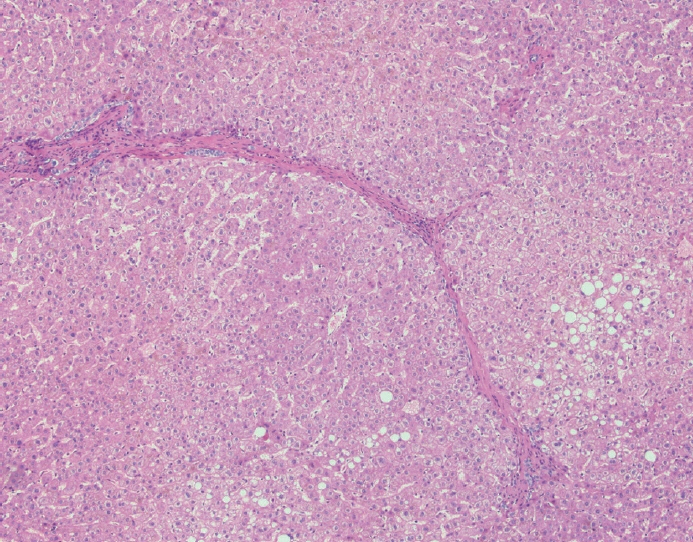
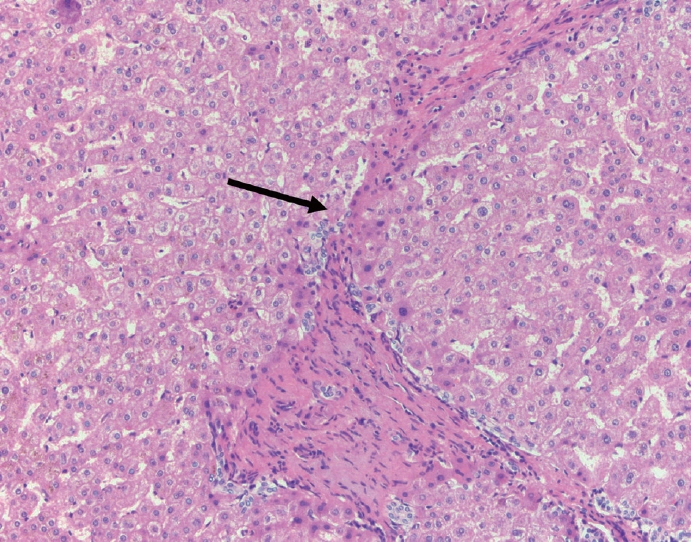
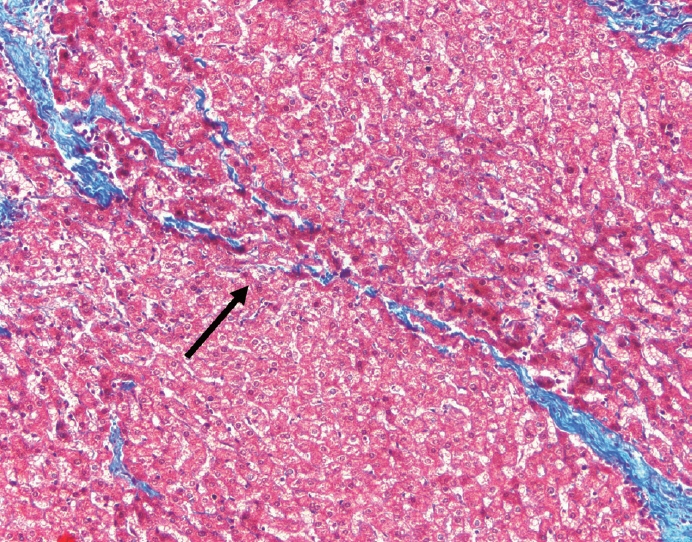
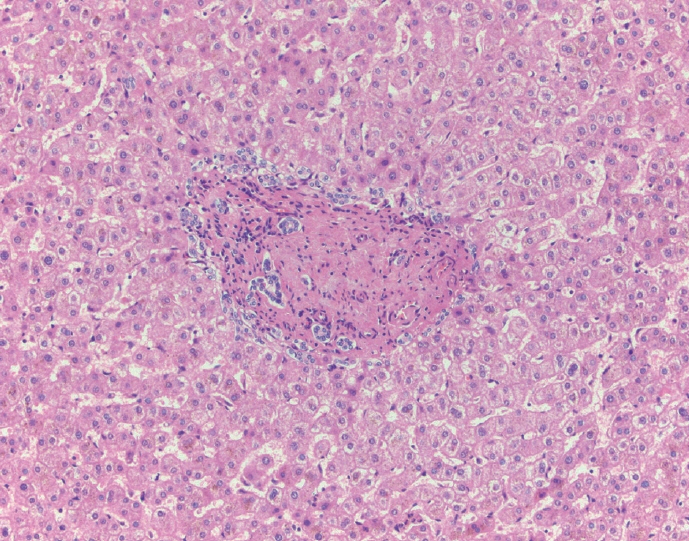
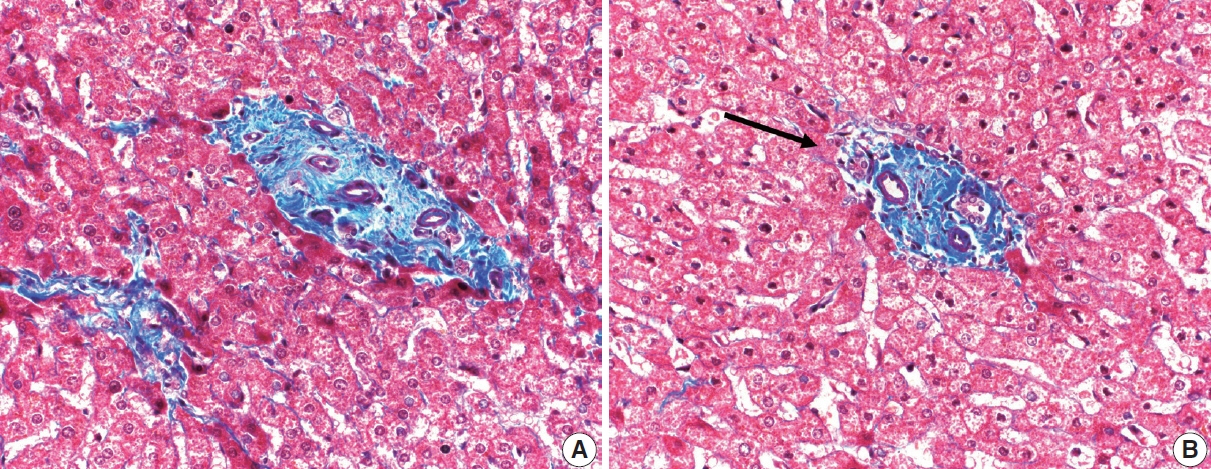
- Cirrhosis has traditionally been considered an irreversible process of end-stage liver disease. With new treatments for chronic liver disease, there is regression of fibrosis and cirrhosis, improvement in clinical parameters (i.e. liver function and hemodynamic markers, hepatic venous pressure gradient), and survival rates, demonstrating that fibrosis and fibrolysis are a dynamic process moving in two directions. Microscopically, hepatocytes push into thinning fibrous septa with eventual perforation leaving behind delicate periportal spikes in the portal tracts and loss of portal veins. Obliterated portal veins during progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis due to parenchymal extinction, vascular remodeling and thrombosis often leave behind a bile duct and hepatic artery within the portal tract. Traditional staging classification systems focused on a linear, progressive process; however, the Beijing classification system incorporates both the bidirectional nature for the progression and regression of fibrosis. However, even with regression, vascular lesions/remodeling, parenchymal extinction and a cumulative mutational burden place patients at an increased risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma and should continue to undergo active clinical surveillance. It is more appropriate to consider cirrhosis as another stage in the evolution of chronic liver disease as a bidirectional process rather than an end-stage, irreversible state.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. MacSween RN, Burt AD, Portman B, et al. Pathology of the liver. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2002.2. Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M. Regression of human cirrhosis: morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:1599–607.3. Hutterer F, Rubin E, Popper H. Mechanism of collagen resorption in reversible hepatic fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1964; 3:215–23.4. Brody JI, Mc KD, Kimball SG. Therapeutic phlebotomies in idiopathic hemochromatosis. Am J Med Sci. 1962; 244:575–86.5. Perez-Tamayo R. Cirrhosis of the liver: a reversible disease? Pathol Annu. 1979; 14 Pt 2:183–213.6. Geller SA. Coming or going? What is cirrhosis? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:1587–8.7. Chejfec G. Controversies in pathology: is cirrhosis of the liver a reversible disease? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:1585–6.8. Martinez-Hernandez A, Martinez J. The role of capillarization in hepatic failure: studies in carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1991; 14:864–74.9. Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1655–69.10. Mori T, Okanoue T, Sawa Y, Hori N, Ohta M, Kagawa K. Defenestration of the sinusoidal endothelial cell in a rat model of cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1993; 17:891–7.11. Guido M, Sarcognato S, Russo FP, et al. Focus on histological abnormalities of intrahepatic vasculature in chronic viral hepatitis. Liver Int. 2018; 38:1770–6.12. Schaffner F, Poper H. Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man. Gastroenterology. 1963; 44:239–42.13. Benyon RC, Arthur MJ. Extracellular matrix degradation and the role of hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis. 2001; 21:373–84.14. de Meijer VE, Sverdlov DY, Popov Y, et al. Broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibition curbs inflammation and liver injury but aggravates experimental liver fibrosis in mice. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e11256.15. Muller D, Quantin B, Gesnel MC, Millon-Collard R, Abecassis J, Breathnach R. The collagenase gene family in humans consists of at least four members. Biochem J. 1988; 253:187–92.16. Yoneda A, Sakai-Sawada K, Niitsu Y, Tamura Y. Vitamin A and insulin are required for the maintenance of hepatic stellate cell quiescence. Exp Cell Res. 2016; 341:8–17.17. Davis BH, Pratt BM, Madri JA. Retinol and extracellular collagen matrices modulate hepatic Ito cell collagen phenotype and cellular retinol binding protein levels. J Biol Chem. 1987; 262:10280–6.18. Theise ND, Jia J, Sun Y, Wee A, You H. Progression and regression of fibrosis in viral hepatitis in the treatment era: the Beijing classification. Mod Pathol. 2018; 31:1191–200.19. Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G. Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1995; 21:1238–47.20. Taguchi K, Asano G. Neovascularization of pericellular fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1988; 38:615–26.21. Wanless IR. The role of vascular injury and congestion in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis: the congestive escalator and the parenchymal extinction sequence. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2020; 19:40–53.22. Batts KP, Ludwig J. Chronic hepatitis: an update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995; 19:1409–17.23. Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996; 24:289–93.24. Kutami R, Girgrah N, Wanless I, et al. The Laennec grading system for assessment of hepatic fibrosis: validation by correlation with wedged hepatic vein pressure and clinical features. Hepatology. 2000; 32:407.25. Sun Y, Zhou J, Wang L, et al. New classification of liver biopsy assessment for fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients before and after treatment. Hepatology. 2017; 65:1438–50.26. Garcia-Tsao G, Friedman S, Iredale J, Pinzani M. Now there are many (stages) where before there was one: in search of a pathophysiological classification of cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1445–9.27. Bochnakova T. Hepatic venous pressure gradient. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021; 17:144–8.28. Mauro E, Crespo G, Montironi C, et al. Portal pressure and liver stiffness measurements in the prediction of fibrosis regression after sustained virological response in recurrent hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2018; 67:1683–94.29. Sanyal AJ, Anstee QM, Trauner M, et al. Cirrhosis regression is associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2022; 75:1235–46.30. Yoon YJ, Friedman SL, Lee YA. Antifibrotic therapies: where are we now? Semin Liver Dis. 2016; 36:87–98.31. Santhakumar C, Gane EJ, Liu K, McCaughan GW. Current perspectives on the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2020; 14:947–57.32. Lin CA, Chang LL, Zhu H, He QJ, Yang B. Hypoxic microenvironment and hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Hepatoma Res. 2018; 4:26.33. Capece D, Fischietti M, Verzella D, et al. The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:187204.34. Levrero M, Zucman-Rossi J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2016; 64(1 Suppl):S84–101.35. Niu B, Hann HW. Hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma: carcinogenesis, prevention, and treatment. In: Abdeldayem HM, ed. Updates in liver cancer. London: IntechOpen Ltd;2017.36. Peiseler M, Tacke F. Inflammatory mechanisms underlying nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and the transition to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13:730.