Korean J Pain.
2023 Jul;36(3):358-368. 10.3344/kjp.23092.
Association between fatty infiltration in the cervical multifidus and treatment response following cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, El Hospital, Namyangju, Korea
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea
- KMID: 2544247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.23092
Abstract
- Background
Recent attention has been directed towards fatty infiltration in the cervical extensor muscles for predicting clinical outcomes in several cervical disorders. This study aimed to investigate the potential association between fatty infiltration in the cervical multifidus and treatment response following cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection (CIESI) in patients with cervical radicular pain.
Methods
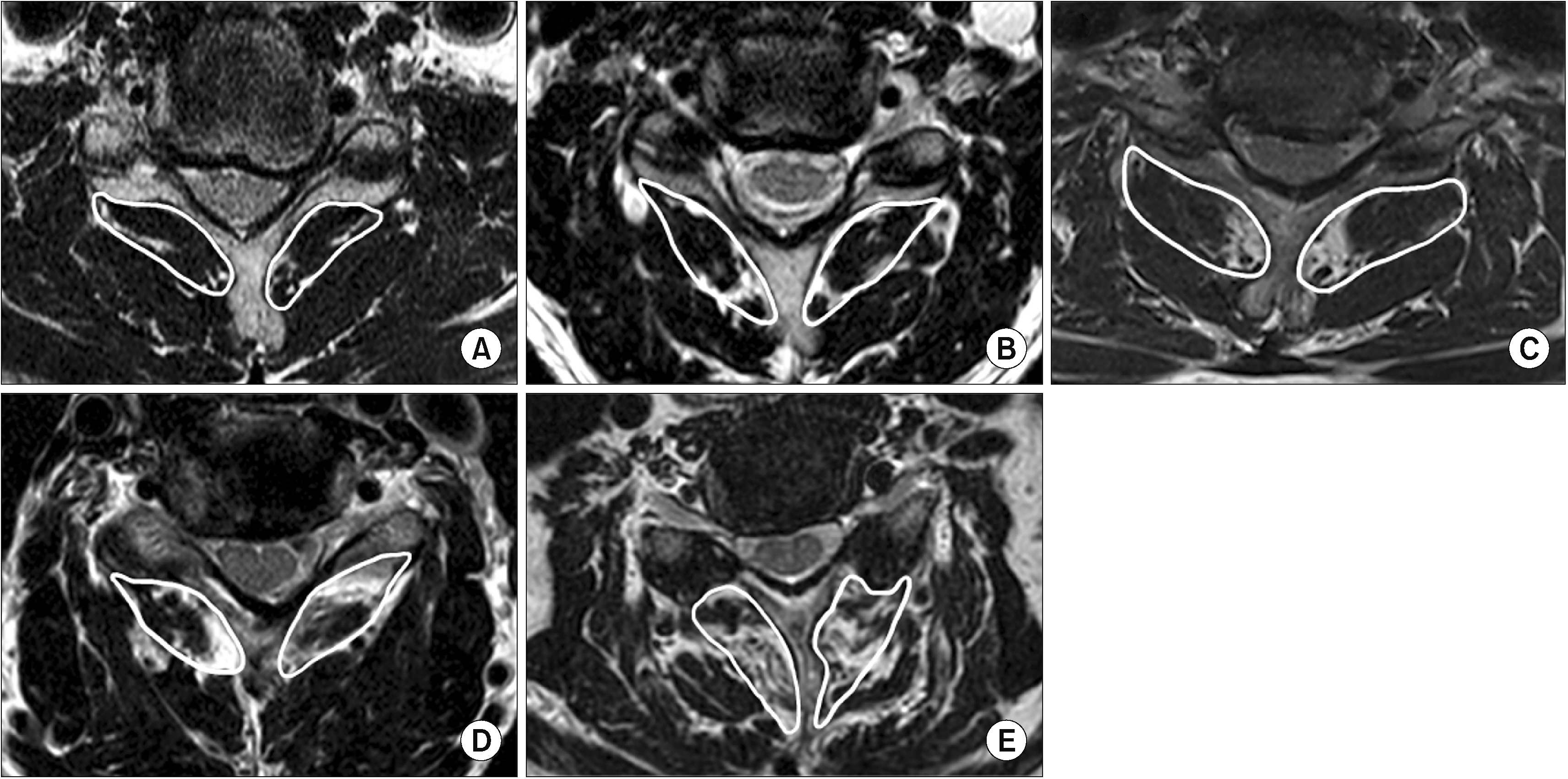
The data of patients with cervical radicular pain who received CIESIs between March 2021 and June 2022 were reviewed. A responder was defined as a patient with a numerical rating scale decrease of ≥ 50% from the baseline to three months after the procedure. The presence of fatty infiltration in the cervical multifidus was assessed, along with patient characteristics, and cervical spine disease severity. To assess cervical sarcopenia, fatty infiltration in the bilateral multifidus muscles was evaluated at the C5–C6 level using the Goutallier classification.
Results
Among 275 included patients, 113 (41.1%) and 162 (58.9%) were classified as non-responders and responders, respectively. The age, severity of disc degeneration, and grade of cervical multifidus fatty degeneration were significantly lower in responders. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that pre-procedural symptoms (radicular pain with neck pain, odd ratio [OR] = 0.527, P = 0.024) and high-grade cervical multifidus fatty degeneration (Goutallier grade 2.5–4, OR = 0.320, P = 0.005) were significantly associated with an unsuccessful response to CIESI.
Conclusions
These results suggest high-grade cervical multifidus fatty infiltration is an independent predictor of poor response to CIESI in patients with cervical radicular pain.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, et al. Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. 2019; Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 48:16–31. Erratum in. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afy169. PMID: 30312372. PMCID: PMC6322506.
Article2. Li CW, Yu K, Shyh-Chang N, Jiang Z, Liu T, Ma S, et al. 2022; Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: descriptive review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:781–94. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12901. PMID: 35106971. PMCID: PMC8977978. PMID: 3e39defbb42c4a7ea134de7c1ad54a66.
Article3. Mitsutake T, Sakamoto M, Chyuda Y, Oka S, Hirata H, Matsuo T, et al. 2016; Greater cervical muscle fat infiltration evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging is associated with poor postural stability in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:E8–14. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001196. PMID: 26571156.
Article4. Paliwal M, Weber KA 2nd, Smith AC, Elliott JM, Muhammad F, Dahdaleh NS, et al. 2021; Fatty infiltration in cervical flexors and extensors in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy using a multi-muscle segmentation model. PLoS One. 16:e0253863. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253863. PMID: 34170961. PMCID: PMC8232539. PMID: 609e1b3cffea4a199baf7220e83306e3.
Article5. Fortin M, Dobrescu O, Courtemanche M, Sparrey CJ, Santaguida C, Fehlings MG, et al. 2017; Association between paraspinal muscle morphology, clinical symptoms, and functional status in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:232–9. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001704. PMID: 28207658.
Article6. Kim CY, Lee SM, Lim SA, Choi YS. 2018; Impact of fat infiltration in cervical extensor muscles on cervical lordosis and neck pain: a cross-sectional study. Clin Orthop Surg. 10:197–203. DOI: 10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.197. PMID: 29854343. PMCID: PMC5964268.
Article7. Manchikanti L, Knezevic NN, Navani A, Christo PJ, Limerick G, Calodney AK, et al. 2021; Epidural interventions in the management of chronic spinal pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) comprehensive evidence-based guidelines. Pain Physician. 24(S1):S27–208. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2021.24.S27-S208. PMID: 33492918.8. Kim HJ, Rho M, Yoon KB, Jo M, Lee DW, Kim SH. 2022; Influence of cross-sectional area and fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles on analgesic efficacy of epidural steroid injection in elderly patients. Pain Pract. 22:621–30. DOI: 10.1111/papr.13141. PMID: 35735193.
Article9. Sim JH, Kwon HJ, Kim CS, Kim EH, Kim DH, Choi SS, et al. 2022; Comparison of contralateral oblique view with the lateral view for fluoroscopic-guided cervical epidural steroid injection: a randomized clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:171–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-103177. PMID: 34853162.
Article10. Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, Beaton D, Cleeland CS, Farrar JT, et al. 2008; Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. J Pain. 9:105–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2007.09.005. PMID: 18055266.11. Grob D, Frauenfelder H, Mannion AF. 2007; The association between cervical spine curvature and neck pain. Eur Spine J. 16:669–78. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-006-0254-1. PMID: 17115202. PMCID: PMC2213543.
Article12. Kang Y, Lee JW, Koh YH, Hur S, Kim SJ, Chai JW, et al. 2011; New MRI grading system for the cervical canal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 197:W134–40. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.10.5560. PMID: 21700974.
Article13. Kim S, Lee JW, Chai JW, Yoo HJ, Kang Y, Seo J, et al. 2015; A new MRI grading system for cervical foraminal stenosis based on axial T2-weighted images. Korean J Radiol. 16:1294–302. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1294. PMID: 26576119. PMCID: PMC4644751.
Article14. Suzuki A, Daubs MD, Hayashi T, Ruangchainikom M, Xiong C, Phan K, et al. 2018; Patterns of cervical disc degeneration: analysis of magnetic resonance imaging of over 1000 symptomatic subjects. Global Spine J. 8:254–9. DOI: 10.1177/2192568217719436. PMID: 29796373. PMCID: PMC5958484.
Article15. Pinter ZW, Salmons HI 4th, Townsley S, Omar A, Freedman BA, Currier BL, et al. 2022; Multifidus sarcopenia is associated with worse patient-reported outcomes following posterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 47:1426–34. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004386. PMID: 35797647.
Article16. Wang XJ, Huang KK, He JB, Wu TK, Rong X, Liu H. 2022; Fatty infiltration in cervical extensor muscle: is there a relationship with cervical sagittal alignment after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 23:641. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05606-0. PMID: 35791024. PMCID: PMC9254416. PMID: e5c6bbaba4434a8c9fbc9303763623b0.
Article17. Binder AI. 2007; Cervical spondylosis and neck pain. BMJ. 334:527–31. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39127.608299.80. PMID: 17347239. PMCID: PMC1819511.
Article18. Haghnegahdar A, Sedighi M. 2016; An outcome study of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion among Iranian population. Neurosci J. 2016:4654109. DOI: 10.1155/2016/4654109. PMID: 27635392. PMCID: PMC5007372.
Article19. Pinter ZW, Wagner S, Fredericks D Jr, Xiong A, Helgeson M, Currier B, et al. 2021; Cervical paraspinal muscle fatty degeneration is not associated with muscle cross-sectional area: qualitative assessment is preferable for cervical sarcopenia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 479:726–32. DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001621. PMID: 33416225. PMCID: PMC8083838.
Article20. Kwon JW, Lee JW, Kim SH, Choi JY, Yeom JS, Kim HJ, et al. 2007; Cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection for neck pain and cervical radiculopathy: effect and prognostic factors. Skeletal Radiol. 36:431–6. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-006-0258-2. PMID: 17340166.
Article21. Cohen SP, Bicket MC, Jamison D, Wilkinson I, Rathmell JP. 2013; Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 38:175–200. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e31828ea086. PMID: 23598728.22. Diwan S, Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Bryce DA, Geffert S, Hameed H, et al. 2012; Effectiveness of cervical epidural injections in the management of chronic neck and upper extremity pain. Pain Physician. 15:E405–34. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2012/15/E405. PMID: 22828692.23. Ferrante FM, Wilson SP, Iacobo C, Orav EJ, Rocco AG, Lipson S. 1993; Clinical classification as a predictor of therapeutic outcome after cervical epidural steroid injection. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 18:730–6. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199305000-00010. PMID: 8516703.
Article24. Choi JW, Lim HW, Lee JY, Lee WI, Lee EK, Chang CH, et al. 2016; Effect of cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection: analysis according to the neck pain patterns and MRI findings. Korean J Pain. 29:96–102. Erratum in: Korean J Pain 2017; 30: 73. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.96. PMID: 27103964. PMCID: PMC4837125.
Article25. De Pauw R, Coppieters I, Kregel J, De Meulemeester K, Danneels L, Cagnie B. 2016; Does muscle morphology change in chronic neck pain patients? - A systematic review. Man Ther. 22:42–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.math.2015.11.006. PMID: 26724855.
Article26. Fortin M, Macedo LG. 2013; Multifidus and paraspinal muscle group cross-sectional areas of patients with low back pain and control patients: a systematic review with a focus on blinding. Phys Ther. 93:873–88. DOI: 10.2522/ptj.20120457. PMID: 23504343. PMCID: PMC3704232.
Article27. Shahidi B, Hubbard JC, Gibbons MC, Ruoss S, Zlomislic V, Allen RT, et al. 2017; Lumbar multifidus muscle degenerates in individuals with chronic degenerative lumbar spine pathology. J Orthop Res. 35:2700–6. DOI: 10.1002/jor.23597. PMID: 28480978. PMCID: PMC5677570.
Article28. Elliott JM, Courtney DM, Rademaker A, Pinto D, Sterling MM, Parrish TB. 2015; The rapid and progressive degeneration of the cervical multifidus in whiplash: an MRI study of fatty infiltration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:E694–700. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000891. PMID: 25785961. PMCID: PMC4466088.29. Cloney M, Smith AC, Coffey T, Paliwal M, Dhaher Y, Parrish T, et al. 2018; Fatty infiltration of the cervical multifidus musculature and their clinical correlates in spondylotic myelopathy. J Clin Neurosci. 57:208–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.03.028. PMID: 30243599.
Article30. Shi L, Yan B, Jiao Y, Chen Z, Zheng Y, Lin Y, et al. 2022; Correlation between the fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles and disc degeneration and the underlying mechanism. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 23:509. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05466-8. PMID: 35637476. PMCID: PMC9150320. PMID: 24157646c47c420ba3892c8936de9b08.
Article31. Kalichman L, Klindukhov A, Li L, Linov L. 2016; Indices of paraspinal muscles degeneration: reliability and association with facet joint osteoarthritis: feasibility study. Clin Spine Surg. 29:465–70. DOI: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e31828be943. PMID: 27137159.32. Doi T, Ohtomo N, Oguchi F, Tozawa K, Nakarai H, Nakajima K, et al. 2023; Association between deep posterior cervical paraspinal muscle morphology and clinical features in patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Global Spine J. 13:8–16. DOI: 10.1177/2192568221989655. PMID: 33504203. PMCID: PMC9837499.
Article33. Snodgrass SJ, Stanwell P, Weber KA, Shepherd S, Kennedy O, Thompson HJ, et al. 2022; Greater muscle volume and muscle fat infiltrate in the deep cervical spine extensor muscles (multifidus with semispinalis cervicis) in individuals with chronic idiopathic neck pain compared to age and sex-matched asymptomatic controls: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 23:973. DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05924-3. PMID: 36357864. PMCID: PMC9647973. PMID: 86043903b31e40d58f8e25ee65870f45.
Article34. Min JH, Choi HS, Ihl Rhee W, Lee JI. 2013; Association between radiculopathy and lumbar multifidus atrophy in magnetic resonance imaging. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 26:175–81. DOI: 10.3233/BMR-130365. PMID: 23640319.
Article35. Hodges P, Holm AK, Hansson T, Holm S. 2006; Rapid atrophy of the lumbar multifidus follows experimental disc or nerve root injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:2926–33. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000248453.51165.0b. PMID: 17139223.
Article36. Pagano AF, Brioche T, Arc-Chagnaud C, Demangel R, Chopard A, Py G. 2018; Short-term disuse promotes fatty acid infiltration into skeletal muscle. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 9:335–47. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12259. PMID: 29248005. PMCID: PMC5879967. PMID: ca59c4247474437991e9ea3e4eea4416.
Article37. James G, Sluka KA, Blomster L, Hall L, Schmid AB, Shu CC, et al. 2018; Macrophage polarization contributes to local inflammation and structural change in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disc injury. Eur Spine J. 27:1744–56. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-018-5652-7. PMID: 29948327.
Article38. Thoma A, Lightfoot AP. 2018; NF-kB and inflammatory cytokine signalling: role in skeletal muscle atrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1088:267–79. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13-1435-3_12. PMID: 30390256.
Article39. Hodges PW, James G, Blomster L, Hall L, Schmid AB, Shu C, et al. 2014; Can proinflammatory cytokine gene expression explain multifidus muscle fiber changes after an intervertebral disc lesion? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1010–7. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000318. PMID: 24718080.
Article40. Ahn H, Kim DW, Ko Y, Ha J, Shin YB, Lee J, et al. 2021; Updated systematic review and meta-analysis on diagnostic issues and the prognostic impact of myosteatosis: a new paradigm beyond sarcopenia. Ageing Res Rev. 70:101398. DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101398. PMID: 34214642.
Article41. Hysing EB, Smith L, Thulin M, Karlsten R, Bothelius K, Gordh T. 2019; Detection of systemic inflammation in severely impaired chronic pain patients and effects of a multimodal pain rehabilitation program. Scand J Pain. 19:235–44. DOI: 10.1515/sjpain-2018-0340. PMID: 30893060.
Article42. Burian E, Franz D, Greve T, Dieckmeyer M, Holzapfel C, Drabsch T, et al. 2020; Age- and gender-related variations of cervical muscle composition using chemical shift encoding-based water-fat MRI. Eur J Radiol. 125:108904. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108904. PMID: 32088656.
Article43. Hicks GE, Simonsick EM, Harris TB, Newman AB, Weiner DK, Nevitt MA, et al. 2005; Cross-sectional associations between trunk muscle composition, back pain, and physical function in the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 60:882–7. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/60.7.882. PMID: 16079212.
Article44. Borghouts JAJ, Koes BW, Bouter LM. 1998; The clinical course and prognostic factors of non-specific neck pain: a systematic review. Pain. 77:1–13. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(98)00058-X. PMID: 9755013.
Article45. Kim MS, Lee DG, Chang MC. 2018; Outcome of transforaminal epidural steroid injection according to severity of cervical foraminal stenosis. World Neurosurg. 110:e398–403. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.014. PMID: 29138074.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Cervical Radiculopathy with Epidural Steroid Injection
- Delayed Pneumocephalus Following Fluoroscopy Guided Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection: A Rare Complication and Anatomical Considerations
- Treatment of Cervical Perineural Cyst by the Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection
- Epidural Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Cervical Radiculopathy
- Epidural Steroid Injection