Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 Jul;27(4):289-298. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.4.289.
Roles of non-coding RNAs in intercellular crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Basic Research Laboratory for Vascular Remodeling Research Laboratory, Hwasun 58128, Korea
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun 58128, Korea
- KMID: 2544131
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.4.289
Abstract
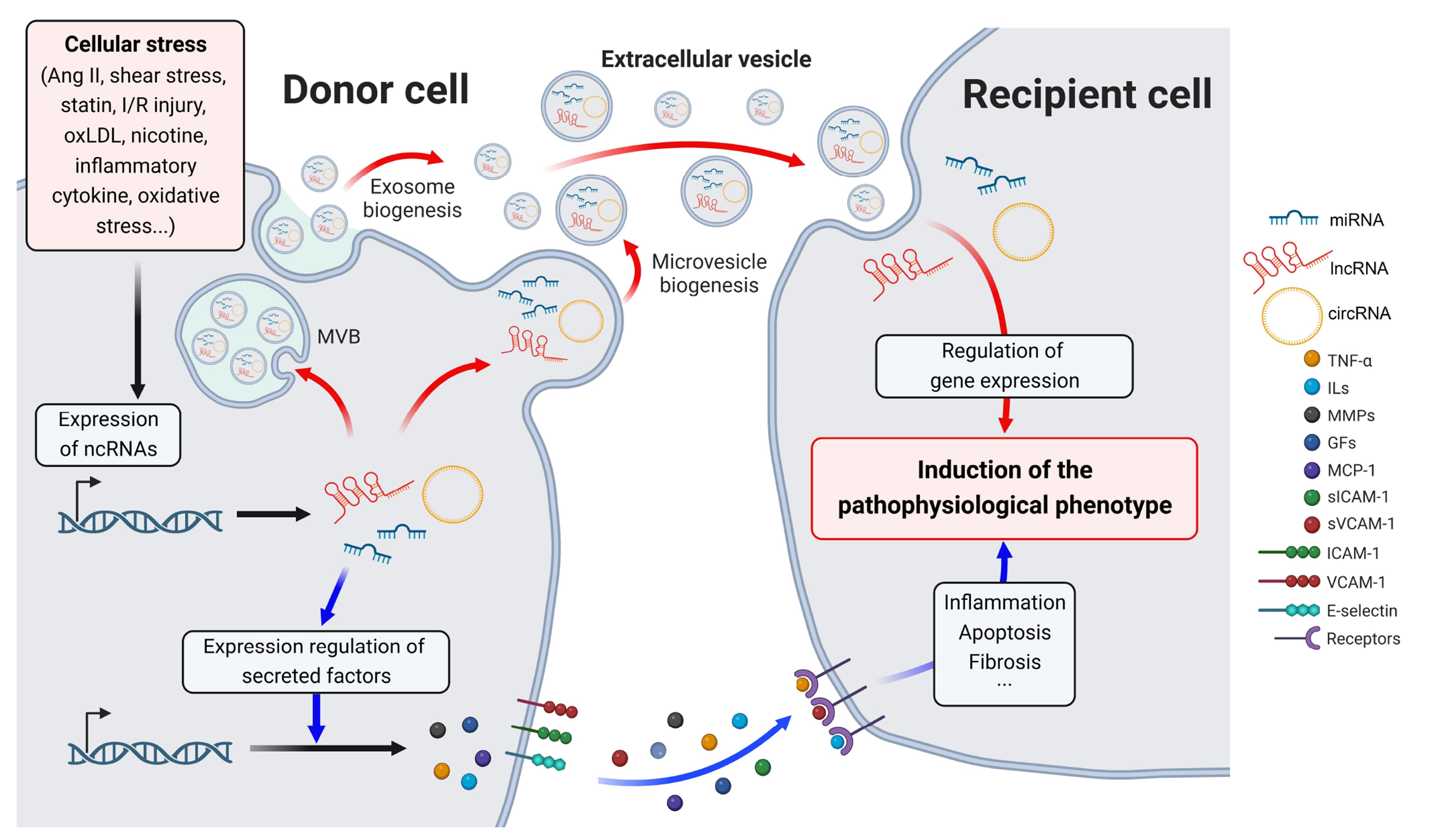
- Complex diseases including cardiovascular disease are caused by a combination of the alternation of many genes and the influence of environments. Recently, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been shown to be involved in diverse diseases, and the functions of various ncRNAs have been reported. Many researchers have elucidated the mechanisms of action of these ncRNAs at the cellular level prior to in vivo and clinical studies of the diseases. Due to the characteristics of complex diseases involving intercellular crosstalk, it is important to study communication between multiple cells. However, there is a lack of literature summarizing and discussing studies of ncRNAs involved in intercellular crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, this review summarizes recent discoveries in the functional mechanisms of intercellular crosstalk involving ncRNAs, including microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs. In addition, the pathophysiological role of ncRNAs in this communication is extensively discussed in various cardiovascular diseases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hawa MI, Beyan H, Buckley LR, Leslie RD. 2002; Impact of genetic and non-genetic factors in type 1 diabetes. Am J Med Genet. 115:8–17. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.10339. PMID: 12116172.
Article2. Pociot F, Lernmark Å. 2016; Genetic risk factors for type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 387:2331–2339. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30582-7. PMID: 27302272.
Article3. Hersi M, Irvine B, Gupta P, Gomes J, Birkett N, Krewski D. 2017; Risk factors associated with the onset and progression of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review of the evidence. Neurotoxicology. 61:143–187. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.03.006. PMID: 28363508.
Article4. Recillas-Targa F. 2022; Cancer epigenetics: an overview. Arch Med Res. 53:732–740. DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.11.003. PMID: 36411173.
Article5. Araújo F, Gouvinhas C, Fontes F, La Vecchia C, Azevedo A, Lunet N. 2014; Trends in cardiovascular diseases and cancer mortality in 45 countries from five continents (1980-2010). Eur J Prev Cardiol. 21:1004–1017. DOI: 10.1177/2047487313497864. PMID: 23884980.
Article6. Pearson-Stuttard J, Buckley J, Cicek M, Gregg EW. 2021; The changing nature of mortality and morbidity in patients with diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 50:357–368. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2021.05.001. PMID: 34399950.
Article7. Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Staels B. 2014; Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. 262:153–166. DOI: 10.1111/imr.12218. PMID: 25319333.
Article8. Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ, Fisher EA. 2013; Macrophages in atherosclerosis: a dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:709–721. DOI: 10.1038/nri3520. PMID: 23995626. PMCID: PMC4357520.
Article9. Park SH. 2021; Regulation of macrophage activation and differentiation in atherosclerosis. J Lipid Atheroscler. 10:251–267. DOI: 10.12997/jla.2021.10.3.251. PMID: 34621697. PMCID: PMC8473962.
Article10. Pan H, Xue C, Auerbach BJ, Fan J, Bashore AC, Cui J, Yang DY, Trignano SB, Liu W, Shi J, Ihuegbu CO, Bush EC, Worley J, Vlahos L, Laise P, Solomon RA, Connolly ES, Califano A, Sims PA, Zhang H, et al. 2020; Single-cell genomics reveals a novel cell state during smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis in mouse and human. Circulation. 142:2060–2075. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048378. PMID: 32962412. PMCID: PMC8104264.
Article11. Sorokin V, Vickneson K, Kofidis T, Woo CC, Lin XY, Foo R, Shanahan CM. 2020; Role of vascular smooth muscle cell plasticity and interactions in vessel wall inflammation. Front Immunol. 11:599415. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.599415. PMID: 33324416. PMCID: PMC7726011. PMID: e2a7ec5af1c6407892d3c44b55dd91a4.
Article12. Depuydt MAC, Prange KHM, Slenders L, Örd T, Elbersen D, Boltjes A, de Jager SCA, Asselbergs FW, de Borst GJ, Aavik E, Lönnberg T, Lutgens E, Glass CK, den Ruijter HM, Kaikkonen MU, Bot I, Slütter B, van der Laan SW, Yla-Herttuala S, Mokry M, et al. 2020; Microanatomy of the human atherosclerotic plaque by single-cell transcriptomics. Circ Res. 127:1437–1455. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316770. PMID: 32981416. PMCID: PMC7641189.
Article13. Mehta JL, Basnakian AG. 2014; Interaction of carbamylated LDL with LOX-1 in the induction of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 35:2996–2997. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu122. PMID: 24694664.
Article14. Jiang H, Zhou Y, Nabavi SM, Sahebkar A, Little PJ, Xu S, Weng J, Ge J. 2022; Mechanisms of oxidized LDL-mediated endothelial dysfunction and its consequences for the development of atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9:925923. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.925923. PMID: 35722128. PMCID: PMC9199460. PMID: 3258c06963e64f5c953c8bf0dfcbdf34.
Article15. Gabunia K, Jain S, England RN, Autieri MV. 2011; Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-19 inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and activation of cytoskeletal regulators of VSMC motility. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 300:C896–906. DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00439.2010. PMID: 21209363. PMCID: PMC3074623.
Article16. Biros E, Reznik JE, Moran CS. 2022; Role of inflammatory cytokines in genesis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 32:138–142. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2021.02.001. PMID: 33571665.
Article17. Battiston KG, Ouyang B, Labow RS, Simmons CA, Santerre JP. 2014; Monocyte/macrophage cytokine activity regulates vascular smooth muscle cell function within a degradable polyurethane scaffold. Acta Biomater. 10:1146–1155. DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.12.022. PMID: 24361424.
Article18. Hajkarim MC, Won KJ. 2019; Single cell RNA-sequencing for the study of atherosclerosis. J Lipid Atheroscler. 8:152–161. DOI: 10.12997/jla.2019.8.2.152. PMID: 32821705. PMCID: PMC7379113.
Article19. Woo SH, Kyung D, Lee SH, Park KS, Kim M, Kim K, Kwon HJ, Won YS, Choi I, Park YJ, Go DM, Oh JS, Yoon WK, Paik SS, Kim JH, Kim YH, Choi JH, Kim DY. 2023; TXNIP suppresses the osteochondrogenic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 132:52–71. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321538. PMID: 36448450. PMCID: PMC9829043.
Article20. Vallejo J, Cochain C, Zernecke A, Ley K. 2021; Heterogeneity of immune cells in human atherosclerosis revealed by scRNA-Seq. Cardiovasc Res. 117:2537–2543. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvab260. PMID: 34343272. PMCID: PMC8921647.
Article21. Williams JW, Winkels H, Durant CP, Zaitsev K, Ghosheh Y, Ley K. 2020; Single cell RNA sequencing in atherosclerosis research. Circ Res. 126:1112–1126. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315940. PMID: 32324494. PMCID: PMC7185048.
Article22. Lim Y, Jeong A, Kwon DH, Lee YU, Kim YK, Ahn Y, Kook T, Park WJ, Kook H. 2021; P300/CBP-associated factor activates cardiac fibroblasts by SMAD2 acetylation. Int J Mol Sci. 22:9944. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22189944. PMID: 34576109. PMCID: PMC8472677. PMID: 597fbda4eb6c40bb8a9c9e55305fa574.
Article23. Cho DI, Ahn MJ, Cho HH, Cho M, Jun JH, Kang BG, Lim SY, Yoo SJ, Kim MR, Kim HS, Lee SJ, Dat LT, Lee C, Kim YS, Ahn Y. 2023; ANGPTL4 stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques and modulates the phenotypic transition of vascular smooth muscle cells through KLF4 downregulation. Exp Mol Med. 55:426–442. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-00937-x. PMID: 36782020. PMCID: PMC9981608. PMID: 39e89f9d113c4639b20e48c9acdb3920.
Article24. Cho DI, Kang HJ, Jeon JH, Eom GH, Cho HH, Kim MR, Cho M, Jeong HY, Cho HC, Hong MH, Kim YS, Ahn Y. 2019; Antiinflammatory activity of ANGPTL4 facilitates macrophage polarization to induce cardiac repair. JCI Insight. 4:e125437. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.125437. PMID: 31434807. PMCID: PMC6777833.
Article25. Cao Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Yang Q, Ma Q, Xu J, Wang J, Kovacs L, Ayon RJ, Liu Z, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Zeng X, Xu Y, Wang Y, Fulton DJ, Weintraub NL, Lucas R, Dong Z, Yuan JX, et al. 2019; PFKFB3-mediated endothelial glycolysis promotes pulmonary hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116:13394–13403. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1821401116. PMID: 31213542. PMCID: PMC6613097.
Article26. Fasolo F, Di Gregoli K, Maegdefessel L, Johnson JL. 2019; Non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular cell biology and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 115:1732–1756. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvz203. PMID: 31389987. PMCID: PMC7967706.
Article27. Hombach S, Kretz M. 2016; Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol. 937:3–17. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_1. PMID: 27573892.
Article28. Uchida S, Dimmeler S. 2015; Long noncoding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 116:737–750. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.302521. PMID: 25677520.
Article29. Liu CX, Chen LL. 2022; Circular RNAs: characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell. 185:2016–2034. Erratum in: Cell. 2022;185:2390. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.021. PMID: 35584701.
Article30. Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. 1976; Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 73:3852–3856. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852. PMID: 1069269. PMCID: PMC431239.
Article31. Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. 1979; Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 280:339–340. DOI: 10.1038/280339a0. PMID: 460409.32. Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. 2014; Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 32:453–461. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2890. PMID: 24811520. PMCID: PMC4121655.
Article33. Emini Veseli B, Perrotta P, De Meyer GRA, Roth L, Van der Donckt C, Martinet W, De Meyer GRY. 2017; Animal models of atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 816:3–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.05.010. PMID: 28483459.
Article34. Getz GS, Reardon CA. 2012; Animal models of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1104–1115. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.237693. PMID: 22383700. PMCID: PMC3331926.
Article35. Kook YM, Jeong Y, Lee K, Koh WG. 2017; Design of biomimetic cellular scaffolds for co-culture system and their application. J Tissue Eng. 8:2041731417724640. DOI: 10.1177/2041731417724640. PMID: 29081966. PMCID: PMC5564857. PMID: 8cd6381b4d754d0a9bf116732288e2cd.
Article36. Donhauser N, Heym S, Thoma-Kress AK. 2018; Quantitating the transfer of the HTLV-1 p8 protein between T-cells by flow cytometry. Front Microbiol. 9:400. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00400. PMID: 29563906. PMCID: PMC5850991. PMID: bd58bb64bfde49289ef8b0d955c7866f.
Article37. Borsci G, Barbieri S, Guardamagna I, Lonati L, Ottolenghi A, Ivaldi GB, Liotta M, Tabarelli de Fatis P, Baiocco G, Savio M. 2020; Immunophenotyping reveals no significant perturbation to PBMC subsets when co-cultured with colorectal adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells exposed to X-rays. Front Immunol. 11:1077. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01077. PMID: 32655551. PMCID: PMC7326036. PMID: aaf81347079c4241986f5a3ae2ecccca.
Article38. Zuniga MC, White SL, Zhou W. 2014; Design and utilization of macrophage and vascular smooth muscle cell co-culture systems in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease investigation. Vasc Med. 19:394–406. DOI: 10.1177/1358863X14550542. PMID: 25204605.
Article39. Chiu JJ, Chen LJ, Lee PL, Lee CI, Lo LW, Usami S, Chien S. 2003; Shear stress inhibits adhesion molecule expression in vascular endothelial cells induced by coculture with smooth muscle cells. Blood. 101:2667–2674. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2560. PMID: 12468429.
Article40. Mosaad E, Chambers K, Futrega K, Clements J, Doran MR. 2018; Using high throughput microtissue culture to study the difference in prostate cancer cell behavior and drug response in 2D and 3D co-cultures. BMC Cancer. 18:592. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4473-8. PMID: 29793440. PMCID: PMC5968610. PMID: e8d35d12755849368460a9a63103d2ff.
Article41. Cattaneo CM, Dijkstra KK, Fanchi LF, Kelderman S, Kaing S, van Rooij N, van den Brink S, Schumacher TN, Voest EE. 2020; Tumor organoid-T-cell coculture systems. Nat Protoc. 15:15–39. DOI: 10.1038/s41596-019-0232-9. PMID: 31853056. PMCID: PMC7610702.
Article42. Long Q, Lv B, Jiang S, Lin J. 2023; The landscape of circular RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 24:4571. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054571. PMID: 36902000. PMCID: PMC10003248. PMID: 5a5ea986f851490985de75fb80dfba40.
Article43. Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Tréguer K, Boettger T, Horrevoets AJ, Zeiher AM, Scheffer MP, Frangakis AS, Yin X, Mayr M, Braun T, Urbich C, Boon RA, Dimmeler S. 2012; Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 14:249–256. DOI: 10.1038/ncb2441. PMID: 22327366.44. Marques-Rocha JL, Samblas M, Milagro FI, Bressan J, Martínez JA, Marti A. 2015; Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and inflammation-related diseases. FASEB J. 29:3595–3611. DOI: 10.1096/fj.14-260323. PMID: 26065857.
Article45. Quintavalle M, Elia L, Condorelli G, Courtneidge SA. 2010; MicroRNA control of podosome formation in vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 189:13–22. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200912096. PMID: 20351064. PMCID: PMC2854384.
Article46. Riches K, Alshanwani AR, Warburton P, O'Regan DJ, Ball SG, Wood IC, Turner NA, Porter KE. 2014; Elevated expression levels of miR-143/5 in saphenous vein smooth muscle cells from patients with Type 2 diabetes drive persistent changes in phenotype and function. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 74:240–250. DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.05.018. PMID: 24927876. PMCID: PMC4121534.
Article47. Sala F, Aranda JF, Rotllan N, Ramírez CM, Aryal B, Elia L, Condorelli G, Catapano AL, Fernández-Hernando C, Norata GD. 2014; MiR-143/145 deficiency attenuates the progression of atherosclerosis in Ldlr-/-mice. Thromb Haemost. 112:796–802. Erratum in: Thromb Haemost. 2015;114:210. DOI: 10.1160/TH15070001. PMID: 25008143. PMCID: PMC4180777.
Article48. Nazari-Jahantigh M, Wei Y, Noels H, Akhtar S, Zhou Z, Koenen RR, Heyll K, Gremse F, Kiessling F, Grommes J, Weber C, Schober A. 2012; MicroRNA-155 promotes atherosclerosis by repressing Bcl6 in macrophages. J Clin Invest. 122:4190–4202. DOI: 10.1172/JCI61716. PMID: 23041630. PMCID: PMC3484435.
Article49. Zheng B, Yin WN, Suzuki T, Zhang XH, Zhang Y, Song LL, Jin LS, Zhan H, Zhang H, Li JS, Wen JK. 2017; Exosome-mediated miR-155 transfer from smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells induces endothelial injury and promotes atherosclerosis. Mol Ther. 25:1279–1294. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.031. PMID: 28408180. PMCID: PMC5475247.
Article50. Wang C, Zhang C, Liu L, Chen B, Li Y, Du J. A X. 2017; Macrophage-derived mir-155-containing exosomes suppress fibroblast proliferation and promote fibroblast inflammation during cardiac injury. Mol Ther. 25:192–204. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.09.001. PMID: 28129114. PMCID: PMC5363311.
Article51. Werfel S, Nothjunge S, Schwarzmayr T, Strom TM, Meitinger T, Engelhardt S. 2016; Characterization of circular RNAs in human, mouse and rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 98:103–107. DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.07.007. PMID: 27476877.
Article52. Cremer S, Michalik KM, Fischer A, Pfisterer L, Jaé N, Winter C, Boon RA, Muhly-Reinholz M, John D, Uchida S, Weber C, Poller W, Günther S, Braun T, Li DY, Maegdefessel L, Perisic Matic L, Hedin U, Soehnlein O, Zeiher A, et al. 2019; Hematopoietic deficiency of the long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes atherosclerosis and plaque inflammation. Circulation. 139:1320–1334. Erratum in: Circulation. 2019;140:e161. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029015. PMID: 30586743.
Article53. Kim J, Piao HL, Kim BJ, Yao F, Han Z, Wang Y, Xiao Z, Siverly AN, Lawhon SE, Ton BN, Lee H, Zhou Z, Gan B, Nakagawa S, Ellis MJ, Liang H, Hung MC, You MJ, Sun Y, Ma L. 2018; Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat Genet. 50:1705–1715. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0252-3. PMID: 30349115. PMCID: PMC6265076.
Article54. Zhang X, Tang X, Liu K, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ. 2017; Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci. 37:1797–1806. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3389-16.2017. PMID: 28093478. PMCID: PMC5320610.
Article55. Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ. 2017; The long noncoding RNA Malat1: its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol. 14:1705–1714. DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1358347. PMID: 28837398. PMCID: PMC5731810.
Article56. Michalik KM, You X, Manavski Y, Doddaballapur A, Zörnig M, Braun T, John D, Ponomareva Y, Chen W, Uchida S, Boon RA, Dimmeler S. 2014; Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell function and vessel growth. Circ Res. 114:1389–1397. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303265. PMID: 24602777.
Article57. Huang C, Han J, Wu Y, Li S, Wang Q, Lin W, Zhu J. 2018; Exosomal MALAT1 derived from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-treated endothelial cells promotes M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Med Rep. 18:509–515. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8982. PMID: 29750307.
Article58. Tang R, Zhang G, Wang YC, Mei X, Chen SY. 2017; The long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)-induced smooth muscle cell differentiation via RNA Smad-binding elements. J Biol Chem. 292:14270–14278. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.790030. PMID: 28659340. PMCID: PMC5572929.
Article59. Chen L, Yang W, Guo Y, Chen W, Zheng P, Zeng J, Tong W. 2017; Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 regulates the apoptosis of macrophages and vascular endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 12:e0185406. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185406. PMID: 28945793. PMCID: PMC5612752. PMID: 00ea6cf240874a76b85fcbe6d7d52a34.
Article60. Zhang S. 2021; The characteristics of circRNA as competing endogenous RNA in pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer. 21:277. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08029-7. PMID: 33722210. PMCID: PMC7962291. PMID: 2d82e4e52e474dce933f68ff21fadfa9.
Article61. Hansen TB, Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Villadsen SB, Statham AL, Clark SJ, Kjems J. 2011; miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J. 30:4414–4422. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.359. PMID: 21964070. PMCID: PMC3230379.
Article62. Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J. 2013; Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. DOI: 10.1038/nature11993. PMID: 23446346.
Article63. Xiong F, Mao R, Zhang L, Zhao R, Tan K, Liu C, Xu J, Du G, Zhang T. 2021; CircNPHP4 in monocyte-derived small extracellular vesicles controls heterogeneous adhesion in coronary heart atherosclerotic disease. Cell Death Dis. 12:948. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-04253-y. PMID: 34650036. PMCID: PMC8516978. PMID: 80afce83d7674017ae7f2865c8800876.
Article64. Wang Y, Li C, Zhao R, Qiu Z, Shen C, Wang Z, Liu W, Zhang W, Ge J, Shi B. 2021; CircUbe3a from M2 macrophage-derived small extracellular vesicles mediates myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 11:6315–6333. DOI: 10.7150/thno.52843. PMID: 33995660. PMCID: PMC8120198.
Article65. Ding F, Lu L, Wu C, Pan X, Liu B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wu W, Yan B, Zhang Y, Yu XY, Li Y. 2022; circHIPK3 prevents cardiac senescence by acting as a scaffold to recruit ubiquitin ligase to degrade HuR. Theranostics. 12:7550–7566. DOI: 10.7150/thno.77630. PMID: 36438474. PMCID: PMC9691369.
Article66. Bazan HA, Hatfield SA, Brug A, Brooks AJ, Lightell DJ Jr, Woods TC. 2017; Carotid plaque rupture is accompanied by an increase in the ratio of serum circR-284 to miR-221 levels. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 10:e001720. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.117.001720. PMID: 28779016. PMCID: PMC5555615.
Article67. Kim YK. 2022; Circular RNAs as a promising biomarker for heart disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 156:113935. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113935. PMID: 36411622.
Article68. Chen LJ, Chuang L, Huang YH, Zhou J, Lim SH, Lee CI, Lin WW, Lin TE, Wang WL, Chen L, Chien S, Chiu JJ. 2015; MicroRNA mediation of endothelial inflammatory response to smooth muscle cells and its inhibition by atheroprotective shear stress. Circ Res. 116:1157–1169. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305987. PMID: 25623956. PMCID: PMC4380766.
Article69. Zhou J, Li YS, Nguyen P, Wang KC, Weiss A, Kuo YC, Chiu JJ, Shyy JY, Chien S. 2013; Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell turnover by endothelial cell-secreted microRNA-126: role of shear stress. Circ Res. 113:40–51. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.280883. PMID: 23603512. PMCID: PMC3772783.
Article70. Frostegård J, Zhang Y, Sun J, Yan K, Liu A. 2016; Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL)-treated dendritic cells promote activation of T cells in human atherosclerotic plaque and blood, which is repressed by statins: microRNA let-7c is integral to the effect. J Am Heart Assoc. 5:e003976. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003976. PMID: 27650878. PMCID: PMC5079044. PMID: 596656a061f04b0eb38e57a011919879.
Article71. Yuan H, Liu H, Liu Z, Owzar K, Han Y, Su L, Wei Y, Hung RJ, McLaughlin J, Brhane Y, Brennan P, Bickeboeller H, Rosenberger A, Houlston RS, Caporaso N, Landi MT, Heinrich J, Risch A, Christiani DC, Gümüş ZH, et al. 2016; A novel genetic variant in long non-coding RNA gene NEXN-AS1 is associated with risk of lung cancer. Sci Rep. 6:34234. DOI: 10.1038/srep34234. PMID: 27713484. PMCID: PMC5054367.
Article72. Hu YW, Guo FX, Xu YJ, Li P, Lu ZF, McVey DG, Zheng L, Wang Q, Ye JH, Kang CM, Wu SG, Zhao JJ, Ma X, Yang Z, Fang FC, Qiu YR, Xu BM, Xiao L, Wu Q, Wu LM, et al. 2019; Long noncoding RNA NEXN-AS1 mitigates atherosclerosis by regulating the actin-binding protein NEXN. J Clin Invest. 129:1115–1128. DOI: 10.1172/JCI98230. PMID: 30589415. PMCID: PMC6391138.
Article73. Zhang DD, Wang WT, Xiong J, Xie XM, Cui SS, Zhao ZG, Li MJ, Zhang ZQ, Hao DL, Zhao X, Li YJ, Wang J, Chen HZ, Lv X, Liu DP. 2017; Long noncoding RNA LINC00305 promotes inflammation by activating the AHRR-NF-κB pathway in human monocytes. Sci Rep. 7:46204. DOI: 10.1038/srep46204. PMID: 28393844. PMCID: PMC5385552.
Article74. Hesselink RW, Findlay JB. 2013; Expression, characterization and ligand specificity of lipocalin-1 interacting membrane receptor (LIMR). Mol Membr Biol. 30:327–337. DOI: 10.3109/09687688.2013.823018. PMID: 23964685.
Article75. Evans BR, Karchner SI, Allan LL, Pollenz RS, Tanguay RL, Jenny MJ, Sherr DH, Hahn ME. 2008; Repression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling by AHR repressor: role of DNA binding and competition for AHR nuclear translocator. Mol Pharmacol. 73:387–398. DOI: 10.1124/mol.107.040204. PMID: 18000031. PMCID: PMC3263532.
Article76. Tian Y, Rabson AB, Gallo MA. 2002; Ah receptor and NF-kappaB interactions: mechanisms and physiological implications. Chem Biol Interact. 141:97–115. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-2797(02)00068-6. PMID: 12213387.
Article77. Simion V, Zhou H, Pierce JB, Yang D, Haemmig S, Tesmenitsky Y, Sukhova G, Stone PH, Libby P, Feinberg MW. 2020; LncRNA VINAS regulates atherosclerosis by modulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling. JCI Insight. 5:e140627. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.140627. PMID: 33021969. PMCID: PMC7710319.
Article78. Zhou H, Simion V, Pierce JB, Haemmig S, Chen AF, Feinberg MW. 2021; LncRNA-MAP3K4 regulates vascular inflammation through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and cis-modulation of MAP3K4. FASEB J. 35:e21133. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202001654RR. PMID: 33184917. PMCID: PMC8443149.
Article79. Ma X, Xu J, Lu Q, Feng X, Liu J, Cui C, Song C. 2022; Hsa_circ_0087352 promotes the inflammatory response of macrophages in abdominal aortic aneurysm by adsorbing hsa-miR-149-5p. Int Immunopharmacol. 107:108691. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108691. PMID: 35286916.
Article80. Ooi JYY, Bernardo BC. 2020; Translational potential of non-coding RNAs for cardiovascular disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1229:343–354. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-1671-9_21. PMID: 32285423.
Article81. Zheng D, Huo M, Li B, Wang W, Piao H, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Li D, Wang T, Liu K. 2021; The role of exosomes and exosomal MicroRNA in cardiovascular disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:616161. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.616161. PMID: 33511124. PMCID: PMC7835482. PMID: ca86a76e45c94682a14020f9faf2347b.
Article82. Li C, Ni YQ, Xu H, Xiang QY, Zhao Y, Zhan JK, He JY, Li S, Liu YS. 2021; Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:383. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00779-x. PMID: 34753929. PMCID: PMC8578673. PMID: d78d97473e6e486fbcce13f6b6709a08.
Article83. Jiapaer Z, Li C, Yang X, Sun L, Chatterjee E, Zhang L, Lei J, Li G. 2023; Extracellular non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmaceutics. 15:155. DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010155. PMID: 36678784. PMCID: PMC9865796. PMID: ef2244091e394132aa1cf71776c3bf2c.
Article84. Lee TL, Lai TC, Lin SR, Lin SW, Chen YC, Pu CM, Lee IT, Tsai JS, Lee CW, Chen YL. 2021; Conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury through the microRNA-221/222/PUMA/ETS-1 pathway. Theranostics. 11:3131–3149. DOI: 10.7150/thno.52677. PMID: 33537078. PMCID: PMC7847683.
Article85. Lai TC, Lee TL, Chang YC, Chen YC, Lin SR, Lin SW, Pu CM, Tsai JS, Chen YL. 2020; MicroRNA-221/222 mediates ADSC-exosome-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion by targeting PUMA and ETS-1. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:569150. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.569150. PMID: 33344446. PMCID: PMC7744807. PMID: 3e58461d0de748459506825f92edb311.
Article86. Zhu J, Liu B, Wang Z, Wang D, Ni H, Zhang L, Wang Y. 2019; Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC migration and proliferation. Theranostics. 9:6901–6919. DOI: 10.7150/thno.37357. PMID: 31660076. PMCID: PMC6815950.
Article87. Liu Y, Zhang WL, Gu JJ, Sun YQ, Cui HZ, Bu JQ, Chen ZY. 2020; Exosome-mediated miR-106a-3p derived from ox-LDL exposed macrophages accelerated cell proliferation and repressed cell apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:7039–7050. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21697. PMID: 32633398.88. Zhou Z, Chen Y, Zhang D, Wu S, Liu T, Cai G, Qin S. 2019; MicroRNA-30-3p suppresses inflammatory factor-induced endothelial cell injury by targeting TCF21. Mediators Inflamm. 2019:1342190. Erratum in: Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9816785. DOI: 10.1155/2019/1342190. PMID: 31354385. PMCID: PMC6636441. PMID: 05b93e6c23024dde9e5e5c25cb854cfe.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deciphering the Role of Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators in the Wound Healing Process
- Select Macrophage Noncoding RNAs of Interest in Cardiovascular Disease
- Role of Long Non-coding Ribonucleic Acid in Gastrointestinal Cancer
- Extracellular Mechanisms of Neutrophils in Immune Cell Crosstalk
- Roles of Oncogenic Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer Development